Managed Security Services (MSS): Features and Benefits
Cybersecurity has become a critical aspect for any organization. Threats evolve rapidly, attackers automate processes, and attack surfaces expand as companies incorporate new systems and tools.
In this context, MSS (managed security services) have become established as an effective option to strengthen digital protection without requiring companies to maintain internal resources that are difficult to sustain.
Before delving into what MSS contributes and why it's so prevalent in modern security strategies, it's worth taking a look at a tool that perfectly complements this model: Kartos, the solution from Enthec designed for companies that need a constant and realistic visibility of your external exposure. . This tool is part of the CTEM philosophy, an approach that continuously analyzes the attack surface, identifies real risks, and enables prioritizing efforts.
At a time when most incidents are triggered by known vulnerabilities or misconfigurations, having this view is crucial for any security strategy, including those based on MSS.
What precisely are Managed Security Services (MSS)?
The MSS are outsourced services offered by specialized providers to continuously monitor, manage, and improve an organization's security.. Although each provider may have its own catalog, the essence is the same: to provide expert knowledge, advanced tools, and constant follow-up.
An approach that frees up internal burden
Many companies don't have dedicated cybersecurity staff, or if they do, they're focused on day-to-day operational tasks. Internal teams are often left out overflowing for tasks such as:
- Analyze alerts that keep growing.
- Review security settings on various systems.
- Prioritize vulnerabilities that change every week.
- Keep an eye on emerging threats.
MSS allows some or all of these tasks to be delegated to specialists who work with technology, processes, and equipment dedicated exclusively to this.

Main features of MSS
Although each model is tailored to specific needs, most managed security services share a standard set of functionalities.
Continuous monitoring
It is one of the central components. MSS providers constantly monitor infrastructure, networks, and services to detect suspicious behavior, failures, or signs of intrusion.
Incident Management
When an attack attempt is detected, the provider not only generates alerts but also assists with analysis, containment, and recovery. Having processes defined and executed by professionals reduces damage, downtime, and financial losses.
Vulnerability Management
MSS typically include periodic scans, configuration reviews, and patch prioritization. However, this is where solutions like Kartos become essential, because they complement this internal view with an external X-ray that reflects what an attacker would see from the outside.
If you want to delve deeper into this topic, visit our blog→ Real-time vulnerability management: a step forward in cybersecurity.
Threat analysis and context
A Security Management System (SMS) doesn't just review logs: it interprets what's happening in the security world. For example, if a critical vulnerability is actively exploited, the provider helps the client assess whether their infrastructure is exposed and what measures they should take.
Periodic reports and advice
Those in charge typically receive accessible analyses that allow them to understand the evolution of risk, the level of exposure, and the impact of the measures taken. This transparency facilitates strategic decision-making.
The value of combining MSS with a CTEM approach
The traditional security model focused on protecting what was already within the perimeter. However, today that perimeter has become blurred: there are cloud services, external applications, remote access, personal devices, databases exposed in error, and a long list of constantly changing threat vectors.
This is where the CTEM and MSS complement each other naturally.
Internal visibility + external visibility
- The MSS review logs, devices, networks, and internal activity.
- Tools such as Kartos analyze what is exposed externally: domains, subdomains, leaks, unknown assets, third-party risks, and poorly published configurations.
By combining both perspectives, the company obtains a more complete and realistic map of its situation.
Prioritization based on actual risk
Many companies have hundreds or even thousands of vulnerabilities detected by their internal systems. The CTEM simplifies this landscape by highlighting what is truly urgent. If something can be exploited from the outside or appears on cybercrime forums, it moves to the top of the list.
Reduction of “noise” in MSS
A managed SOC receives thousands of alerts every week. When the provider leverages a CTEM platform, it eliminates noise and focuses on relevant threats. This results in more effective defense and faster response times.
Benefits of MSS for organizations
The Managed Security Services have become a key solution for businesses of all types. Their most valued advantages are usually:
1. Controlled and predictable costs
Hire cybersecurity specialists is complex and expensive; keeping them trained is even more so. MSSs allow access to complete teams at a known monthly or annual cost.
2. Greater security maturity without increasing staff
Especially useful for SMEs and companies that cannot (or do not want to) create an internal team.
3. Rapid incident response
Response time is critical. MSS drastically reduces the hours (or days) that an internal team would spend detecting a problem on its own.
4. Regulatory compliance
Many standards, such as the ENS or the NIS2,require continuous monitoring and risk management. An MSS service facilitates compliance with these requirements through appropriate documentation and processes.
5. Tranquility
Perhaps the least technical benefit, but the one most valued by management. Knowing that experts are monitoring the infrastructure 24/7 provides security and prevents improvised decisions.
Kartos and the MSS: a strategic combination
Companies across all sectors use Kartos to strengthen their security processes, and many integrate it directly into their MSS strategy. At Enthec, we've observed that this combination enables:
- Reduce actual exposure to attacks.
- Optimize response times.
- Improve coordination with internal or external security teams.
- Avoid breaches caused by unknown or misconfigured assets.
Furthermore, Kartos provides clear, practical reports that facilitate the work of both the MSS provider and the client. This alignment between internal and external capabilities is, today, one of the cornerstones of effective security.
MSS have become established because they help organizations protect themselves in an increasingly complex environment.. However, monitoring is not enough: it is necessary to understand the exposure, prioritize what really matters, and act continuously.
That's where the combination of managed services and solutions like Kartos, based on CTEM, comes in to elevate security to a more practical, intelligent level, adapted to current reality.
If your company wants to strengthen its security strategy, improve its external visibility, and have a modern, comprehensive, and sustainable approach, we invite you to learn how Enthec can help you achieve this. Contact us.
Cybersecurity and the human factor: the most common mistake in digital protection
Cybersecurity is one of those issues we all know we should be taking care of, but we keep putting it off. Updating passwords, checking permissions, verifying links… These are simple tasks, yes, but they're often overlooked. And that's precisely the root of the problem: In cybersecurity, the human factor remains the weakest link.
This isn't about blaming anyone, but about acknowledging an apparent reality. Human error is, currently, the most common cause of digital incidents.
In recent years, the rise of remote work, the fast pace of life, and the daily use of connected devices have made this vulnerability even more pronounced. And if we think about it for a moment, it makes sense: an impulsive click or a weak password can open the door to problems that cost time, money, and reputation.
Before moving on, it's worth introducing a tool that's helping to reduce this exposure in the daily lives of all users: Qondar, Enthec's cyber-surveillance solution for individuals. Qondar is a key component of Continuous Threat Exposure Management, providing timely warnings about data breaches, password leaks, and other risks that directly affect a person's digital life.
Understanding the relationship between cybersecurity and the human factor
The expression “cybersecurity and the human factor” encompasses a straightforward idea: Digital security does not depend solely on systems, firewalls, or artificial intelligence,but also on how we use technology. Companies can invest in advanced tools, but they're of little use if an employee falls for a phishing email or unintentionally shares sensitive information.
Why do we keep failing at the same things?
Several reasons explain this phenomenon:
- Information overload. We live surrounded by notifications and simultaneous tasks. In that pace, double-checking a suspicious email isn't always a priority.
- Overconfidence. In both our professional and personal lives, we often think, "It won't happen to us." But no one is safe: neither individuals nor companies.
- Lack of ongoing training. Many attacks evolve so rapidly that what we knew a year ago is no longer sufficient. And this is where the CTEM concept comes into play.

The importance of Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM)
Cybersecurity can no longer be viewed as a one-off project. It's not enough to conduct a single audit and assume everything is under control. Threats evolve. Data moves. And attackers refine their techniques.
Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) seeks precisely this: to constantly monitor which vulnerabilities we have and which risks are active at any given time. . It's not just about reacting, but about detecting before the damage occurs.
What does CTEM contribute to the field of human factors?
- Constant visibility: allows you to see if leaked credentials, breaches, or risk signals associated with common errors have appeared.
- Realistic prioritization: It helps determine which vulnerabilities require immediate attention and which do not.
- Data-based prevention: The sooner a problem is identified, the easier it is to correct.
This is where solutions like Kartos (for businesses) and Qondar (for individuals) play an instrumental role. Both allow this continuous exposure approach to be implemented without complex processes or specialized equipment.
Most frequent human errors in cybersecurity
Below are some of the most common mistakes in both the business and personal spheres. All of them are directly related to cybersecurity and the human factor, and many could be avoided with minimal monitoring or training.
1. Reusing passwords
A classic. According to a NordPass study, most users still reuse the same password across more than 10 different services. If one of those platforms suffers a data breach, they are all exposed.
You may be interested in→ How to manage business passwords and credentials easily and securely to avoid online threats.
2. Falling for fraudulent emails or messages
Phishing is becoming increasingly sophisticated. Many attacks perfectly mimic well-known companies, banks, or even coworkers. An innocent click can compromise the entire device.
3. Underestimating “harmless” information
Sometimes we share seemingly irrelevant data: a photo with location, a personal email on a website without HTTPS, an automatic response on vacation… All of that can be useful to an attacker.
4. Trusting open Wi-Fi networks
Having a coffee while we work is tempting, but connecting to an open network can expose sensitive information to third parties.
5. Failure to monitor personal data leaks
Many users are unaware whether their credentials have been exposed on forums, in leaked databases, or on the dark web. This lack of control fuels risks that accumulate without us even realizing it.
How to reduce human vulnerability: habits and tools
The good news is that improving cybersecurity and the human factor doesn't require being an engineer or dedicating hours every week. Often, simple measures are enough.
Basic digital hygiene
- Use unique and strong passwords.
- Activate two-step verification.
- Be wary of unsolicited links or files.
- Review application permissions.
- Keep systems updated.
Continuing education in companies
It's not just about giving an annual talk. Organizations that reduce incidents typically implement short, dynamic, and frequent training sessions. Even small reminders have a real impact.
Cyber surveillance for individuals
This is where Qondar comes in, designed so that anyone can:
- Find out if passwords have been leaked.
- Detect digital identity theft.
- Monitor mentions or data in high-risk areas.
- Receive clear and actionable notifications.
It's a simple way to effortlessly integrate the CTEM mindset into your daily routine, helping to make the human factor no longer a permanent problem.
Technology helps, but the responsibility is shared.
Although tools like Kartos or Qondar facilitate risk management, cybersecurity remains a shared responsibility. The sum of human behavior and technological surveillance is what truly builds a safe environment.
The key is to create a culture where asking questions, checking, and being skeptical are the norm, not the exception, where it's understood that a mistake isn't a personal failing, but a reminder that we are all vulnerable.
The relationship between cybersecurity and the human factor is undeniable. As long as distractions, overconfidence, and a lack of healthy digital habitsexist, incidents that could have been avoided will continue to occur. That's why it's so important to integrate continuous monitoring at both the company and individual levels.
If you want to improve your personal protection,whether it's your own data or that of your close circle, Qondar is an accessible, practical option that lets you see what's happening with your data in real time. Discover our tool and start controlling your digital exposure today. More conscious cybersecurity is just a step away.
The relevance of cybersecurity audits in companies
Any company, even the smallest ones, operates in some way connected to the online world and depends on data, devices, and applications. The reality is simple: if your business uses the internet, it's also exposed to threats. And that's precisely why the cybersecurity audit has become a fundamental tool for maintaining operational continuity and preventing further damage.
Before delving deeper into this type of analysis, it is worth mentioning a solution driving a remarkable evolution in the sector: Kartos by Enthec,. a platform designed for companies that need a clear, consistent view of their exposure. More than just a monitoring tool, Kartos is part of the Continuous Management of Threat Exposure.
Throughout the article, you will understand why both things need each other and how integrating them can strengthen the security of any company.
What is a cybersecurity audit, and why should you care?
Although it may sound technical, this type of audit is simply a detailed analysis of an organization's systems to assess its actual level of protection. When someone asks what a cybersecurity audit is, the answer involves checking processes, infrastructure, internal policies, and any weaknesses that attackers could exploit.
Unlike other technical reviews, an audit examines habits, roles, access, security culture, and the way things are done. It's not enough to have good firewalls: you have to review how information is managed daily.
Cybersecurity auditing for companies is a necessity
In practice, security incidents don't only affect banks or large technology companies. Therefore, cybersecurity audits in businesses are no longer just a recommendation; they are now a mandatory step for any organization that depends, even minimally, on its systems.
The most interesting thing is that the result of a good audit is not just a report. It also provides:
- A clear record of vulnerabilities.
- A roadmap to solve them.
- Indicators of the return on investment in security.
- Guidelines for improvement, both technical and organizational.
- A higher level of regulatory compliance (GDPR, ENS, ISO 27001…).
And if the company combines this one-off audit with CTEM tools like Kartos, continuous monitoring allows it to detect new threats even after correcting previous ones.
Types of cybersecurity audits: approaches according to need
When discussing the types of cybersecurity audits, they are usually divided into three main categories:
1. Internal cybersecurity audit
The internal cybersecurity audit is conducted from within the organization. It is typically carried out by in-house teams or consultants who work closely with the company.. Their main advantage is that they understand the real context, procedures, and potential points of friction.
It is beneficial for:
- Verify compliance with internal policies.
- Review access and permissions.
- Analyze data management.
- Check the staff's level of awareness.
2. External Audit
The external audit aims to obtain an independent and unbiased view.. Specialized third parties usually intervene, analyzing the system from the perspective of a real attacker and combining methodologies such as OWASP or OSINT analysis.
It adds value by allowing you to identify failures that have gone unnoticed and to validate whether internal measures actually work.
3. Specialized technical audits
They include tests such as:
- Pentesting (controlled attacks).
- Code review.
- Network analysis.
- Phishing simulations.
- Cloud security review.
This set allows for a comprehensive view and is suitable for companies with more specific needs or complex infrastructures.
Why an audit is not enough without continuous monitoring
This is where Enthec's CTEM perspective becomes especially relevant. Although the audit provides a detailed snapshot of the moment, that snapshot can become outdated in a matter of weeks. Systems change, new updates are installed, vulnerable software appears, or information is unintentionally exposed.
Platforms like Kartos allow the company to:
- Detect data leaks or exposures in real time.
- Identify open services that shouldn't be open.
- Continuously monitor domains, subdomains, or IPs.
- Receive direct alerts when a relevant threat appears.
- Prioritize risks according to their actual impact.

Main benefits of auditing cybersecurity
Everything learned during the audit is a dynamic process that evolves in tandem with the business. This allows us to gain various advantages for the organization.
1. Reduction of economic risks
An attack can paralyze operations for days. The average cost of a security breach is estimated to exceed $4.45 million. Obviously, these figures are lower for small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs), but the proportional impact remains enormous.
2. Better decision making
When a company has clear, well-explained, and prioritized results, it knows where to invest and what to expect in return.
3. Alignment with legal requirements
In regulated sectors, demonstrating that regular audits are conducted is almost mandatory. Audits facilitate this traceability and provide verifiable reports.
4. Strengthening customer confidence
More and more users and companies are asking about security before hiring services. Demonstrating formal auditing processes can be a deciding factor.
How Kartos fits into the audit cycle
We can summarize the relationship between both elements in three steps:
1. Before the audit
Kartos identifies exposures, neglected domains, vulnerable services, leaked information, and emerging risks. This allows for audit preparation using real-world data.
2. During the audit
Auditors can use Kartos' findings to delve deeper into critical areas, reducing time and improving accuracy.
3. After the audit
Instead of leaving the report in a drawer, Kartos maintains active surveillance, detects new flaws, and alerts when something is at risk again.
In other words, the audit establishes the framework, and Kartos keeps it up to date.
The combination of traditional auditing and continuous monitoring is currently the most realistic way to protect a business. Auditing detects structural weaknesses; a CTEM platform, such as Kartos, prevents those weaknesses from recurring without warning.
If your company has not yet conducted a cybersecurity audit, or if you have been putting it off, now is the time to do it.
Do you want to discover how to improve your company's security with Kartos? Contact Enthec to learn how to combine regular audits with a continuous monitoring system to help you anticipate real threats.
Mobile device security: the key to protecting your digital identity
Mobile devices have become an extension of our daily lives. We store photos, documents, conversations, passwords, and even banking information on them.
This level of dependence has made mobile device security a crucial issue not only for businesses but also for individual users seeking to protect their digital identity.
Today, cybercrime is no longer limited to large corporations or sophisticated attacks on corporate networks. Every mobile phone is a potential entry point for attackers. That's why understanding mobile device security and implementing effective protective measures is essential to keeping our personal information safe.
Before delving into practical recommendations, it's worth getting to know a tool that helps more and more people every day: Qondar, Enthec's cyber-surveillance solution designed to protect people from digital threats.. Through Continuous Threat Exposure Management, Qondar helps detect vulnerabilities, data leaks, and potential incidents before they can be exploited. In other words, it allows you to understand and control your digital footprint to keep your identity safe.
The growing digital exposure: a silent challenge
Every app we install, every public Wi-Fi network we connect to, or every file we download can open a door to cyberattacks. According to Verizon's "Mobile Security Index 2025" report, 70% of companies acknowledge having experienced security incidents on their employees' personal mobile devices in the past year.
But the problem doesn't only affect the business sector. Individuals are also frequent targets. Fake apps, malicious links on social media and even simple fraudulent SMS messages can compromise a large amount of personal data. The main problem is that most users underestimate the factors that affect mobile device security, trusting that common sense is enough to prevent an attack.
However, the reality is that cybercriminals evolve as fast as technology.. New techniques, such as “smishing” (phishing through SMS) or attacks through seemingly legitimate applications, have become increasingly sophisticated.
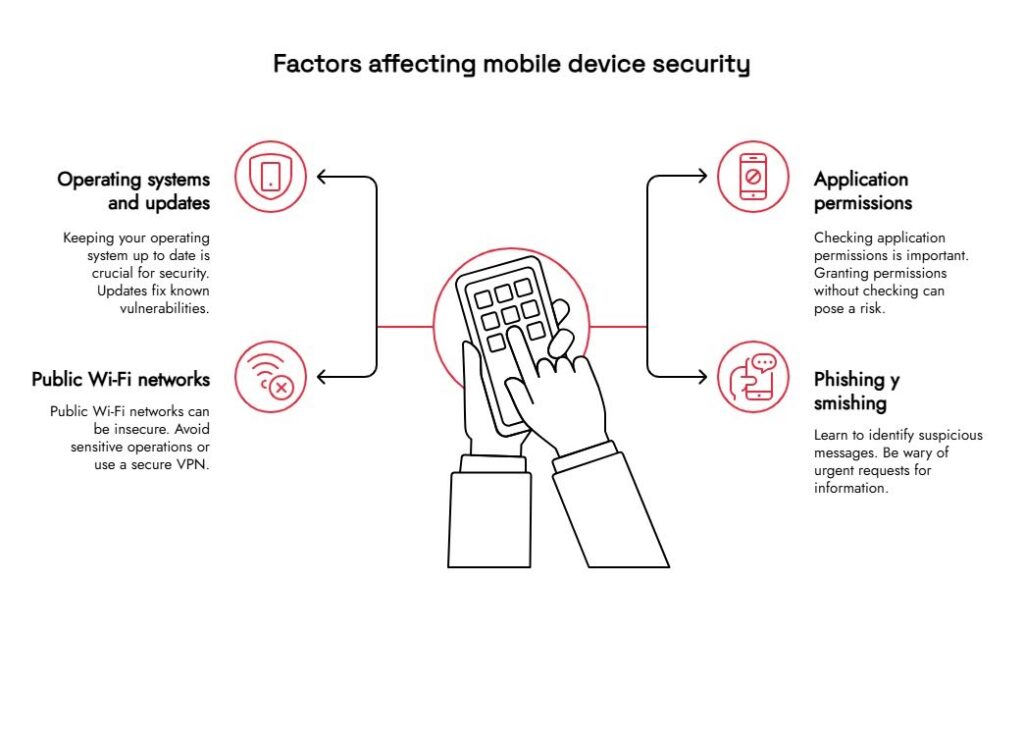
Factors that affect the security of mobile devices
Security in the mobile environment depends on multiple factors. Some of these are readily controllable by the user, but others require more advanced monitoring and protection tools.
1. Operating systems and updates
One of the most relevant aspects of mobile device security is operating system maintenance. . Each new version of Android or iOS includes patches that fix known vulnerabilities. Even so, many users delay these updates, leaving their devices vulnerable.
2. Application permissions
Apps often request permission to access the camera, contacts, or location. While many of these requests are legitimate, granting them without review can pose a risk.. Periodically reviewing which applications have access to what information is a basic but effective measure.
3. Public Wi-Fi networks
Open Wi-Fi networks, such as those found in cafes or airports, can be a point of attack. Criminals can intercept traffic and obtain passwords or confidential information. It is advisable to avoid performing sensitive operations (such as online banking) on public networks or, if that is not possible, use a secure VPN
4. Phishing and smishing
Through emails or messages, attackers try to trick users into revealing information or downloading malware. Learning to identify suspicious messages, checking URLs before clicking, and being wary of urgent requests for data are fundamental steps to avoid these mobile device security incidents.
Mobile device security measures that actually work
In addition to good digital habits, there are mobile device security measures that anyone can easily and effectively implement:
- Secure screen lock: use fingerprint, facial recognition, or a strong PIN.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA): mainly used on social media, in banking, or for email.
- Device encryption: systems activate it by default, but it's best to double-check.
- Review the download sources: Only install apps from official stores like Google Play or the App Store.
- Regular backups: This minimizes losses if the device is compromised.
These measures do not eliminate the risk, but they significantly reduce the exposed area. And it is precisely in this constant reduction that we must apply the proactive cyber surveillance that Enthec proposes with Qondar.
Qondar: personalized digital surveillance
Qondar is not an antivirus or a cleaning application. It is an advanced digital surveillance solution that continuously analyzes a user's online exposure. Through the CTEM methodology, the tool identifies vulnerabilities, monitors for personal data leaks, and alerts in real time about threats.
For example, if your data appears in a data breach or your phone number is published on an information marketplace forum, Qondar detects it immediately and notifies you. This way, you can take action before the damage becomes irreparable.
The most interesting thing is that Qondar does not require advanced technical knowledge.. Its approach is designed for individual users concerned about their digital privacy, from professionals who manage sensitive information to people who simply want to avoid being victims of fraud or identity theft.
Mobile security as part of your digital well-being
Thinking of mobile device security as merely a technical matter falls short. It's really a matter of personal well-being. Protecting your phone means protecting your memories, your conversations, your finances, and ultimately, your identity.
Adopt a proactive approach, review permissions, keep updates current, and use monitoring tools like Qondar not only reinforces security but also peace of mind.
Furthermore, t demand for CTEM tools will grow by 35%, especially in hybrid environments where professional and personal life are intertwined.
How to start protecting yourself today
To improve the security of your mobile devices, the first step is to understand your digital exposure. Knowing what information about you is accessible on the Internet, what applications have access to your data, and what vulnerabilities you might have is essential.
Qondar, from Enthec, offers you that visibility.. It is a continuous cyber-surveillance tool that turns information into protection, helping you make informed decisions about your online security.
Mobile device security is no longer optional; it's a basic necessity in today's connected world. Cyberattacks don't discriminate between large corporations and individual users: we are all potential targets.
Taking simple steps, staying informed, and having continuous monitoring tools are the best ways to maintain peace of mind.
Protecting your digital identity starts with your mobile phone. And today, you have solutions at your fingertips that make it easier than ever.
Discover how Qondar can help you stay one step ahead of threats. Contact us and take the first step towards a safer digital life.
How to implement industrial cybersecurity in your company
If your company is on a path of digital transformation, you should know that industrial cybersecurity is a critical asset to manage.
In this article, we explain, in a clear and accessible way, how to implement industrial cybersecurity in your company, what you should consider, and the role solutions like Kartos by Enthec can play in helping you.
Suppose you're looking for a tool that continuously manages threat exposure in industrial environments. In that case, it's worth considering Kartos,. a continuous monitoring solution designed for organizations that lets you monitor, assess, and respond to cybersecurity risks on an ongoing basis.
Why is industrial cybersecurity critical now?
The adoption of technologies characteristic of the “fourth industrial revolution” (also known as Industry 4.0) is expanding the scope and complexity of risks in industrial environments.
For example, many companies in the industrial sector are integrating previously unconnected control systems, robots, and IoT sensors, thereby expanding the attack surface.
In this context, implementing a robust cybersecurity strategy for Industry 4.0 is no longer only about protecting data, but also about safeguarding critical operational processes, controlling physical and digital risks, and ensuring business continuity.
You might be interested in→ IoT and cybersecurity: Risks and strategies to protect connected devices.
Step 1: Diagnosis and awareness
Before taking action, you need to understand the situation. This first step involves analyzing your company's current state, identifying vulnerabilities, and building a knowledge base to support a solid strategy. Without a precise diagnosis, any action will be incomplete or ineffective.
Initial assessment
The first thing you need to do is understand your company's current state regarding industrial cybersecurity.. This implies:
- Map assets: machinery, control systems, OT (operational technology) networks, IoT devices.
- Identify connections within the IT environment (information technology) and OT.
- Knowing which protocols, standards, and policies already exist (for example, is your company aligned with the ISA/IEC 62443 standard for industrial control systems?).
- Evaluate the safety culture: What do employees know, what practices are followed, what training is available?
Raising awareness
Technology is not enough if people don't know what they are doing or what risks they face. Here, training and awareness remain key for Industry 4.0 cybersecurity.

Step 2: Defining a strategy adapted to the industrial environment
Once you understand your weaknesses and your organization's maturity level, it's time to define a coherent strategy. This lays the foundation for industrial cybersecurity, guiding technical, human, and operational decisions.
Governance and roles
Your company must determine who is responsible for cybersecurity:IT, OT, security, and production teams. A clear governance structure facilitates the integration of industrial cybersecurity into daily operations.
Policies, standards, and controls
Define internal policies that:
- Segregate IT and OT networks or establish adequate security perimeters.
- Review and update industrial hardware and software.
- Monitor the entire network: connected devices, anomalous traffic, access controls, etc.
Continuous defense strategy
This is where the concept of CTEM (Continuous Threat Exposure Management) comes in. A single assessment is not enough: Risks change, vulnerabilities emerge, attackers evolve.. Solutions such as Kartos by Enthec enable continuous monitoring, tailored for industrial environments, to detect, assess, and respond dynamically.
Implementing industrial cybersecurity with this philosophy implies a change of mindset: from reacting to incidents to anticipating them.
Step 3: Technical Implementation. Best practices for cybersecurity in Industry 4.0
Now comes the practical part. It's time to implement the technical measures that bring the strategy to life. Here, theory becomes concrete action: segmenting networks, controlling access, monitoring, protecting, and responding.
Network segmentation and isolation
In an industrial environment, it's common to have control networks (e.g., SCADA and PLCs), production networks, and administrative networks. You must segment to limit damage in case of an attack.. This measure appears among the most recommended in Industry 4.0 studies.
Updates and patches
One of the most frequent intrusion vectors is legacy or outdated systems.. Industrial cybersecurity requires regularly reviewing industrial equipment (sensors, controllers, gateways) and implementing proactive security measures.
Threat monitoring and detection
Here again, continuous monitoring is key. Thanks to CTEM systems like Kartos, you can monitor anomalies, events, unusual access, and OT device behavior.
Identity and access management
Limit who can access which system.. This includes privileged access management, strong authentication, activity logging, and deletion of inactive accounts. In Industry 4.0, with an ever-increasing number of connected devices, this aspect becomes critical.
Incident response
Have a plan: What should be done if a device is compromised? How should a segment be isolated? How should operations be restored? As noted, many facilities still lack an adequate response plan.
Step 4: Practical cases and examples in cybersecurity of Industry 4.0
- A manufacturing plant that has deployed IoT sensors to monitor machinery conditions can be exposed if those sensors are not on a segmented network or under constant supervision; an attacker could access the control network and alter parameters.
- Another example: the convergence of IT and OT without security coordination, which can result in administrative access (from IT) granting unauthorized access to OT systems. This lack of synchronization between IT and OT is a key risk.
- Also, facilities that lack continuous monitoring of OT traffic and have not assessed emerging vulnerabilities. According to recent studies, industry protection must evolve toward a multi-layered, continuous, and adaptive approach.
Step 5: How to integrate a solution like Kartos into your plan
The Kartos tool from Enthec enables you to implement a continuous threat monitoring system tailored to the industrial environment. Here are some key points on how it fits in:
- Visualizing the risk landscape: Kartos groups incidents, vulnerabilities, and connected devices, enabling you to gain a global view of your company's exposure.
- Active monitoring: not only specific analyses, but constant monitoring of behaviors, early warnings, and response capacity.
- Recommendations and prioritization of actions: In the face of multiple vulnerabilities, Kartos helps prioritize based on operational impact and real risk.
- Integration with your industrial cybersecurity strategy: relying on defined processes, policies, and training, Kartos becomes an ally, not only a tool.
If your company works with industrial systems, control networks, connected sensors, and automated machinery, a solution like Kartos enables you to shift from a reactive to a proactive approach to industrial cybersecurity.
Step 6: Measurement, review, and continuous improvement
Industrial cybersecurity is not a finish line, but a process of continuous improvement. You must establish indicators (for example: number of vulnerabilities detected, average response time, percentage of segmented devices, number of OT incidents detected), review them periodically, and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Furthermore, production environments are changing (new devices, new interconnections, new suppliers), and therefore, Industry 4.0 cybersecurity requires updated plans and controls.. Adapting to a rapidly evolving threat landscape is becoming increasingly important.
Implementing industrial cybersecurity in your company is a challenge, but also a great opportunity: an opportunity to strengthen your operations, protect your assets, ensure continuity, and trust that digitalization will not expose you to preventable attacks.
To do it successfully:
- Start with the diagnosis and awareness.
- Define a clear strategy with governance, policies, and continuous monitoring.
- Apply specific good technical practices: segmentation, updates, monitoring, controlled access, and incident response.
- Integrate tools adapted to the industrial environment.
- Establish a continuous cycle of measurement, review, and improvement.
The transformation to Industry 4.0 opens many doors, but it also demands that cybersecurity be an integral part of the process.. In Enthec, we are prepared to help you take this step with confidence and vision.
Would you like us to design an industrial cybersecurity plan tailored to your company? Contact our team. Let's begin today.
Financial data protection: the difference between reacting and anticipating
Financial data has become one of the most valuable assets for both individuals and businesses. But they are also one of the most coveted by cybercriminals.
Credential theft, fraud, leaks, or identity theft are threats that grow daily and are no longer limited to large corporations or banks. Today, anyone with a bank account or investments is a potential target.
Protecting financial data is not just about security but also about trust, stability, and prevention. However, most of the time we continue to act when the damage is already done. and therein lies the significant difference between reacting and anticipating: in the first case, we try to put out the fire; in the second, we prevent it from starting.
Qondar, the tool that helps you anticipate
Before we delve into how to protect your financial data effectively, we want to mention a solution we've designed precisely for that purpose: Qondar.
Qondar is a tool for cyber surveillance designed for individuals and grounded in the principles of Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM). Simply put, it means not waiting for an attack to occur before taking action. Its approach consists of monitoring, detecting, and anticipating potential data leaks or exposures of personal and financial information online, on both the visible and dark webs.
Thanks to this continuous monitoring, Qondar helps identify early signs of risk, such as leaked credentials, compromised accounts, or sensitive information published on forums or in databases. In this way, users can react before the problem becomes a real loss.
If you're worried about digital security, of your personal and financial information, now is a great time to try Qondar and discover how it can help you stay one step ahead of threats.
Why protecting financial data should be a priority
In Spain and around the world, we've seen an increase in attacks related to the theft of financial data. It's not just about large-scale operations: many begin with simple phishing emails or unauthorized access to personal financial accounts.
At an individual level, the most frequent risks are:
- Theft of bank credentials through phishing or malware.
- Identity theft to apply for credit or to make fraudulent purchases.
- Unauthorized access to wallets or investment applications.
- Personal data leaks that allow for the creation of financial profiles.
For companies, the impact can be devastating: loss of customers, legal penalties, reputational damage, and recovery costs.
Reacting vs. anticipating: two very different strategies
When a data breach occurs, many people and organizations follow the same pattern: they discover the problem when it's already too late. This is the reactivo: se actúa después del ataque, tratando de reparar los daños, avisar a los afectados y reforzar las medidas de seguridad que ya han sido vulneradas.
In contrast, the proactive or anticipatory approach seeks to detect vulnerabilities before they are exploited . by providing visibility into where and how financial data could be compromised and acting proactively.
The practical difference between the two approaches is enormous.
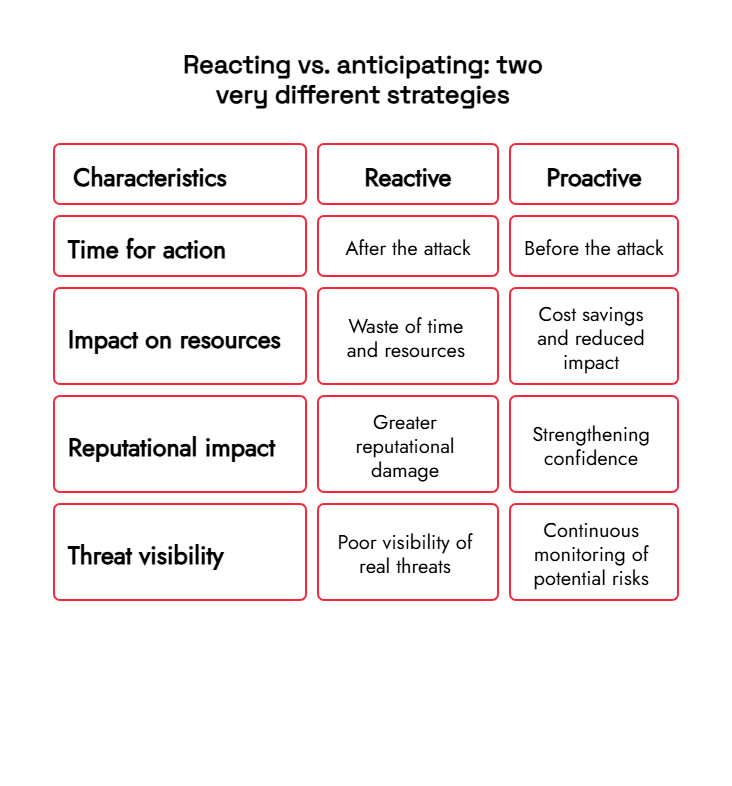
In other words, anticipation not only protects but also strengthens.
If you want to delve deeper into the term proactive approach, access our blog post→ Proactive security: what is it and why use it to prevent and detect threats and cyberattacks?
How to anticipate: the importance of the CTEM model
The CTEM approach starts with a simple idea: It is not enough to analyze risks once a year or after an incident.. Threats change every day, and security solutions must change too.
The CTEM model, used in solutions such as Qondar (for individuals) and Kartos (for companies), is based on three fundamental pillars:
1. Constant visibility
This is about maintaining active, continuous vigilance over the information circulating online. This includes detecting whether your financial data appears on forums, in illegal marketplaces, or in compromised databases.
With Qondar, this process is automated and updated in real time, avoiding reliance on manual or occasional reviews.
2. Exposure assessment
Not every exposure poses an immediate threat, but it's crucial to know what information is at risk and which one could be used against you. This analysis allows you to prioritize protective actions, focusing on what is truly urgent.
3. Early response and correction
The last step is to act quickly. When an exposure is detected. Qondar provides early alerts so users can cambiar contraseñas, revocar accesos o contactar con su entidad financiera antes de sufrir un ataque directo.
What can a person do to protect their financial data?
Although technology is essential, awareness and good practices remain the first line of defense. Some basic measures include:
- Avoid reusing passwords, especially for bank or investment accounts.
- Activate the two-step authentication on all platforms that allows it.
- Do not share personal or banking information through unverified emails or messages.
- Periodically check if your email address or data appears in filtered databases.
- Keep your device and app software up to date.
The key is to make protecting financial data a continuous habit, not in a one-off reaction to a threat.
Enthec: Cybersecurity as a process, not a patch
At Enthec, we specialize in offering solutions that integrate with this continuous, proactive approach. Our Kartos tool, for businesses, and Qondar, for individuals, enable dynamic management of exposure to threats and adaptation to changes in the digital environment.
Both solutions are designed under the philosophy that cybersecurity is not a product, but a living process that requires constant review, learning, and evolution.
In matters of financial data protection, responding can be costly. Not only in economic terms, but also emotionally: stress, loss of confidence, or the time spent regaining control are invisible but real costs.
Anticipating, on the other hand, is a way of safeguarding peace of mind.. Thanks to tools like Qondar; this prevention is no longer a luxury reserved for experts or large companies, but something accessible and valuable for anyone connected to the digital world.
Take the step towards more conscious and preventative security. Discover how Qondar can help you protect your information and your financial peace of mind Contact us
Why cyber surveillance is key to any CISO's strategy
Today, we can observe threats evolving rapidly and attackers operating with sophistication. Cyber surveillance has become an essential pillar for anyone responsible for an organization's security.
If you are a CISO or security manager, simply reacting is no longer enough: you must anticipate, monitor, and continuously manage risk exposure.
Before delving deeper into this topic, let's talk about Kartos, Enthec's solution designed for businesses. Kartos is a cyber surveillance tool designed to provide continuous insight into your company's exposure to threats, helping discover vulnerabilities, validate which risks are real, and prioritize mitigation actions.
Kartos is part of the operational muscle a CISO needs to sustain a modern cybersecurity program.
What is cyber surveillance: definition and scope
We could say that the most useful definition of cyber surveillance today is:
The practice of continuously monitoring the digital environment (both internal and external) for signs of threats, data exposure, emerging vulnerabilities, or suspicious activity, to respond as quickly as possible and reduce impact.
But that definition does not fully capture its strategic meaning. Cyber surveillance is not just about "being vigilant," but about doing so in a structured, automated way, focusing on what really matters to the company.
In more technical terms, cyber surveillance falls under the Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) framework, which goes beyond one-off vulnerability scans.
Why every CISO needs to incorporate cyber surveillance
1. The pace of risk doesn't wait.
Modern organizations typically identify tens of thousands of potential exposures each month. For example, according to a study by XM Cyber, an average of 15,000 exploitable exposures is identified across many organizations, with some exceeding 100,000.
With that volume, it is not feasible to manually review or prioritize without automating the risk criteria.
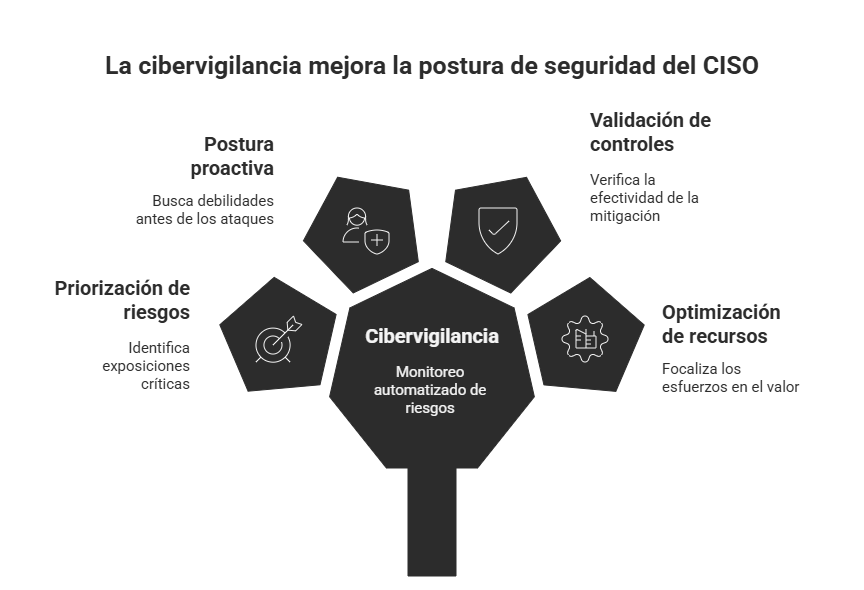
2. From reactive to proactive
Traditional security strategies (periodic scans, ad hoc tests) tend to fall behind in the face of constant change. CTEM, supported by cyber surveillance, allows us to move from a model in which we act after detecting an incident to one in which we look for weaknesses before they are exploited against us.
3. Risk-based and business-based approach
Not all vulnerabilities have the same impact. Cyber surveillance allows us to differentiate which exposures are critical to the business (for example, those that compromise sensitive data or critical processes) versus those that have little effect.
4. Continuous validation of controls
Detecting vulnerabilities is good, but how do you know if your controls effectively mitigate them? A cybersecurity surveillance solution like Kartos not only discovers flaws but can also validate whether the controls actually work in real-world scenarios through simulated attacks.
5. Alignment with the security strategy and resource optimization
A CISO cannot waste effort addressing minor risks. Properly implemented cyber surveillance allows a focus on the budget, team, and technical resources on what adds the most value.
How to apply cyber surveillance within the CTEM framework: key steps
For cyber surveillance to be effective, it should be framed within a clear CTEM cycle. The following are the recommended steps:
1. Scoping (delimitation)
Define which parts of the environment you are observing: assets, services, applications, cloud, external networks, etc. Set clear boundaries based on business value.
2. Discovery / Active Monitoring
This is where cyber surveillance, in the strict sense, comes in:it is crucial for detecting new assets, incorrect configurations, external exposures, leaked credentials, and suspicious activity. This monitoring must be automatic and continuous.
3. Prioritization of exposures
Not all detections warrant the same urgency. Here, each finding is evaluated based on ease of exploitation, potential impact, and business context. Cyber surveillance provides data (for example, whether that point is under attack) to improve this prioritization.
4. Validation / Simulation of attacks
It is not enough to see the vulnerability: It is necessary to validate whether it can actually be exploited. . Controlled simulations or advanced network teaming tests verify whether the risk is real. This bridges the gap between detection and action.
5. Remediation / Mobilization
Once validated, resources are allocated to mitigate or eliminate the exposure. Cyber-monitoring continues to confirm that the remediation is effective and does not generate side effects.
This cycle does not end: it returns to step 1 with continuous adjustments to maintain constant monitoring of the system.
Specific advantages offered by cyber surveillance
- Greater visibility without blind spots: what was previously unseen is revealed.
- The faster the earlier an exposure is detected, the smaller the window of risk.
- Reduction of actual risk: It is not enough to detect; it is also necessary to act reasonably and quickly.
- Continuous improvement: strategy evolves as threats and assets change.
- Better resource prioritization based on real risk avoids focusing efforts on irrelevant threats.
- Communication to the committee/managers: With quantified data on mitigated exposures, the CISO can demonstrate real impact on the business.
How Kartos fits into the CISO's strategy
Kartos, as a cyber-surveillance solution for businesses, is designed to be an active part of the CTEM cycle.. Some of its advantages are:
- It integrates detection, validation, and prioritization into a single platform.
- It provides a continuous view of the exposure, not just spot scans.
- It adapts to changes in the environment (new services, cloud environments, structural changes).
- It allows the CISO to demonstrate quantitatively how risk decreases over time.
- Connects with operational security processes (tickets, actions, tracking).
When cyber surveillance becomes an operational security muscle (rather than merely an informational layer), the CISO gains control over digital exposure.
If you are interested in learning how Kartos can fit into your organization and deploy an effective cyber surveillance program, you can request a demo or a personalized consultation. Contact us and we'll show you how to transform your security.
Today, more than ever, a CISO cannot rely solely on one-off scans or reacting only after an incident occurs. Cyber surveillance, understood as continuous, automated, and risk-based monitoring, is becoming essential for monitoring the digital landscape and reducing exposure.
By integrating it into a structured cycle like CTEM, cyber surveillance ceases to be an auxiliary function and becomes the backbone of the security strategy. In this context, solutions like Kartos by
Enthec can offer a real advantage: constant visibility, practical validation, and prioritization based on business criteria.
Act today. Strengthen your security with real and continuous cyber surveillance.
10 tips to protect your digital assets from cybercriminals
Our online history, bank accounts, family photos, and sensitive personal data are all part of what we might call your "digital treasure." And like any treasure, some try to steal it, damage it, or blackmail you with it.
Before analyzing this topic, we want to introduce Qondar, our solution designed for individual users to perform constant threat monitoring. With Qondar, you can automatically monitor potential leaks of your personal data on dark web sites, filter out relevant alerts, and receive support to address incidents.
If you want to take a step further to protect your digital assets, Qondar is a tool that you can use directly, without relying on an extensive infrastructure.
Below, we offer 10 practical tips along with small actions that will be very useful when an attacker tries to compromise your digital assets.
Why is it urgent to protect your digital heritage?
Every year, the volume of attacks targeting individuals and businesses grows significantly. In Spain, for example, a recent increase of more than 20% in malware detections has been observed (
Cybersecurity in Spain: Impact and Keys to the Rise of Malware in Europe
)
In addition, the financial losses from cybercrime can be severe: Many ransomware, phishing, and credential theft attacks target both businesses and individuals.
Therefore, it is not enough to “hope it doesn’t happen to me”: we must act in advance.

1. Take an inventory of your digital assets
Before you can protect something, you need to know what you have to protect. . That includes:
- Online accounts (email, social media, banking, trading platforms, cloud storage services)
- Passwords, private keys, cryptographic keys
- Backups, important files
- Photos, videos, scanned documents
- Personal data such as scanned ID, passports, and medical certificates
- Digital identities: profiles, online reputation
Having an inventory will help you prioritize based on asset value and vulnerability. categorization (e.g., “very critical,” “important,” “less critical”). You can apply different measures depending on the risk level.
2. Use strong passwords and manage authentication well
This advice is more vital than many think:
- Avoid using overly obvious passwords (names, birth dates, dictionary words).
- Use long passwords with mixed characters (uppercase, lowercase, numbers, symbols).
- Do not repeat passwords between services.
- Use a secure password manager to generate and store strong combinations reliably.
If you want to delve deeper into this aspect, we recommend you take a look at our content→
How to manage business passwords and credentials easily and securely to avoid online threats
.
And, in addition:
- Activate the
multi-factor authentication
whenever possible. - Use the second step based on an app (Google Authenticator, Authy) or physical keys (such as YubiKey), instead of SMS, which can be intercepted.
- If your manager allows it, configure additional authentication or a local lock.
A strong password combined with 2FA significantly reduces the likelihood of someone accessing your accounts without your permission.
3. Make backups (and check their integrity)
Even the best-protected system can fail. So:
- Have regular backups of your most valuable files.
- Save these copies in different places: external drive, cloud server, and offline storage.
- Encrypt the copies, especially if they contain sensitive data.
- Check from time to time that the backups are working and that you can restore them correctly.
Backup is your digital insurance. against an attack that deletes or encrypts your files; having copies gives you a recovery option.
4. Keep your devices and software always up to date
Many attacks exploit known vulnerabilities that already have
patches
available:
- Activate automatic updates whenever possible (operating system, browser, antivirus, applications).
- If a critical application is no longer updated (due to manufacturer abandonment), reconsider using it or look for alternatives.
- Don't neglect obsolete systems: Even older smartphones or routers can become vulnerable if you don't update them.
An updated system significantly reduces classic attack vectors (known exploits).
5. Beware of phishing and digital scams
Many cybercriminals choose to trick you into giving them your keys:
- Don't click on suspicious links, even if they appear to be from reliable sources.
- Always check the sender's real domain.
- Be wary of urgent messages (e.g., “your account will be blocked”) that demand immediate action.
- Do not provide personal information (ID, card numbers) via email or text message.
- Always verify through another channel whether a message you receive really comes from the entity it claims to.
This type of scam is one of the most common, precisely because many users let their guard down.
You might be interested→
Phishing: what it is and how many types there are
.
6. Monitor your digital exposure (detect leaks and infiltrations)
One of the keys to protecting digital heritage is to find out if your data has already been compromised:
- Use monitoring tools to find out if your credentials or data appear on leaked lists or on the dark web.
- Qondar (Enthec's solution for individuals) offers precisely this capability: continuous threat monitoring, alerts when it detects that any of your data has been exposed, and practical instructions for action.
- When an alert occurs, act quickly: Change passwords, block access, verify account integrity.
Detecting a leak early minimizes damage.
7. Segment and control access to your accounts
Do not give more permissions than necessary:
-
- Use user accounts with limited permissions for everyday tasks (avoid always using the administrator account).
- In home networks, segment equipment (e.g., guest network, IoT device network).
- Check which apps have access to your accounts (OAuth authorizations, social media permissions) and revoke the ones you don't use.
- If you share devices, create separate profiles and prevent others from using your session.
The fewer privileges an access has, the less damage it can cause.
8. Encrypt your sensitive data
Encryption is a powerful barrier:
- Encrypt entire disks (BitLocker, FileVault, LUKS)
- Use encryption when transferring data (TLS/SSL, VPN connections).
- Use storage services that are end-to-end encrypted (so that not even the provider can read your data).
- For very sensitive data, you can use file encryption software (e.g., VeraCrypt).
This additional level means that even if someone accesses the file or disk, they cannot read it without the key.
9. Maintain an attitude of vigilance and habit
Protection is not a single action, but a habit:
- Regularly review logs, alerts, and access to your accounts.
- Don't ignore alerts, even if some are false; analyzing them is better than ignoring them.
- Update your digital inventory with new services, accounts, or devices.
- Stay informed: threats are evolving. Read news, specialized blogs, and cybersecurity reports.
10. Plan your incident response
Protecting isn't just about preventing: you must be prepared to act if something goes wrong:
- Define a simple plan: what to do first if you detect unauthorized access, leaked data, or receive a blackmail attempt.
- Have contacts for technical support, suppliers, banks, or services you work with on hand.
- Use recovery tools (e.g., restore from backup).
- Keep records of the incident (logs, screenshots) that could be used in a legal claim or complaint.
- Consider hiring specialized protection: Qondar can help you not only detect threats, but also manage ongoing exposure and provide incident support.
Today, digital exposure is constant,from email to the cloud to your smartphone. But protecting your digital assets is possible if you take the proper measures. You don't need to be an expert: with discipline, good tools, and a little vigilance, you can significantly reduce the risk.
If you are concerned about your safety and
personal privacy
in the digital world, we invite you to learn about Qondar, a practical tool for individuals who desire constant monitoring and active alertness.
Want to learn how to get started with Qondar or create a personalized digital protection plan? Contact us and we will help you.
Red team in cybersecurity: how it works
The term red team is sparking interest in the world of computer security: what exactly does it mean, how does it work, and why is it useful? In this article, we'll clearly and comprehensively explain what it is, its advantages, its limitations, and how it fits into a modern defense strategy like the one we offer at Enthec with our Kartos solution.
Before diving in, it's a good idea to learn a little about Kartos: it's a cyber surveillance solution designed for businesses that seeks to offer Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM). In other words, Kartos helps you permanently identify weak points in your infrastructure, prioritize the most dangerous ones, and ensure that vulnerabilities don't reappear.
What is a red team?
A red team is a specialized team that simulates the role of a real attacker to test an organization's security. Rather than just performing spot tests, their approach seeks to replicate advanced techniques, combining technical, human, and sometimes physical methods to determine if an adversary could compromise critical assets without being detected.
In the cybersecurity sector, “red teaming” means turning those simulations into intentional and structured exercises, with defined objectives, clear rules, and mechanisms to learn from the results.
Unlike a routine vulnerability audit or scan, a red team seeks to emulate how a real attacker, with the resources, skills, and patience, would attempt to infiltrate, hide, move laterally, and achieve a goal (e.g., exfiltrate data).
A red team executes an adversary emulation exercise on a network, system, or IT environment to identify critical flaws and gaps that are difficult to detect using other methods.
Red teaming vs. penetration testing (pentesting)
It is common to confuse red team with pentesting, but there are key differences:
- Pentesting is usually more limited in time or scope, focusing on finding specific known vulnerabilities.
- The red team, on the other hand, is more free and prolonged, aimed at seeing if an attacker can achieve a fundamental objective, not just list faults.
- Red teaming also assesses the detection and response capabilities of internal teams, not just the presence of vulnerabilities.
- The red team often operates without warning or with minimal visibility to simulate real-life conditions.
A red team exercise can last weeks, involve multiple vectors (email, remote access, phishing, deception, social engineering), and conclude with a report detailing the progress made, the detections, and the defensive flaws that need to be addressed.

How a red team works: typical stages
To better understand this, I'll break down the typical phases of a red team exercise:
1. Definition of objectives and scope
Before attacking, the intended targets are agreed upon (e.g., accessing sensitive data, gaining administrator access, leaking information), and systems are evaluated as either within or outside the perimeter (what is excluded). Rules of engagement are also established to prevent unwanted damage.
2. Reconnaissance/intelligence
The team gathers public, internal, or compromised information about the organization: domains, employees, networks, exposed services... This allows for the construction of realistic attack scenarios.
3. Initial exploitation/entry point
Here, the red team uses vulnerabilities, phishing, weak credentials, or social engineering to gain a foothold within the target network. This involves gaining initial access without being detected.
4. Persistent access and lateral movement
Once inside, the simulated attacker escalates privileges, moves laterally, explores the network, searches for other vulnerable systems, and moves toward the defined target.
5. Goal achievement / final scenario
The red team, if successful, carries out the planned scenario: data extraction, maintaining a hidden presence, etc.
6. Report and recommendations
The team delivers a report with findings, attack routes used, points where attacks were stopped or detected, and recommendations for correcting weaknesses.
7. Correction and validation phase
Recommendations are reviewed, issues are corrected or mitigated, and in some cases, a subsequent verification (light re-red teaming) is performed to confirm that the improvements have been practical.
These stages allow us to understand not only where there are vulnerabilities, but also how an intelligent attacker would exploit them in a real-life environment.
Advantages of the red team within a CTEM strategy
Incorporating red teaming as part of a CTEM strategy brings benefits that go beyond simple fault finding:
- Dynamic visibility: With red teaming, you discover how holes interact with each other and how they might combine to form critical attack paths.
- Realistic prioritization: It is not enough to fix all the bugs; you have to know which ones can actually be exploited.
- Continuous evaluation of defenses: Helps test detection, alerts, and response capabilities.
- Culture of constant improvement: Encourages security and operations teams to advance and evolve.
When integrated with a platform like Kartos, red teaming becomes part of the CTEM cycle, as it is not a one-off exercise but rather an ongoing process of monitoring exposure to threats.
Furthermore, by being part of a CTEM framework, the red team's results are automatically fed back: new findings are integrated into the platform, prioritized based on their impact and risk, and periodic measurements are taken to verify that exposure is being reduced. This is the core of the Continuous Threat Exposure Management approach.
Limits and risks of the red team
Although the red team is very valuable, it's not a perfect or magic solution. It's essential to understand its limitations:
- Cost and time: these exercises often require specialized human resources and extended deadlines. Not all organizations have the budget for frequent red teaming.
- Partial coverage: An exercise cannot attack all possible systems, environments, or vectors, so there are “blind spots” in areas.
- Risk of interruptions: If not well planned, the simulated attack could cause failures or overloads in production systems.
- Limited in time: The threat landscape is changing; what works today may not work tomorrow. That's why red teaming, as a stand-alone exercise, is no substitute for ongoing vigilance.
For all these reasons, a good approach is to use red teaming in combination with other forms of assessment (continuous analysis, automated scans, more frequent simulations) within a CTEM framework.
How Kartos fits into this equation
Here is Enthec with its Kartos tool, a CTEM platform that allows:
- Integrate the red team's results into the ongoing exposure vision.
- Prioritize detected risks based on impact, probability, and complete attack paths.
- Monitor whether the proposed fixes have actually been applied or whether errors reappear.
- Automate alerts, reports, and follow-up tasks to maintain a secure posture over time.
Good practices for successfully using Red Team
For a red team exercise to truly deliver value, it's recommended to follow these practices:
- Define clear, realistic, and business-aligned objectives.
- Establish strict rules of engagement (what can be touched, what can't, what levels of risk do you accept).
- Maintain secrecy or controlled visibility (depending on the purpose).
- Involve the internal response team, at least in the reporting and correction phase.
- Incorporate lessons learned into the CTEM cycle so that they are not isolated.
- Repeat with partial frequency (for example, with minor exercises) to prevent the organization from settling.
- Measure its effectiveness with detection times, percentage of compromises detected, improvements after corrections, etc.
With these practices, red teaming ceases to be an isolated event and becomes a powerful lever for ongoing improvement and strengthening.
Red teaming is an advanced and powerful technique for simulating real attacks, assessing an organization's defenses, and discovering attack paths that other methods would miss. Red teaming within a CTEM framework, for example, by integrating it with the solution Kartos by
Enthec,
multiplies its value: it is not a one-off exercise, but part of a continuous mechanism for evaluating and improving the security posture.
If your company is already using monitoring or scanning tools, adding red teaming (in a well-balanced way) can significantly increase the level of security. Ideally, these results shouldn't be isolated but rather integrated into a CTEM strategy to ensure improvements are maintained over time.










