The relevance of cybersecurity in telecommunications
Sending an email, holding a video meeting, or saving files to the cloud are actions we take for granted in our businesses. But behind this apparent simplicity lies a complex network that sustains telecommunications: networks, devices, providers, data…
And in that sea of constant information, cybersecurity has become an absolutely essential element for business continuity.
We're no longer just talking about protecting computers or servers, but the telecommunications infrastructure that shapes our lives. From data centers to employees' smartphones, cybersecurity in telecommunications is a key component of ensuring digital, economic, and social stability.
In an environment such as telecommunications, where the exhibition area is vast and dynamic, a solution such as Kartos is advisable and essential to ensure business continuity and protect reputation and user trust.
Unlike other more reactive approaches, our Kartos solution uses a continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) model.. This means it helps organizations maintain a constant and up-to-date view of all their exposed assets, detect vulnerabilities, and anticipate possible attacks.
Why is cybersecurity so critical in telecommunications?
Telecommunications are the nervous system of our digital society,. and cybersecurity in telecommunications is a structural priority for all sectors.
A highly exposed sector
Telecommunications is one of the world's sectors that is attacked the most. It's no coincidence: Operators manage massive volumes of data,critical network infrastructures, and connections with millions of users. Any security breach can have devastating consequences: service interruptions, theft of sensitive data, espionage, or even attacks on national infrastructure.
Threats are constantly evolving
Cybercriminals never rest. New techniques, exploits, and ways to break into systems are developed daily. From ransomware attacks targeting service providers to signal interception or large-scale identity theft, having an antivirus or firewall is no longer enough.
It is necessary to have tools that proactively analyze and identify weaknesses before they are exploited, and maintain constant surveillance of the digital ecosystem. As we propose with Kartos, continuous threat management makes a substantial difference.
You may be interested in→ 6 online threats that can affect your business.
Towards a more preventive and strategic approach
The traditional security model, based on reacting once an incident occurs, is no longer enough.. In an environment as changing as the digital one, prevention and anticipation are essential.

CTEM: continuous management against threats
The traditional IT security model involved periodically reviewing systems, searching for flaws, and applying patches. However, in today's context, this methodology is insufficient. The key is constant vigilance.
Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) is a more dynamic and adaptive approach. It allows companies to:
- Know what assets are exposed on the Internet (servers, domains, applications, etc.).
- Detect misconfigurations or vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
- Prioritize what to fix first based on the actual level of risk.
Our tool, Kartos, is explicitly designed to implement this model. Its noninvasive approach allows monitoring without the need to install agents and offers a clear view of any organization's external security posture.
What your company can do now
If you work in a company that relies on digital infrastructure (which is practically all of them), there are some steps you can start considering today:
1. Perform an exposure diagnosis
Do you know how many of your company's assets are visible from the outside? How many might have insecure configurations? Having Kartos allows you to take this photo without affecting your systems.
2. Implement a CTEM strategy
Leave behind ad hoc cybersecurity, surveillance must be continuous and automated.. Threats don't wait for you to audit.
3. Teach your team
No tool can replace the human factor. Make sure your team understands the risks and knows how to respond.
In a world where everything is digital, guaranteeing cybersecurity in telecommunications is not an add-on: it's the core. Exposure to threats is constant, and the consequences of carelessness can be irreversible.
Solutions like the ones we offer with Kartos help companies of all sizes regain control of their digital security. It's not about fear but visibility, strategy, and responsiveness.
Do you want to know how exposed your organization is? Try Kartos and get a clear, actionable view of your external digital security.
Digital consent: Why accepting conditions doesn't guarantee the security of your data
We live connected lives. We browse, download, share, and accept every moment we spend on the internet. And right there, with that quick click of "Accept terms and conditions," lies one of the biggest problems of the digital age: digital consent.
Do we really know what we're agreeing to? Do we understand the implications these seemingly small decisions have on our privacy?
Even though we virtually sign that invisible contract with every app or service we use, that doesn't mean we're truly protected. In fact, it's often just the opposite.
Qondar: The tool that helps you understand and protect your digital footprint
Before we discuss the intricacies of digital consent, it's worth pausing to introduce Qondar, our solution designed for people who want to better understand what happens to their data on the Internet and how to protect their digital footprint.
Qondar focuses on helping you continuously monitor your exposure to online threats, which is known in the cybersecurity world as CTEM (Continuous Threat Exposure Management).
In other words, Qondar gives you a real-time snapshot of what the internet knows about you, so you don't have to rely solely on the privacy promises of the platforms you use.
Want to know what information about you is circulating online? Discover how Qondar can help you regain control of your data.
What is digital consent really?
The digital consent is the authorization we give, usually with a click, for an app, service, or website to use our personal data. This can include everything from our location and browsing habits to our photos, contacts, or messages.
In theory, this consent should be free, informed, specific, and revocable.. In theory, this consent should be free, informed, specific, and revocable. However, in practice, these requirements are rarely met. How many times have you read the terms and conditions before accepting them? That's right, almost never.

The problem: Accepting does not always mean understanding
This is where comes in the concept of Digital informed consent.. Because it is not just about accepting but also doing so with full knowledge of the facts. And that means understanding what data is being collected, for what purpose, for how long, and who else may have access to it.
But the reality is different:
- Many terms are ambiguous or overly technical.
- Consent is presented in very long texts that are almost impossible to read without investing a lot of time.
- You can "accept all" with a single click, but to manage each permission, you'll need to make additional clicks, drill down through menus, read external policies, etc.
This is not accidental; it is called Dark patterns, and they are techniques designed to manipulate you into making decisions that benefit the company, not you.
Why doesn't digital consent guarantee security?
Even if you give your consent, that doesn't mean your data is secure. There are several compelling reasons for this:
1. Non-transparent third parties
The data you share with a platform often doesn't stay there and is shared with third parties:
advertisers, business partners, analytics platforms... And even if you agreed to the original terms of service, that doesn't mean you've approved what these third parties do with your data.
2. Security violations
Data breaches are becoming more frequent. According to the IBM report “Cost of a Data Breach 2024", the average cost of a data breach is $4.88 million,and often, the user doesn't even realize their information has been compromised. Digital consent, no matter how clear, doesn't protect against a cyberattack.
3. Policy changes
Many companies modify their privacy policies over timeand don't always communicate clearly. What you consented to in 2021 may have changed in 2025. And if you don't find out, your data may be being used in ways you never approved.
Digital informed consent is a basis, but not a guarantee
It's not about demonizing digital consent, but understanding it for what it is: a part of the process, not a solution.. Digital informed consent is a step toward transparency, but as long as we continue to grant permission without knowing what it means, we will continue to give up control.
And what can you do as a user?
Here are some practical recommendations:
1. Don't accept for the sake of accepting
Try to take a minute to read the key points before agreeing. If an app asks for access to your microphone or photos for no obvious reason, it's a red flag.
2. Use digital surveillance tools
That's where Qondar excels. With this solution, you can:
- To know what data of yours is publicly exposed.
- Receive alerts if your information appears in suspicious places (forums, dark web, etc.).
- Evaluate your digital exposure level and make informed decisions.
3. Review permissions periodically
On your phone, in your accounts, in your browser... From time to time, review what permissions you've granted and delete any that aren't necessary.
4. Be wary of freebies
When a service is free, the product is often you,. that is, your data. Consider whether it's worth giving up personal information in exchange for functionality you can get elsewhere, more securely.
Digital consent needs to evolve
We are at a time when legislation is advancing more slowly than technology.. Meanwhile, the user remains the weakest party in the agreement.
That is why Enthec is committed to solutions like Qondar, which inform and empower. It's not about viewing the digital environment as a negative space but rather making it fairer, safer, and more humane.
Digital consent should be a free and conscious decision, not a trap camouflaged in small print.
Your data is part of you, your reflection in the digital world, and as such, it deserves to be protected. Accepting terms and conditions should not be an act of faith but a conscious choice.. You need tools that help you see beyond the click to do that.
Start protecting your digital identity today with Qondar. Analyze your exposure and take control of your privacy. Contact us and discover everything you can do.
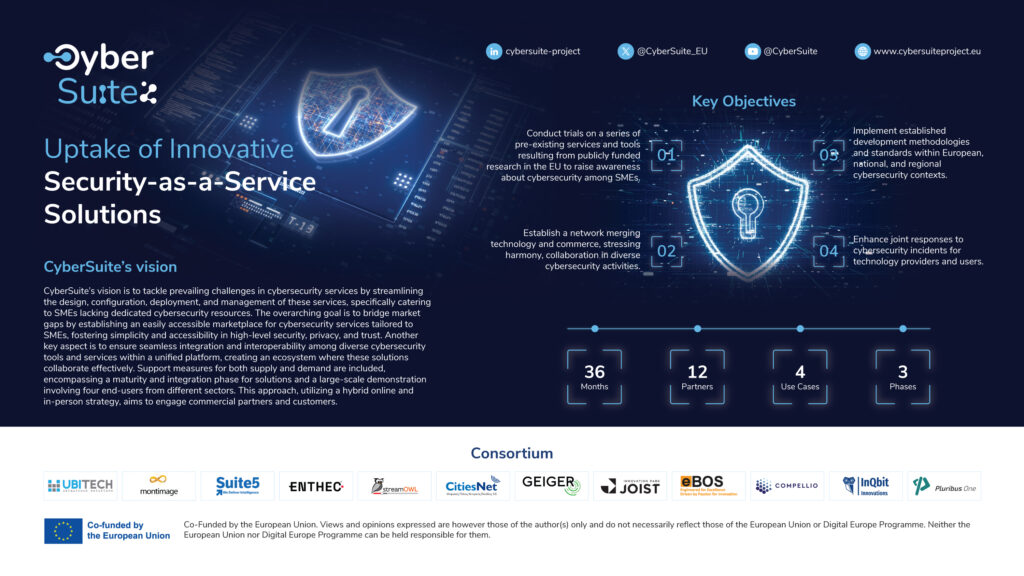
CyberSuite: Strengthening the cybersecurity of European SMEs
The 4th Plenary Meeting of the European Cybersuite Project was recently held in Basel, Switzerland, with Enthec Solutions attending as a member of the Consortium.
In today's digital universe, cybersecurity has become critical, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) who often lack the resources and experience necessary to protect themselves effectively. In this context, CyberSuite, a project funded by the Digital Europe Program, aims to facilitate access to advanced cybersecurity solutions for European SMEs through a Security-as-a-Service.
What is CyberSuite?
CyberSuite, a consortium formed by 12 organizations from 8 European countries, was released on January 1, 2024, and is estimated to be completed by December 2026.. This project seeks to close the gap in the cybersecurity market for SMEs through a unified platform that integrates easily accessible and manageable security tools and services.
Who is part of the consortium?
CyberSuite brings together a strategic combination of industry players:
- UBITECH Limited (coordinator, United Kingdom)
- JOIST Innovation Park (Greece)
- MONTIMAGE EURL (Francia)
- SUITE5 Data Intelligence Solutions Limited (Cyprus)
- ENTHEC Solutions SL (Spain)
- STREAMOWL IKE (Greece)
- Intermunicipal Development Company Digital Cities of Central Greece SA (Greece)
- CYBERGEIGER GmbH (Germany)
- EBOS Technologies Limited (Cyprus)
- Compellio SA (Luxemburg)
- INQBIT Innovations SRL (Romania)
- Pluribus One SRL (Italy)
This diverse group includes specialized technology companies, innovation organizations, and public entities, ensuring a comprehensive and robust approach to digital security challenges in diverse environments.
Key objectives and pillars
CyberSuite is based on six main lines of work:
- Improving the CyberSuite portfolio means enhancing the functionality of tools and services to offer competitive proposals in the market.
- DevSecOps Integration: ensuring that solutions are developed under modern secure and collaborative development practices.
- Demonstrations based on real cases: validating the platform's impact in sectors such as energy, health, mobility, and agri-food.
- CyberSuite Academy: Promoting ongoing training through an online academy that combines technical training with good operational practices.
- Building a market ecosystem: Connecting cybersecurity service providers and consumers to ensure broad adoption
- Dissemination and exploitation: Maximizing impact through communication campaigns, dissemination channels, and early activities to drive adoption.
Benefits for SMEs
The CyberSuite platform offers a security-as-a-service framework adapted to the needs of SMEs:
- Access to integrated solutions without requiring complex architectures.
- Centralized management that reduces the operational load of the equipment.
- Training and awareness through resources from the CyberSuite Academy.
- Interoperability between tools thanks to a common platform prepared to integrate with previous technologies (legacy systems).
- Real use cases, proven in key sectors, which validate the effectiveness and adaptability of CyberSuite solution
European collaborative ecosystem
One of CyberSuite's strengths is its strong commitment to European-wide collaboration. Through its ecosystem:
- It encourages open cooperation between suppliers and SMEs.
- Results from previous EU-funded research are reused, avoiding duplication and accelerating deployments.
- A critical mass adoption is generated that makes investment in cybersecurity more attractive.
- The diversity of the consortium ensures that technological, regulatory, and sector integration aspects are covered.
Expected results
By the end of 2026, CyberSuite is expected to achieve:
- A functional platform that allows SMEs to adopt advanced cybersecurity without needing large infrastructures.
- Certified and market-ready modules, with verifiable levels of maturity.
- Pilots in 4 key sectors: energy, eHealth, transportation, and agri-food.
- More than 200 users trained through the CyberSuite Academy.
- An active market of providers and consumers of security services, generating real impact on the economic fabric.
Why is the CyberSuite project important?
- Because it offers SMEs an accessible alternative to the complexity and cost of traditional cybersecurity.
- Because it creates a European collaborative environment that powers innovative solutions.
- Because it supports the digital sovereignty of the EU and avoids technological dependence on third countries.
- Because it delivers continuing education and tools that reduce long-term cyber risks.
- Because it aligns the EU with its strategic priorities regarding digitalization and technological autonomy.
Looking to the future
CyberSuite seeks to transform the cybersecurity model for European SMEs, from the technical foundation to training, including the development of a dynamic and efficient marketplace. Its collaborative approach, multidisciplinary consortium, and real-user focus make it an exemplary project for driving a more secure, interconnected, and sovereign digital Europe. Together, we are building the future of cybersecurity for SMEs.
5 essential practices for protecting databases with high-value information
Data is one of a company's most valuable assets, and protecting a database is not just a recommendation but a necessity.
Leaks, unauthorized access, and targeted attacks are commonplace, and a compromised database can result in significant financial loss or irreparable damage to a company's reputation.
Whether we're talking about financial information, personal customer data, or intellectual property, the reality is there's no room for error. Databases are the digital heart of many organizations, and understanding how to protect a database effectively has become an essential part of any serious technology strategy.
It's worth considering a tool that can make a difference in protecting a database from external threats: Kartos, developed by Enthec. Kartos is a continuous cyber surveillance tool designed for businesses and is part of the Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) approach.
Do you want to know how to effectively protect a database? Join us as we explore 5 essential practices for keeping your most valuable digital assets safe.
1. Access control: less is more
One of the basic safety rules is providing the minimum necessary access.. Not all employees or collaborators need access to the entire database. Therefore, it is essential to implement a clear and strict privilege control policy.
How to put it into practice?
- Define user profiles according to responsibilities.
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems.
- Record and review access periodically.
- Automate the expiration of temporary permits.
Misconfigured access can open a direct door to attackers.. Therefore, it is advisable to audit this aspect regularly and apply the principle of least privilege.

2. Data encryption: an extra layer that makes the difference
Although it sounds technical, data encryption simply converts said data into an unreadable format for those without the proper password. And it's one of the pillars of protecting a database.
Two types of encryption you should consider
- Encryption at rest: Protects stored data, even if the server is physically accessed.
- Encryption in transit: protects information that travels between the database and users or applications.
Both are necessary, especially if you use sensitive or regulated data (such as medical, financial, or personal identifier information).
3. Secure and frequent backups
Nobody wants that day to come… but sometimes it happens: a system failure, a ransomware attack, or an unforeseen catastrophe. And if you don't have a recent backup, the consequences can be devastating.
Good backup practices
- Automate daily or weekly backups, depending on activity level.
- Store copies in separate environments (ideally in the cloud and on-premises).
- Periodically test the restoration processes.
- Make sure your copies are also encrypted and protected.
A well-executed backup is the lifeline that allows you to recover critical information and continue operating without too many setbacks.
4. Active monitoring and incident response
A key aspect of database protection is anticipating incidents and detecting warning signs before it is too late.
Cyberattacks don't always leave visible signs. In fact, attackers often infiltrate for weeks before being detected. That's why continuous monitoring is essential to alert you to unusual behavior.
This is where solutions like Kartos come into play.
Kartos stays ahead of threats by detecting data breaches or vulnerabilities exposed in public and hidden sources on the Internet. With this information, the security team can act proactively, avoiding greater damages.
In addition, an incident response plan, which defines roles, steps to follow, and internal and external communication in case something goes wrong, is highly recommended.
Rapid detection and response can distinguish between a scare and a major crisis.
5. Updates and patches: small gestures, big impact
Many cyberattacks take advantage of known bugs in the software,which could have been avoided with a simple update. However, these tasks are often postponed due to convenience or lack of planning... until it's too late.
Tips to keep everything up to date
- Turn on automatic updates whenever possible.
- Schedule regular reviews of critical patches.
- Prioritize updates to systems that manage sensitive data.
Outdated software is like a door that is not closed correctly: It seems safe, but anyone with bad intentions can get in.
Why is it so important to know how to protect a database?
The answer is clear: because data is the new gold.. Whether you run a small business or a large corporation, risks are present, and cyber criminals are relentless. Furthermore, current legislation (such as the General Data Protection Regulation or GDPR) requires active measures to safeguard the privacy and integrity of information.
By applying these five practices, you'll be taking concrete steps to reduce your risk exposure, comply with regulations, and maintain the trust of your customers and partners.
What if you don't know where to start?
Not all companies have technical teams capable of implementing these measures independently. That's why there are solutions such as Kartos by Enthec, which allows for complete visibility of the exposure risk without the need for a cybersecurity expert.
Kartos detects vulnerabilities in real time, prioritizes threats according to their risk level, and facilitates corrective actions—all from a clear, accessible dashboard designed for informed decision-making.
Knowing how to protect a database is no longer knowledge reserved solely for technical profiles: it is a cross-cutting priority that affects the entire organization, from IT to management. It is a strategic necessity for any company that values its digital assets. With good practices, appropriate tools like Kartos, and a proactive approach, it's possible to drastically reduce risks and anticipate problems before they occur.
Don't wait for a data breach to take action. Your data's security deserves constant attention and professional solutions.
Do you want us to help you protect your most important digital assets? Contact us and start building a solid defense.
What is SIM swapping, and how can an early warning tool prevent identity theft
Our mobile phone is more than just a device: it's the center of our digital lives. We use it to access our social media, online banking, medical services, and work communications.
But have you ever thought about what would happen if someone hijacked your phone number? This is precisely what happens with SIM swapping, a impersonation technique that is on the rise.
Before going into details, it's worth presenting a solution that can be very useful when it comes to detecting an attack in time. Qondar, our tool, is a platform for individual cyber-surveillance to anticipate digital threats.
Qondar is an early warning system that identifies potential exposure of your personal information online and can help you detect signs of SIM swapping before it's too late.
What is SIM swapping?
You may have read about it in recent news or heard it called SIM swap or SIM swapping, but what exactly is SIM swapping?It is a digital scam that involves duplicating your SIM card without your consent.
In other words, a cybercriminal can take over your phone line, redirecting your calls, messages, and, most worryingly, the verification codes that many services send via SMS.
The objective is clear: access your accounts using popular two-step verification (2FA) systems. Many banks, social media platforms, and emails use this method to confirm your identity, but if the attacker already has your phone number, they can receive these codes and access your data as if they were you.
SIM swap: how does it work?
The technique is not new, but it has gained popularity in recent years. The modus operandi usually follows this scheme:
- Obtaining personal data.. Through leaks, social engineering, or even social networks, the criminal collects enough information about you (name, ID, address, phone number, etc.).
- Impersonation. With this information, they contact your phone provider, pretending to be you, and request a duplicate SIM card, claiming the device has been lost or damaged.
- Activating the new SIM.. Once the operator validates the request, the new SIM is activated, and your line will no longer be available on your device.
- Account access:. The attacker tries to access your accounts. If you have SMS authentication enabled, he is already on the hook.
In minutes, someone can gain complete control over your personal data, networks, online banking, and more.

How to protect yourself from SIM swapping?
It is normal to wonder how to avoid SIM swapping or what we can do to protect ourselves from this dangerous technique. Here are some recommended measures:
1. Minimize the information exposed on networks
Avoid sharing information such as your phone number, date of birth, or address on social media. Even seemingly harmless information can be used to create a fake profile and impersonate you.
2. Change authentication methods
Whenever possible, avoid SMS authentication. Opt for authentication apps like Google Authenticator, Authy, or physical keys (like YubiKey), independent of your mobile phone line.
3. Activate notifications on your operator
Some carriers allow you to notify them of any line changes, such as SIM card duplication or portability requests. Activate these notifications if available.
4. Use a monitoring tool like Qondar
Qondar, Enthec's solution for personal users, is the best way to continuously monitor the exposure of your personal data. Whether online, in forums, on the dark web, or elsewhere, Qondar lets you detect leaks and signs that can anticipate a SIM swapping scam attempt.
SIM swapping: How to prevent it with an early warning tool
Attacks don't always come in visible form. Often, before a SIM swap occurs a personal data leak occurs online. Emails, passwords, phone numbers, or addresses leaked in stolen databases are the cybercriminal's first step.
Qondar lets you know if your data has appeared in a security breach,if someone is trying to steal your identity, or if your phone number has been compromised. This information is vital so you can take timely measures, such as changing your password, contacting your carrier, or even temporarily blocking certain services.
Thanks to its model-based approach, CTEM (Continuous Threat Exposure Management), Qondar doesn't just analyze a snapshot of your digital situation, but continuously assesses your risks, adapting to the changing cybersecurity environment.
¿Why is SIM swapping a growing threat?
SIM swapping is not an isolated problem.. According to data from Europol and the National Cryptologic Center, these types of scams are rising in Europe. Attackers are targeting prominent public figures as well as ordinary citizens whose data has been exposed online.
And it's not just about losing access to an account. The consequences can include:
- Unauthorized bank transfers
- Identity theft used to commit crimes
- Blocking of personal and professional accounts
- Access to medical services or insurance in your name
That's why it's so important to have tools that watch over you, automatically and constantly.
What can you do today?
Now that you know what SIM swap is and how easy it is to fall victim to this scam, you can make more informed decisions to protect yourself.
We recommend:
- Review your authentication methods in the most important digital services.
- Avoid using the phone number as the only verification method.
- Try Qondar, our cyber surveillance platform for individuals that helps you keep your data safe through personalized alerts.
SIM swapping is a real, silent, and dangerous threat.. You don't have to be a celebrity to be targeted: all it takes is for your data to have been leaked, even if it's on a website you registered with years ago.
Protecting yourself requires a combination of prevention, good digital practices, and tools that work for you.
Qondar by Enthec is precisely that: a digital shield that alerts you when something is wrong, when your data appears where it shouldn't. Thanks to its continuous monitoring capacity and threat exposure management, it becomes a key ally in preventing SIM swapping before it happens.
Want to check if your information has already been exposed?
Get access to Qondar and take the first step to protecting your digital identity. Visit Enthec and protect your data before it's too late.
Cybersecurity in hotels: key strategies for the sector
Cybersecurity in hotels has become an essential pillar of operational and reputational management in the tourism sector. As guest experiences become digital, from booking to checkout, the risks of cyberattacks, data loss, and fraud also increase.
It's not just about protecting a Wi-Fi network; we're talking about protecting sensitive information, such as thousands of customers' personal and financial data.
The hotel sector needs to adapt to new digital threats, incorporating proactive strategies, cybersecurity tools, and ongoing processes for reviewing their risk exposure.
This is where technological innovation comes into play, with solutions specifically designed to secure these businesses' digital infrastructure.
One of these solutions is Kartos.. This is not just a simple analytics platform but a Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) platform.. This means it helps businesses continuously identify, measure, and mitigate digital vulnerabilities, constantly assessing their exposure to real threats.
In the hotel industry, Kartos can detect everything from network breaches to leaked customer data on forums without requiring any implementation within hotel chains' complex internal structures.
Want to reduce your exposure to cyber threats before it's too late? Learn more about how Enthec and its Kartos platform can help to protect your hotel starting today.
Why is cybersecurity in hotels more critical than ever?
The digitalization of the tourism sector has brought great benefits, but has opened new doors for cybercriminals. A report by IBM Security revealed that the hospitality sector is one of the ten most attacked globally, mainly due to the volume of personal and financial information it handles.
Hotels often operate with legacy systems, insecure configurations, or outdated password policies. Added to this are connected devices, such as smart locks or IoT HVAC systems, which, if not adequately protected, become entry points for attackers.
And what are hackers looking for in a hotel?
- Customer bank details.
- Booking information and behavior patterns.
- Access to internal systems for identity theft or blackmail.
- Vulnerable infrastructure that can be used as a “bridge” for other attacks.
Trend in hotel cybersecurity: moving from reaction to prevention
One of the main trends in hotel cybersecurity is a change in focus. Previously, people waited for something to go wrong before acting. Today, the goal is to detect threats before they have consequences.
Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM), powered by platforms like Kartos, is based precisely on that principle. It's no longer enough to perform audits once a year. What works is constant, agile, and frictionless control, which allows for the detection, classification, and addressing of each vulnerability in a prioritized manner.
In this sense, CTEM solutions such as Kartos allow:
- Monitor the hotel's digital display 24 hours a day.
- Detect leaked credentials in real time.
- Analyze subdomains, DNS settings, and information leaks.
- Receive personalized alerts based on the level of criticality.

Specific challenges of cybersecurity in hotels
Cybersecurity in hotels presents unique challenges that go beyond the typical technological challenges of any business. Every establishment must face risks that evolve at the same pace as guest connectivity and operational demands.
Multiplicity of devices and entry points
The attack surface is vast, including computers, servers, POS terminals, IoT devices, and employee and customer smartphones. If not correctly monitored, any misconfigured device can be a gateway.
Rotating staff and insufficient training
The high level of staff turnover in many establishments makes it challenging to implement strong cybersecurity protocols. . Without proper training, employees can easily fall for phishing attacks or handle sensitive information without the necessary precautions.
Open Wi-Fi networks
Although offering free Wi-Fi to guests is a standard service, many hotels do not segment their networks properly, which can compromise the security of clients and internal systems.
Highlighted strategies to strengthen hotel cybersecurity
To address the above challenges successfully, a clear and realistic roadmap must be designed. The key is to combine technology, processes, and corporate culture, always with an eye toward the guest experience and the business's reputation.
1. Implement a CTEM system like Kartos
Incorporating a Continuous Threat Exposure Management solution allows for an updated map of the hotel's security status,allowing quick action and staying ahead of cybercriminals. Kartos, in particular, is designed to operate without interfering with the hotel's internal systems, making it easier to adopt and maintain.
2. Continuous staff training
It is not enough to install software: the first line of defense is people.. Training your team on best practices, recognizing fraudulent emails, and responding to incidents is essential. Some companies even organize cyberattack simulations to reinforce this knowledge.
3. Segment networks and apply access policies
Separating the hotel's customer network from its operational network is a basic, yet often overlooked, step. Furthermore, employees should only have access to the information and systems they need.
4. Backup and recovery policies
Having encrypted backups and a well-defined recovery plan can be the difference between a scare and a catastrophe. Especially in ransomware attacks, having up-to-date backups allows you to get back to business quickly without giving in to blackmail.
5. Active monitoring of exposed assets
One of Kartos's most innovative aspects is its ability to detect digital assets exposed on the public network.. From vulnerable IP addresses to misconfigured cloud documents, each finding is presented with an associated criticality and remediation advice.
What if your hotel has already been the victim of an attack?
It's not always easy to detect. Sometimes, stolen data is sold or used months later. That's why one of Kartos' standout features is the ability to conduct cyber surveillance in open sources and forums, where leaked data often appears. You can act quickly to contain and respond to the incident by identifying any mentions related to your domain.
In an environment where reputation is everything, a security breach can mean much more than a fine or a financial loss. It can translate into customers who don't return, negative comments, and loss of trust in the brand.
From Enthec, with our Kartos platform, we offer hotels a practical, immediate, and proactive way to manage their digital security through technology designed to be used by large chains and independent hotels that want to protect their business without complications.
Do you want to know if your hotel is exposed to cyber threats? Make a diagnosis with Kartos and start preventing from today.
Taking care of your guests also starts with protecting their data.
Google bombing: How to defend your digital reputation against this type of attack
A Google search can define who you are, what you stand for, or whether someone trusts you. What appears on the first page of results can significantly impact your digital reputation, whether you're an individual or a business. This is where a little-known but highly damaging phenomenon comes into play: Google bombing.
Although its name sounds distant or technical, its consequences can be felt very close at hand. Google bombings in Spain, as in other countries, have been used to damage public images, manipulate opinions, or even attack professionals and companies without them being aware of what is happening.
What is Google bombing?
The term Google bombing refers to a technique for manipulating search results on Google. It involves linking certain keywords to a specific page to artificially alter its position in the results.
Let's imagine that many websites link the phrase "corrupt company" to a specific company's website. Over time, Google may eventually show that company as the first result when someone searches for that phrase. It doesn't matter if the content is fake or the link lacks context; the algorithm doesn't judge intentions; it only interprets signals.
This technique, which began as a form of political joke or protest in the early 2000s, has evolved into a tool for digital defamation. It is often silent and difficult to detect until it's too late.
Who can it affect?
Any person or entity with a digital presence is susceptible to Google bombing. This includes politicians, public figures, entrepreneurs, independent professionals, SMEs, and even anonymous users who, due to a specific conflict, are targeted by this type of campaign.
Although not always reported in the media, cases of Google bombing have been on the rise in Spain. Just look at forums, social media, or anonymous smear campaigns that go viral and negatively affect search results.
The problem is that reputational damage can have real consequences: loss of customers, cancellation of contracts, deterioration of personal branding, and even legal problems.
Why is it so difficult to detect it in time?
One of the big challenges of Google bombing is its ability to go unnoticed.. Unlike a direct attack, such as hacking or online insults, this technique works by accumulating links, many on seemingly harmless pages or those created explicitly for that purpose.
By the time an affected person realizes it, the content has already taken root, and reversing the damage is much more complex.
Furthermore, Google doesn't automatically respond to these cases, except in obvious manipulation cases. Reporting content doesn't guarantee its disappearance or that the associated results will be removed. Therefore, prevention and continuous monitoring are fundamental to maintaining control of your online presence.

The importance of personal cyber surveillance
Given this situation, Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) is becoming an essential tool. A good antivirus or avoiding suspicious links is no longer enough; today, protecting your image on search engines, social networks, and digital forums is equally essential.
This is where our solution appears. Qondar, is designed for individual cyber-surveillance.. While other platforms are designed only for large companies, Qondar focuses on protecting individuals, whether professionals, freelancers, or citizens concerned about their online reputation.
This solution automatically analyzes what is said about you on the Internet, detects patterns of suspicious behavior, identifies potential smear campaigns, and alerts you if there are signs that someone is trying to manipulate the results associated with your name.
How to defend yourself against Google bombing?
Although Google bombing has become less effective, a site can still be affected. To defend yourself, it's important to remember the following recommendations.
1. Monitor your digital footprint regularly
A Google search for your name or your company's name should be part of your routine. Do it from different devices, logged in, and in incognito mode. What pops up? Is there anything odd? Are negative phrases being repeated on unfamiliar websites?
If you notice a sudden change or a strange association of your name with offensive terms, you could be a victim of Google bombing.
You may be interested in→ 9 healthy digital habits that will protect you from identity theft and leaks.
2. Act quickly: prevention is better than a cure
The sooner you detect an attack, the easier it will be to stop it. You can start by:
- Report suspicious links to Google.
- Request the removal of defamatory content from the page administrators.
- Generate positive and truthful content (posts, interviews, blogs, optimized profiles, etc.) that improves your natural positioning.
In more severe cases, a solution like Qondar may be enough to prevent serious repercussions, such as a far-reaching reputational crisis.
3. Don't fight alone: surround yourself with tools and professionals
The reality is that no one is 100% protected. Not even the biggest brands. But having a strong digital shield helps a lot. In addition to Qondar for individuals, Enthec offers Kartos, our platform for businesses and organizations, which is also focused on continuous digital threat management.
These solutions allow you to detect not only Google bombing but also information leaks, improper mentions, or more sophisticated attack patterns.
What if you've already been a victim?
In that case, the key is to reverse the impact.. Here are some actions:
- Positive positioning: Work on publishing content that displaces negative results. Search engines value relevance and authority, so it's essential to feed your footprint with legitimate and quality content.
- Legal assistance: You can contact digital law experts if the published content is false or defamatory. In Spain, favorable case law in cases of online reputation attacks is increasing.
- Technical reports: Tools like Qondar can generate reports supporting complaints or legal proceedings, demonstrating that a coordinated strategy was used to harm you.
From Enthec, we work with solutions like Qondar so that each person can have control of their online presence.. Because protecting your digital identity on the Internet shouldn't be a lonely battle.
Why DNS health is critical to your company's cybersecurity
Digital threats are evolving faster than ever. Companies, large or small, cannot afford to look the other way when it comes to protecting their digital infrastructure. Here is one aspect that is often overlooked, yet is key to digital security: DNS health.
But what does this mean exactly? And why is it so important to control DNS health within the strategy of business cybersecurity?
Before we dive in, let's make a crucial point. If your company doesn't yet have Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) tools, you may be leaving windows open to the outside without realizing it.
This is where Kartos, our solution for cyber surveillance for companies,specifically designed to detect, assess, and continuously reduce your organization's digital exposure, appears. Kartos not only monitors your digital attack surface but also allows you to protect your DNS and detect related vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them.
What exactly is DNS health?
When discussing DNS health, we refer to the security status, configuration, and maintenance of an organization's domain name system. DNS acts as a “phone book” for the internet: it converts domain names (like enthec.com) into IP addresses that machines can understand.
A secure DNS server isn't just a technical issue; it's an essential pillar of your digital defense. Cybercriminals can exploit a misconfigured DNS to carry out attacks such as:
- Pharming: redirect your employees or customers to fake websites.
- DNS hijacking: hijack your web traffic for espionage or fraud.
- DDoS through DNS amplification: take advantage of your DNS as a vector to saturate other servers.
These risks affect large corporations as well. SMEs are also frequent targets precisely because they neglect aspects like this.
Why do so many companies ignore DNS health?
There are several reasons, but one of the main ones is the false sense of security.. Many organizations believe they are protected by having antivirus systems or firewalls. However, these devices do not monitor or manage your domain name system configuration.
On the other hand, DNS is usually managed by third parties (such as hosting or domain providers), which means that, despite being a critical element, companies do not include it in their security audits.
What does it mean to have good DNS control
Having effective DNS control means keeping a series of good practices active and up-to-date. These include:
- Audit your DNS records and detect outdated or unnecessary settings.
- Ensure your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records are correctly configured to prevent email phishing.
- Use secure and redundant DNS servers.
- Protect access to your DNS management with strong authentication.
- Monitor unauthorized access attempts or changes.
These steps are essential to ensure a business environment free of invisible breaches.
Kartos and continuous DNS monitoring
This is where Kartos comes into play. It proactively monitors your DNS status and alerts you to any suspicious changes. It's not just about protecting them but anticipating the future.
Kartos allows you:
- See your digital display surface in real time.
- Detect uncontrolled or misconfigured assets (including DNS and subdomains).
- Prioritize vulnerabilities with an approach based on real risk.
- Receive early warnings on possible attack vectors involving DNS.
You may be interested in→ Real-time vulnerability management: a step forward in cybersecurity.
Comprehensive, continuous management distinguishes a company that reacts to an attack from one that neutralizes it before it occurs.
How do you know if your DNS server is secure?
Some tools allow for spot checks, but that's not enough. The digital environment changes daily, and attackers find new ways to exploit weaknesses. Therefore, a CTEM solution like Kartos is essential.
Kartos not only tells you if your DNS is secure now but also helps you maintain that security continuously.. This includes automated analysis, detailed reporting, and remediation suggestions tailored to your technological reality.
Practical recommendations to improve your company's DNS health
If you don't yet have a solution like Kartos, we recommend that you at least consider the following points:
- Update your DNS records frequently. Discard any unused items. frequently. Discard any unused items.
- Activate DNSSEC to protect the integrity of queries.
- Audit your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC registers with the help of specialists.
- Avoid using public DNS servers as the principal solution.
- Control who has access to your DNS console.. Not all technicians need to have full permissions.
The good news is that it's never too late to improve your organization's DNS health.
Neglecting your digital infrastructure's DNS health can have serious financial and reputation consequences. DNS control and a secure DNS server should be at the heart of any modern cybersecurity policy.
With our solution, Kartos, you are protecting your DNS and taking a step towards a smarter, more preventative, and continuous security model.
9 healthy digital habits that will protect you from identity theft and leaks
We live connected lives. We check our phones before breakfast, share photos, use the cloud, shop online, and work remotely… and sometimes, without realizing it, we leave doors open for cybercriminals to exploit.
Identity theft and personal data leaks are the order of the day.And you don't have to be famous or work for a multinational company to be objective. Just having an email address or active social media accounts is enough.
In this context, maintaining healthy digital habits isn't just advisable: it's essential. Protecting our digital identity should be part of our daily routine.
Some tools can help, such as Qondar,which is our solution designed for individuals. Through Qondar, you can monitor your online exposure in real time, detect if your data has been compromised, and receive alerts when your digital security is at risk.
Good Healthy digital habits to protect yourself
1. Change your passwords regularly
Although it may seem like a basic recommendation, most people have continued to use the same passwords for years.. The worst part is that they often reuse the same key for everything. This is like having one key for your house, car, and office.
Use different passwords for each account, change them every three or four months, and rely on secure password managers whenever possible.. Do you have any clues about whether yours has been stolen? Qondar can help you detect it.
You may be interested in→ How to manage business passwords and credentials easily and securely to avoid online threats.
2. Activate two-step verification
Also known as two-factor authentication (2FA), it's one of the most effective measures against unauthorized access. Even if someone gains access to your password, they won't be able to log in without that second step (usually a code you receive on your phone).
Almost all major platforms offer this free option, which can save you from a big scare.
3. Be wary of suspicious links
You receive an email claiming to be from your bank but asking you to click a link and update your information, or a message on social media with a shortened link and no context. Be very careful: you could be facing a case of phishing.
Always check the sender. Do not click on dubious links or provide personal information outside of official channels.. If you have any doubts, it's best not to interact.
4. Update your devices and apps
Yes, sometimes updating the operating system of your mobile or computer can be a pain, but these updates often include crucial security patches.. Older versions are fertile ground for cyber attackers.
Configure automatic updates and ensure your apps come from official sources (App Store, Google Play, etc.).
5. Be careful with public Wi-Fi networks
Connecting to Wi-Fi at the airport or mall is fine for checking the weather or reading the news, but you should not use it to perform sensitive tasks such as accessing your online banking or sending important documents.
If you need to, you'd better use a VPN (Virtual Private Network). These tools encrypt your connection, making it much harder for someone to intercept what you're doing.
6. Review your app permissions
Many apps ask for access to your camera, contacts, and location; often, they don't need it to work. Automatically granting permissions can put you at risk.
Take a few minutes to review your apps' permissions on your mobile or browser and modify those that are not strictly necessary.

7. Be careful what you share on social media
Posting vacation photos while you're away from home, showing tickets with QR codes, giving out personal details (like your address or phone number) on public profiles... This may seem innocent, but it can be used against you.
Think before you post and check your privacy settings.. Not everyone needs to know everything about you.
Access our post→ Public image on the internet: how to protect it from digital risks.
8. Do regular digital cleaning
Do you have old accounts you no longer use? Apps you've installed for years? Every profile and every app is a potential entry point for cybercriminals.
Delete accounts you no longer need,delete unused apps, and back up your important data. Qondar can also help you identify the data you still have floating around online.
9. Monitor your digital footprint with tools like Qondar
Did you know that databases containing millions of leaked emails, passwords, and phone numbers are being sold on the dark web? And often, those affected don't even know it. So, being vigilant and learning how to erase your digital footprint is essential
This is where tools like Qondar become crucial. This tool alerts you if your email appears in a leak,your password has been compromised, or your identity has been stolen. It's like having a personal security guard for your digital identity, working 24/7.
Why does all this matter so much?
According to the report IBM Cost of a Data Breach 2024, the average global cost of a personal data breach amounts to $4.88 million. While this data typically refers to companies, individuals suffer consequences, from financial losses to legal issues and reputational damage.
Having healthy digital habits doesn't make you invulnerable, but it significantly reduces your chances of falling victim to identity theft or a data leak. Just as you don't leave your front door unlocked, you shouldn't expose your digital identity.
Protect yourself today with Qondar
If you want to go further and have absolute control over your digital exposure, try Qondar by Enthec. It's intuitive, effective, and designed for people like you, who don't necessarily need to be cybersecurity experts, but still want peace of mind.
Start protecting your digital identity today. Take advantage of all Qondar's benefits and discover how we can help you.
Technology makes our lives easier, but it also demands responsibility. Implementing these nine healthy digital habits is a simple but essential step toward a safer digital life. Remember: It is not about living in fear but with awareness. And with the right tool,s you can do it with confidence.