What is SIM swapping, and how can an early warning tool prevent identity theft
Our mobile phone is more than just a device: it's the center of our digital lives. We use it to access our social media, online banking, medical services, and work communications.
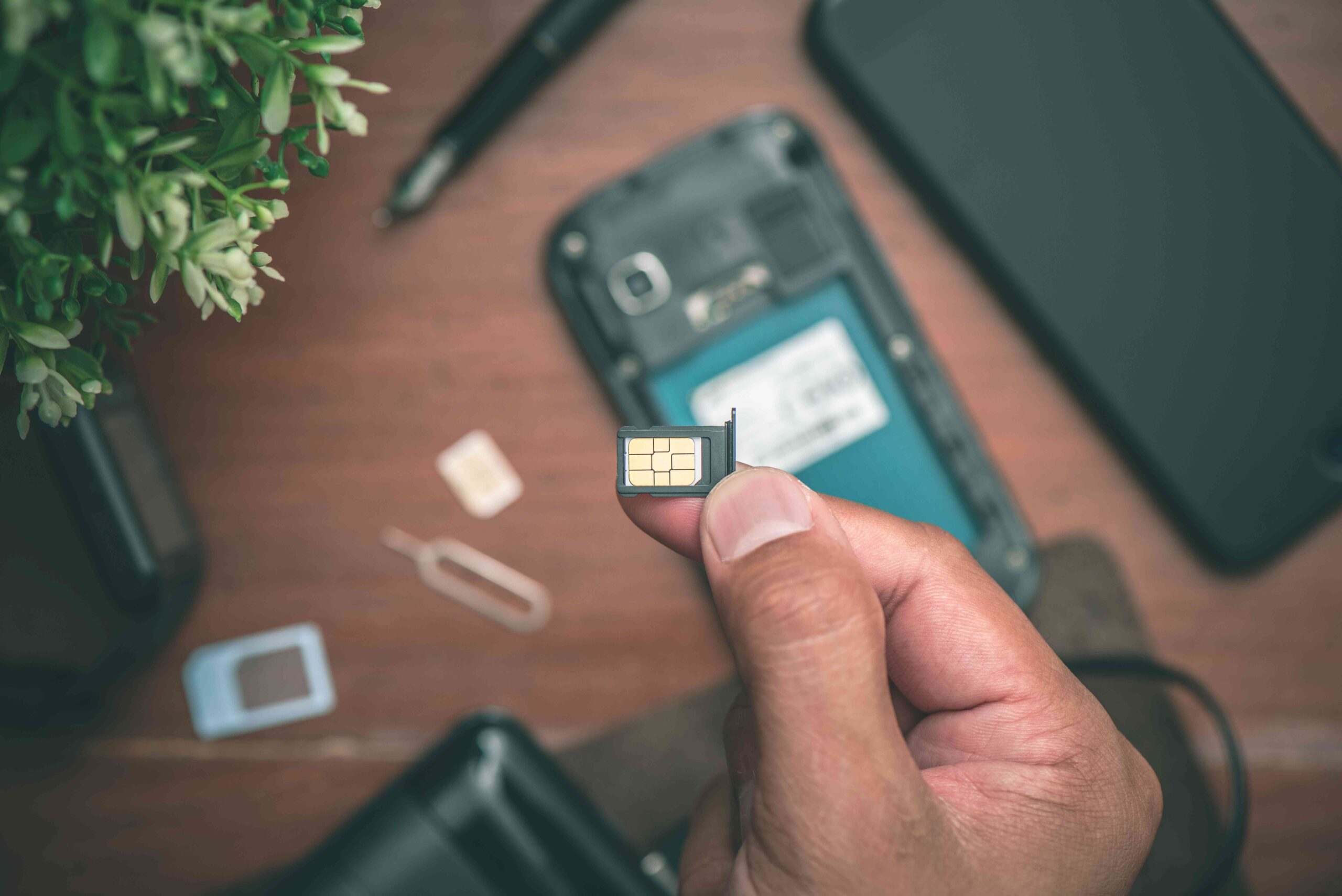
But have you ever thought about what would happen if someone hijacked your phone number? This is precisely what happens with SIM swapping, a impersonation technique that is on the rise.
Before going into details, it's worth presenting a solution that can be very useful when it comes to detecting an attack in time. Qondar, our tool, is a platform for individual cyber-surveillance to anticipate digital threats.
Qondar is an early warning system that identifies potential exposure of your personal information online and can help you detect signs of SIM swapping before it's too late.
What is SIM swapping?
You may have read about it in recent news or heard it called SIM swap or SIM swapping, but what exactly is SIM swapping?It is a digital scam that involves duplicating your SIM card without your consent.
In other words, a cybercriminal can take over your phone line, redirecting your calls, messages, and, most worryingly, the verification codes that many services send via SMS.
The objective is clear: access your accounts using popular two-step verification (2FA) systems. Many banks, social media platforms, and emails use this method to confirm your identity, but if the attacker already has your phone number, they can receive these codes and access your data as if they were you.
SIM swap: how does it work?
The technique is not new, but it has gained popularity in recent years. The modus operandi usually follows this scheme:
- Obtaining personal data.. Through leaks, social engineering, or even social networks, the criminal collects enough information about you (name, ID, address, phone number, etc.).
- Impersonation. With this information, they contact your phone provider, pretending to be you, and request a duplicate SIM card, claiming the device has been lost or damaged.
- Activating the new SIM.. Once the operator validates the request, the new SIM is activated, and your line will no longer be available on your device.
- Account access:. The attacker tries to access your accounts. If you have SMS authentication enabled, he is already on the hook.
In minutes, someone can gain complete control over your personal data, networks, online banking, and more.

How to protect yourself from SIM swapping?
It is normal to wonder how to avoid SIM swapping or what we can do to protect ourselves from this dangerous technique. Here are some recommended measures:
1. Minimize the information exposed on networks
Avoid sharing information such as your phone number, date of birth, or address on social media. Even seemingly harmless information can be used to create a fake profile and impersonate you.
2. Change authentication methods
Whenever possible, avoid SMS authentication. Opt for authentication apps like Google Authenticator, Authy, or physical keys (like YubiKey), independent of your mobile phone line.
3. Activate notifications on your operator
Some carriers allow you to notify them of any line changes, such as SIM card duplication or portability requests. Activate these notifications if available.
4. Use a monitoring tool like Qondar
Qondar, Enthec's solution for personal users, is the best way to continuously monitor the exposure of your personal data. Whether online, in forums, on the dark web, or elsewhere, Qondar lets you detect leaks and signs that can anticipate a SIM swapping scam attempt.
SIM swapping: How to prevent it with an early warning tool
Attacks don't always come in visible form. Often, before a SIM swap occurs a personal data leak occurs online. Emails, passwords, phone numbers, or addresses leaked in stolen databases are the cybercriminal's first step.
Qondar lets you know if your data has appeared in a security breach,if someone is trying to steal your identity, or if your phone number has been compromised. This information is vital so you can take timely measures, such as changing your password, contacting your carrier, or even temporarily blocking certain services.
Thanks to its model-based approach, CTEM (Continuous Threat Exposure Management), Qondar doesn't just analyze a snapshot of your digital situation, but continuously assesses your risks, adapting to the changing cybersecurity environment.
¿Why is SIM swapping a growing threat?
SIM swapping is not an isolated problem.. According to data from Europol and the National Cryptologic Center, these types of scams are rising in Europe. Attackers are targeting prominent public figures as well as ordinary citizens whose data has been exposed online.
And it's not just about losing access to an account. The consequences can include:
- Unauthorized bank transfers
- Identity theft used to commit crimes
- Blocking of personal and professional accounts
- Access to medical services or insurance in your name
That's why it's so important to have tools that watch over you, automatically and constantly.
What can you do today?
Now that you know what SIM swap is and how easy it is to fall victim to this scam, you can make more informed decisions to protect yourself.
We recommend:
- Review your authentication methods in the most important digital services.
- Avoid using the phone number as the only verification method.
- Try Qondar, our cyber surveillance platform for individuals that helps you keep your data safe through personalized alerts.
SIM swapping is a real, silent, and dangerous threat.. You don't have to be a celebrity to be targeted: all it takes is for your data to have been leaked, even if it's on a website you registered with years ago.
Protecting yourself requires a combination of prevention, good digital practices, and tools that work for you.
Qondar by Enthec is precisely that: a digital shield that alerts you when something is wrong, when your data appears where it shouldn't. Thanks to its continuous monitoring capacity and threat exposure management, it becomes a key ally in preventing SIM swapping before it happens.
Want to check if your information has already been exposed?
Get access to Qondar and take the first step to protecting your digital identity. Visit Enthec and protect your data before it's too late.
Cybersecurity in hotels: key strategies for the sector
Cybersecurity in hotels has become an essential pillar of operational and reputational management in the tourism sector. As guest experiences become digital, from booking to checkout, the risks of cyberattacks, data loss, and fraud also increase.
It's not just about protecting a Wi-Fi network; we're talking about protecting sensitive information, such as thousands of customers' personal and financial data.
The hotel sector needs to adapt to new digital threats, incorporating proactive strategies, cybersecurity tools, and ongoing processes for reviewing their risk exposure.
This is where technological innovation comes into play, with solutions specifically designed to secure these businesses' digital infrastructure.
One of these solutions is Kartos.. This is not just a simple analytics platform but a Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) platform.. This means it helps businesses continuously identify, measure, and mitigate digital vulnerabilities, constantly assessing their exposure to real threats.
In the hotel industry, Kartos can detect everything from network breaches to leaked customer data on forums without requiring any implementation within hotel chains' complex internal structures.
Want to reduce your exposure to cyber threats before it's too late? Learn more about how Enthec and its Kartos platform can help to protect your hotel starting today.
Why is cybersecurity in hotels more critical than ever?
The digitalization of the tourism sector has brought great benefits, but has opened new doors for cybercriminals. A report by IBM Security revealed that the hospitality sector is one of the ten most attacked globally, mainly due to the volume of personal and financial information it handles.
Hotels often operate with legacy systems, insecure configurations, or outdated password policies. Added to this are connected devices, such as smart locks or IoT HVAC systems, which, if not adequately protected, become entry points for attackers.
And what are hackers looking for in a hotel?
- Customer bank details.
- Booking information and behavior patterns.
- Access to internal systems for identity theft or blackmail.
- Vulnerable infrastructure that can be used as a “bridge” for other attacks.
Trend in hotel cybersecurity: moving from reaction to prevention
One of the main trends in hotel cybersecurity is a change in focus. Previously, people waited for something to go wrong before acting. Today, the goal is to detect threats before they have consequences.
Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM), powered by platforms like Kartos, is based precisely on that principle. It's no longer enough to perform audits once a year. What works is constant, agile, and frictionless control, which allows for the detection, classification, and addressing of each vulnerability in a prioritized manner.
In this sense, CTEM solutions such as Kartos allow:
- Monitor the hotel's digital display 24 hours a day.
- Detect leaked credentials in real time.
- Analyze subdomains, DNS settings, and information leaks.
- Receive personalized alerts based on the level of criticality.

Specific challenges of cybersecurity in hotels
Cybersecurity in hotels presents unique challenges that go beyond the typical technological challenges of any business. Every establishment must face risks that evolve at the same pace as guest connectivity and operational demands.
Multiplicity of devices and entry points
The attack surface is vast, including computers, servers, POS terminals, IoT devices, and employee and customer smartphones. If not correctly monitored, any misconfigured device can be a gateway.
Rotating staff and insufficient training
The high level of staff turnover in many establishments makes it challenging to implement strong cybersecurity protocols. . Without proper training, employees can easily fall for phishing attacks or handle sensitive information without the necessary precautions.
Open Wi-Fi networks
Although offering free Wi-Fi to guests is a standard service, many hotels do not segment their networks properly, which can compromise the security of clients and internal systems.
Highlighted strategies to strengthen hotel cybersecurity
To address the above challenges successfully, a clear and realistic roadmap must be designed. The key is to combine technology, processes, and corporate culture, always with an eye toward the guest experience and the business's reputation.
1. Implement a CTEM system like Kartos
Incorporating a Continuous Threat Exposure Management solution allows for an updated map of the hotel's security status,allowing quick action and staying ahead of cybercriminals. Kartos, in particular, is designed to operate without interfering with the hotel's internal systems, making it easier to adopt and maintain.
2. Continuous staff training
It is not enough to install software: the first line of defense is people.. Training your team on best practices, recognizing fraudulent emails, and responding to incidents is essential. Some companies even organize cyberattack simulations to reinforce this knowledge.
3. Segment networks and apply access policies
Separating the hotel's customer network from its operational network is a basic, yet often overlooked, step. Furthermore, employees should only have access to the information and systems they need.
4. Backup and recovery policies
Having encrypted backups and a well-defined recovery plan can be the difference between a scare and a catastrophe. Especially in ransomware attacks, having up-to-date backups allows you to get back to business quickly without giving in to blackmail.
5. Active monitoring of exposed assets
One of Kartos's most innovative aspects is its ability to detect digital assets exposed on the public network.. From vulnerable IP addresses to misconfigured cloud documents, each finding is presented with an associated criticality and remediation advice.
What if your hotel has already been the victim of an attack?
It's not always easy to detect. Sometimes, stolen data is sold or used months later. That's why one of Kartos' standout features is the ability to conduct cyber surveillance in open sources and forums, where leaked data often appears. You can act quickly to contain and respond to the incident by identifying any mentions related to your domain.
In an environment where reputation is everything, a security breach can mean much more than a fine or a financial loss. It can translate into customers who don't return, negative comments, and loss of trust in the brand.
From Enthec, with our Kartos platform, we offer hotels a practical, immediate, and proactive way to manage their digital security through technology designed to be used by large chains and independent hotels that want to protect their business without complications.
Do you want to know if your hotel is exposed to cyber threats? Make a diagnosis with Kartos and start preventing from today.
Taking care of your guests also starts with protecting their data.
Google bombing: How to defend your digital reputation against this type of attack
A Google search can define who you are, what you stand for, or whether someone trusts you. What appears on the first page of results can significantly impact your digital reputation, whether you're an individual or a business. This is where a little-known but highly damaging phenomenon comes into play: Google bombing.
Although its name sounds distant or technical, its consequences can be felt very close at hand. Google bombings in Spain, as in other countries, have been used to damage public images, manipulate opinions, or even attack professionals and companies without them being aware of what is happening.
What is Google bombing?
The term Google bombing refers to a technique for manipulating search results on Google. It involves linking certain keywords to a specific page to artificially alter its position in the results.
Let's imagine that many websites link the phrase "corrupt company" to a specific company's website. Over time, Google may eventually show that company as the first result when someone searches for that phrase. It doesn't matter if the content is fake or the link lacks context; the algorithm doesn't judge intentions; it only interprets signals.
This technique, which began as a form of political joke or protest in the early 2000s, has evolved into a tool for digital defamation. It is often silent and difficult to detect until it's too late.
Who can it affect?
Any person or entity with a digital presence is susceptible to Google bombing. This includes politicians, public figures, entrepreneurs, independent professionals, SMEs, and even anonymous users who, due to a specific conflict, are targeted by this type of campaign.
Although not always reported in the media, cases of Google bombing have been on the rise in Spain. Just look at forums, social media, or anonymous smear campaigns that go viral and negatively affect search results.
The problem is that reputational damage can have real consequences: loss of customers, cancellation of contracts, deterioration of personal branding, and even legal problems.
Why is it so difficult to detect it in time?
One of the big challenges of Google bombing is its ability to go unnoticed.. Unlike a direct attack, such as hacking or online insults, this technique works by accumulating links, many on seemingly harmless pages or those created explicitly for that purpose.
By the time an affected person realizes it, the content has already taken root, and reversing the damage is much more complex.
Furthermore, Google doesn't automatically respond to these cases, except in obvious manipulation cases. Reporting content doesn't guarantee its disappearance or that the associated results will be removed. Therefore, prevention and continuous monitoring are fundamental to maintaining control of your online presence.

The importance of personal cyber surveillance
Given this situation, Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) is becoming an essential tool. A good antivirus or avoiding suspicious links is no longer enough; today, protecting your image on search engines, social networks, and digital forums is equally essential.
This is where our solution appears. Qondar, is designed for individual cyber-surveillance.. While other platforms are designed only for large companies, Qondar focuses on protecting individuals, whether professionals, freelancers, or citizens concerned about their online reputation.
This solution automatically analyzes what is said about you on the Internet, detects patterns of suspicious behavior, identifies potential smear campaigns, and alerts you if there are signs that someone is trying to manipulate the results associated with your name.
How to defend yourself against Google bombing?
Although Google bombing has become less effective, a site can still be affected. To defend yourself, it's important to remember the following recommendations.
1. Monitor your digital footprint regularly
A Google search for your name or your company's name should be part of your routine. Do it from different devices, logged in, and in incognito mode. What pops up? Is there anything odd? Are negative phrases being repeated on unfamiliar websites?
If you notice a sudden change or a strange association of your name with offensive terms, you could be a victim of Google bombing.
You may be interested in→ 9 healthy digital habits that will protect you from identity theft and leaks.
2. Act quickly: prevention is better than a cure
The sooner you detect an attack, the easier it will be to stop it. You can start by:
- Report suspicious links to Google.
- Request the removal of defamatory content from the page administrators.
- Generate positive and truthful content (posts, interviews, blogs, optimized profiles, etc.) that improves your natural positioning.
In more severe cases, a solution like Qondar may be enough to prevent serious repercussions, such as a far-reaching reputational crisis.
3. Don't fight alone: surround yourself with tools and professionals
The reality is that no one is 100% protected. Not even the biggest brands. But having a strong digital shield helps a lot. In addition to Qondar for individuals, Enthec offers Kartos, our platform for businesses and organizations, which is also focused on continuous digital threat management.
These solutions allow you to detect not only Google bombing but also information leaks, improper mentions, or more sophisticated attack patterns.
What if you've already been a victim?
In that case, the key is to reverse the impact.. Here are some actions:
- Positive positioning: Work on publishing content that displaces negative results. Search engines value relevance and authority, so it's essential to feed your footprint with legitimate and quality content.
- Legal assistance: You can contact digital law experts if the published content is false or defamatory. In Spain, favorable case law in cases of online reputation attacks is increasing.
- Technical reports: Tools like Qondar can generate reports supporting complaints or legal proceedings, demonstrating that a coordinated strategy was used to harm you.
From Enthec, we work with solutions like Qondar so that each person can have control of their online presence.. Because protecting your digital identity on the Internet shouldn't be a lonely battle.
Why DNS health is critical to your company's cybersecurity
Digital threats are evolving faster than ever. Companies, large or small, cannot afford to look the other way when it comes to protecting their digital infrastructure. Here is one aspect that is often overlooked, yet is key to digital security: DNS health.
But what does this mean exactly? And why is it so important to control DNS health within the strategy of business cybersecurity?
Before we dive in, let's make a crucial point. If your company doesn't yet have Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) tools, you may be leaving windows open to the outside without realizing it.
This is where Kartos, our solution for cyber surveillance for companies,specifically designed to detect, assess, and continuously reduce your organization's digital exposure, appears. Kartos not only monitors your digital attack surface but also allows you to protect your DNS and detect related vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them.
What exactly is DNS health?
When discussing DNS health, we refer to the security status, configuration, and maintenance of an organization's domain name system. DNS acts as a “phone book” for the internet: it converts domain names (like enthec.com) into IP addresses that machines can understand.
A secure DNS server isn't just a technical issue; it's an essential pillar of your digital defense. Cybercriminals can exploit a misconfigured DNS to carry out attacks such as:
- Pharming: redirect your employees or customers to fake websites.
- DNS hijacking: hijack your web traffic for espionage or fraud.
- DDoS through DNS amplification: take advantage of your DNS as a vector to saturate other servers.
These risks affect large corporations as well. SMEs are also frequent targets precisely because they neglect aspects like this.
Why do so many companies ignore DNS health?
There are several reasons, but one of the main ones is the false sense of security.. Many organizations believe they are protected by having antivirus systems or firewalls. However, these devices do not monitor or manage your domain name system configuration.
On the other hand, DNS is usually managed by third parties (such as hosting or domain providers), which means that, despite being a critical element, companies do not include it in their security audits.
What does it mean to have good DNS control
Having effective DNS control means keeping a series of good practices active and up-to-date. These include:
- Audit your DNS records and detect outdated or unnecessary settings.
- Ensure your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records are correctly configured to prevent email phishing.
- Use secure and redundant DNS servers.
- Protect access to your DNS management with strong authentication.
- Monitor unauthorized access attempts or changes.
These steps are essential to ensure a business environment free of invisible breaches.
Kartos and continuous DNS monitoring
This is where Kartos comes into play. It proactively monitors your DNS status and alerts you to any suspicious changes. It's not just about protecting them but anticipating the future.
Kartos allows you:
- See your digital display surface in real time.
- Detect uncontrolled or misconfigured assets (including DNS and subdomains).
- Prioritize vulnerabilities with an approach based on real risk.
- Receive early warnings on possible attack vectors involving DNS.
You may be interested in→ Real-time vulnerability management: a step forward in cybersecurity.
Comprehensive, continuous management distinguishes a company that reacts to an attack from one that neutralizes it before it occurs.
How do you know if your DNS server is secure?
Some tools allow for spot checks, but that's not enough. The digital environment changes daily, and attackers find new ways to exploit weaknesses. Therefore, a CTEM solution like Kartos is essential.
Kartos not only tells you if your DNS is secure now but also helps you maintain that security continuously.. This includes automated analysis, detailed reporting, and remediation suggestions tailored to your technological reality.
Practical recommendations to improve your company's DNS health
If you don't yet have a solution like Kartos, we recommend that you at least consider the following points:
- Update your DNS records frequently. Discard any unused items. frequently. Discard any unused items.
- Activate DNSSEC to protect the integrity of queries.
- Audit your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC registers with the help of specialists.
- Avoid using public DNS servers as the principal solution.
- Control who has access to your DNS console.. Not all technicians need to have full permissions.
The good news is that it's never too late to improve your organization's DNS health.
Neglecting your digital infrastructure's DNS health can have serious financial and reputation consequences. DNS control and a secure DNS server should be at the heart of any modern cybersecurity policy.
With our solution, Kartos, you are protecting your DNS and taking a step towards a smarter, more preventative, and continuous security model.
9 healthy digital habits that will protect you from identity theft and leaks
We live connected lives. We check our phones before breakfast, share photos, use the cloud, shop online, and work remotely… and sometimes, without realizing it, we leave doors open for cybercriminals to exploit.
Identity theft and personal data leaks are the order of the day.And you don't have to be famous or work for a multinational company to be objective. Just having an email address or active social media accounts is enough.
In this context, maintaining healthy digital habits isn't just advisable: it's essential. Protecting our digital identity should be part of our daily routine.
Some tools can help, such as Qondar,which is our solution designed for individuals. Through Qondar, you can monitor your online exposure in real time, detect if your data has been compromised, and receive alerts when your digital security is at risk.
Good Healthy digital habits to protect yourself
1. Change your passwords regularly
Although it may seem like a basic recommendation, most people have continued to use the same passwords for years.. The worst part is that they often reuse the same key for everything. This is like having one key for your house, car, and office.
Use different passwords for each account, change them every three or four months, and rely on secure password managers whenever possible.. Do you have any clues about whether yours has been stolen? Qondar can help you detect it.
You may be interested in→ How to manage business passwords and credentials easily and securely to avoid online threats.
2. Activate two-step verification
Also known as two-factor authentication (2FA), it's one of the most effective measures against unauthorized access. Even if someone gains access to your password, they won't be able to log in without that second step (usually a code you receive on your phone).
Almost all major platforms offer this free option, which can save you from a big scare.
3. Be wary of suspicious links
You receive an email claiming to be from your bank but asking you to click a link and update your information, or a message on social media with a shortened link and no context. Be very careful: you could be facing a case of phishing.
Always check the sender. Do not click on dubious links or provide personal information outside of official channels.. If you have any doubts, it's best not to interact.
4. Update your devices and apps
Yes, sometimes updating the operating system of your mobile or computer can be a pain, but these updates often include crucial security patches.. Older versions are fertile ground for cyber attackers.
Configure automatic updates and ensure your apps come from official sources (App Store, Google Play, etc.).
5. Be careful with public Wi-Fi networks
Connecting to Wi-Fi at the airport or mall is fine for checking the weather or reading the news, but you should not use it to perform sensitive tasks such as accessing your online banking or sending important documents.
If you need to, you'd better use a VPN (Virtual Private Network). These tools encrypt your connection, making it much harder for someone to intercept what you're doing.
6. Review your app permissions
Many apps ask for access to your camera, contacts, and location; often, they don't need it to work. Automatically granting permissions can put you at risk.
Take a few minutes to review your apps' permissions on your mobile or browser and modify those that are not strictly necessary.

7. Be careful what you share on social media
Posting vacation photos while you're away from home, showing tickets with QR codes, giving out personal details (like your address or phone number) on public profiles... This may seem innocent, but it can be used against you.
Think before you post and check your privacy settings.. Not everyone needs to know everything about you.
Access our post→ Public image on the internet: how to protect it from digital risks.
8. Do regular digital cleaning
Do you have old accounts you no longer use? Apps you've installed for years? Every profile and every app is a potential entry point for cybercriminals.
Delete accounts you no longer need,delete unused apps, and back up your important data. Qondar can also help you identify the data you still have floating around online.
9. Monitor your digital footprint with tools like Qondar
Did you know that databases containing millions of leaked emails, passwords, and phone numbers are being sold on the dark web? And often, those affected don't even know it. So, being vigilant and learning how to erase your digital footprint is essential
This is where tools like Qondar become crucial. This tool alerts you if your email appears in a leak,your password has been compromised, or your identity has been stolen. It's like having a personal security guard for your digital identity, working 24/7.
Why does all this matter so much?
According to the report IBM Cost of a Data Breach 2024, the average global cost of a personal data breach amounts to $4.88 million. While this data typically refers to companies, individuals suffer consequences, from financial losses to legal issues and reputational damage.
Having healthy digital habits doesn't make you invulnerable, but it significantly reduces your chances of falling victim to identity theft or a data leak. Just as you don't leave your front door unlocked, you shouldn't expose your digital identity.
Protect yourself today with Qondar
If you want to go further and have absolute control over your digital exposure, try Qondar by Enthec. It's intuitive, effective, and designed for people like you, who don't necessarily need to be cybersecurity experts, but still want peace of mind.
Start protecting your digital identity today. Take advantage of all Qondar's benefits and discover how we can help you.
Technology makes our lives easier, but it also demands responsibility. Implementing these nine healthy digital habits is a simple but essential step toward a safer digital life. Remember: It is not about living in fear but with awareness. And with the right tool,s you can do it with confidence.
Main advantages and disadvantages of pentesting in a company
Cybersecurity is, now more than ever, a priority for any organization. As digital threats evolve, so must the strategies to detect and prevent them.
In this context, pentesting (or penetration testing) has become a key practice for assessing the security level of a company's computer systems.
But is it enough to make a pentesting punctual? What limitations does it have? And most importantly, how can a company complement this practice to maintain an active and continuous security posture?
Throughout this article, we will answer these questions, addressing the main advantages and disadvantages of pentesting, and analyzing how tools such as Kartos by Enthec can take threat management further.
What is pentesting, and what is it for?
Pentesting, also known as pentesting, consists of a controlled simulation of a computer attack to detect vulnerabilities in systems, networks, applications, or IT infrastructures. That is, it is about putting yourself in the shoes of an attacker to see what weaknesses could be exploited.
This exercise, conducted by security experts, allows organizations to identify critical failures before cybercriminals can exploit them. It's one of the most direct ways to test whether current security measures work.
Main phases of pentesting
A professional penetration test usually follows a well-defined methodology. These are the main phases of pentesting:
- Recognition: collection of information about the target (such as IP addresses, domains, services, etc.).
- Scanning and enumeration: identification of active systems and open services.
- Exploitation: attempt to exploit detected vulnerabilities.
- Privilege escalation: if access is gained, an attempt is made to increase control.
- Pentesting report: compilation of all findings, including vulnerabilities, risk level, and recommendations.
The pentesting report is, in many cases, the starting point for correcting security errors and strengthening systems.

Highlighted advantages of pentesting
1. Discovery of real vulnerabilities
Unlike automatic scanners, pentesting goes further by reproducing real attack scenarios. This allows for detecting weaknesses that could go unnoticed by other methods.
2. Impact assessment
Pentesting not only identifies vulnerabilities but also helps measure the real impact they could have if exploited. This helps prioritize the most urgent corrective actions.
3. Improved security awareness
Performing pentesting periodically allows technical and management teams to better understand the risks they face. It can also serve as a basis for internal training plans.
4. Regulatory compliance
Many safety regulations and standards (such as ISO 27001, PCI-DSS, or RGPD) recommend or require penetration testing as part of security audits.
Disadvantages of pentesting
Although it is a very valuable tool, pentesting is not without limitations. Knowing your weaknesses is key to complementing this practice effectively.
1. Photograph of a specific moment
One of the biggest drawbacks of pentesting is that it offers a static vision of security: Analysis is performed at a specific point in time. Without ongoing review, new threats can easily slip under the radar.
2. It does not cover 100% of possible vectors
No matter how hard you try to cover all fronts, there is always a margin of error. New vulnerabilities may emerge the next day of the test, or even remain hidden during the test.
3. Economic cost and limited resources
Pentesting requires time, qualified experts, and sometimes a considerable investment. Furthermore, their frequency is limited by the available budget.
4. Operational risk
Although controlled tests, pentests can generate interruptions or system crashes if not executed cautiously.
Kartos: the perfect complement to pentesting
This is where Kartos, Enthec's solution for companies, comes in. While pentesting gives us a snapshot, Kartos offers continuous cyber surveillance, allowing changes in a company's exhibition area to be detected almost in real time.
Kartos is designed as a Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) tool. This means that instead of performing an annual or semi-annual review, it maintains constant monitoring, detecting new vulnerabilities, incorrect configurations, or information leaks on the network.
Its advantages include:
- Early detection of threats that may appear between pentestings.
- Automated and updated monitoring, without the need for constant manual intervention.
- Global visibility of the organization's external exposure, including domains, subdomains, services, open ports, and more.
- Proactive alerts to avoid unpleasant surprises.
Are pentesting and Kartos mutually exclusive?
Not at all. In fact, they are complementary strategies. Pentesting remains essential to validate security from an offensive perspective, but does not replace the need for constant vigilance.
Imagine a company that conducts a pentesting in January. By March, it had implemented new cloud services, incorporated new technologies, and suffered a data breach in an external environment. If the company doesn't have a tool like Kartos, it will not see these changes until the next test, which may be several months away.
The combination of both approaches allows for a comprehensive and adaptive coverage in the face of current risks.
Thinking beyond pentesting
Pentesting is, without a doubt, a crucial piece in any company's cybersecurity strategy. But it is not enough to take a test occasionally and consider the issue resolved.. The changing nature of the digital environment demands a continuous, dynamic, and automated approach.
Kartos responds to this need, complementing the work of the pentesters with an up-to-date and persistent view of threat exposure. Thanks to its CTEM approach, it helps companies always stay one step ahead, minimizing risks and improving their overall security posture.
Do you want to see how Kartos can help you keep your business protected beyond the pentesting? Request a demo in Enthec and discover the future of continuous cybersecurity.
Interested in learning more about how to proactively protect your business?
Know more about our Kartos and Qondar Solutions. Cybersecurity isn't a checkpoint; it's a continuous journey.
Passive cybersecurity attacks: Keys to identifying these types of invisible threats
When discussing cybersecurity, we often imagine exaggerated and obvious attacks: viruses that lock your computer, malicious emails demanding ransoms, or fake websites trying to steal your passwords. However, other types of threats are much more silent, but equally dangerous: the passive attacks in cybersecurity.
These attacks sneak in, watch, and wait. And that's precisely why they're so difficult to detect. In this article, we'll unravel what they are, how they work, and, most importantly, what you can do to protect yourself, whether you are a company or browsing as a private user.
What is a passive attack in cybersecurity?
In cybersecurity, a passive attack is one in which the attacker does not directly interfere with the system's operationbut rather simply spies, gathers information, or monitors network traffic without detection. Unlike active attacks, which seek to modify, damage, or control a system, passive attacks act as invisible observers.
Some typical examples of this type of threat include:
- Packet sniffing on public or poorly protected networks.
- Passive tracking to obtain browsing habits or device data without the user's consent.
- Monitoring encrypted communications, waiting for vulnerabilities to exploit in the future.
These attacks may seem less aggressive, but the information they collect can later be used for targeted attacks, blackmail, or impersonation.. In addition, many cybercriminals use this data as raw material to sell on the dark web.
Why are passive attacks so dangerous?
The main problem with passive cybersecurity attacks is that they go unnoticed for long periods.. They don't generate any prominent warnings, and in many cases, the victim won't even know they've been spied on.
This allows the attacker to:
- Gather detailed information about his objectives (IP addresses, browsing habits, credentials, etc.).
- Wait for the best moment to act (for example, to launch a follow-up active attack).
- Design social engineering campaigns that are highly personalized and effective.
That is to say, a Passive attack is the first silent step before a more decisive blow.
Passive cybersecurity: a contradiction?
The term passive cybersecurity can be confusing. It sometimes refers to measures that don't act directly on a threat but merely observe or record it. However, when discussing in cybersecurity, passive tracking refers to monitoring a malicious actor's actions without directly intervening in the systems.
We must not confuse legitimate surveillance with malicious spying. Today, many platforms monitor user behavior to offer personalized services. But when this monitoring is carried out without consent, for opaque purposes, or by external actors, it goes from legitimate to dangerous.

How to detect a passive attack: Main signs
Detecting a passive attack can be tricky,but it's not impossible. Some signs can help you identify that something isn't right:
1. Unusual activity on your networks or devices
If you notice a strange use of bandwidth, suspicious connections, or unexpected encrypted traffic, it may be a sign that someone is listening.
2. Too many coincidences
If you start receiving very personalized phishing campaigns, messages with details that should only be known by legitimate sources, or targeted attacks, someone may have been collecting information before without realizing it.
3. Cybersecurity tool alerts
Good security systems don't just act against active attacks. Some advanced threat management systems, like the ones we offer from Enthec, allow you to identify suspicious patterns even in quiet environments.
How to protect yourself? The importance of continuous cyber surveillance
In a world where threats don't always make noise, prevention becomes your best ally,. and this is where a key concept comes in: Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM).
This approach is not only based on responding to attacks when they occur but also on constantly monitoring what information is being exposed without your knowledge.. Because others may be seeing your data even if you don't.
Qondar, your silent shield against invisible threats
Qondar, one of our cyber surveillance solutions, is designed for private users. who want to know what information about them is appearing and circulating on the internet. Has your email been leaked on dark web forums? Has one of your passwords been shared without your knowledge? Is someone impersonating you digitally?
Qondar answers these questions with regular reports, personalized alerts, and a constant monitoring system that lets you sleep more peacefully, knowing that someone is watching over you.
One of the most interesting advantages is that Qondar doesn't need access to your devices or keys.. It works from the outside, watching the net like a passive attacker would, but to your advantage.
What if I've already been spied on?
If you suspect you've been the victim of a passive attack, you first must strengthen your passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and audit your digital presence.
Tools like Qondar allow you to do just that: see what footprints yours are exposed to and which ones others may be taking advantage of. Acting quickly is essential.. The sooner you identify a leak or vulnerability, the less likely it is to become an active attack.
Just because a passive cybersecurity attack doesn't directly damage your systems doesn't mean it's not serious. On the contrary, its invisibility makes it a real threat that can go undetected for months.
Monitoring what others see about you is essential to protecting your digital identity. That's why it's so important to have tools like Qondar, which allow you to manage your digital exposure proactively, easily, and effectively.
Don't leave your safety to chance. Start monitoring your digital footprint with Qondar today and discover if someone is spying on you without your knowledge.
Cybersecurity in hospitals: How continuous monitoring protects sensitive patient data
Medical information is as valuable as it is sensitive. Hospitals and health centers, traditionally focused on caring for people's physical and emotional health, today face a new challenge: protecting their patients' sensitive data.
Every medical record, diagnostic report, and treatment stored in a digital system represents critical information. Its exposure, theft, or alteration compromises privacy and can endanger human lives. Therefore, cybersecurity in hospitals has become a strategic priority.
The risk is real: why are hospitals targeted?
If you've ever wondered why someone would attack a hospital, the answer is more straightforward: medical data is worth a lot on the black market.. In addition, health centers often have complex, usually outdated computer systems, which makes them relatively easy targets for cybercriminals.
According to data from SonicWall's Global Threats Report (2025), the health sector was among the most attacked during the year. 95% of ransomware was used in attacks on the industry, and more than 198 million patients were affected in 2024 alone in the United States.
Spain is no stranger to this reality: public and private hospitals have suffered leaks, data hijackings, and service outages that have directly affected healthcare.
These cybersecurity attacks in hospitals not only involve economic and reputational losses.. On many occasions, they force us to delay operations, refer patients, or go back to using paper, with all the complications that this entails.
What does it mean to protect a hospital?
In the current context, cybersecurity can no longer be understood as a set of isolated measures implemented once and forgotten. Attacks evolve, techniques change, and exposure to threats is constant.
For this reason, more and more healthcare organizations are adopting models such as CTEM (Continuous Threat Exposure Management), or in Spanish, Continuous Threat Exposure Management. This strategy is based on actively and permanently monitoring all possible attack vectors: from network configurations to exposed credentials or known vulnerabilities.
This is where Kartos,our specialized cyber-surveillance solution for organizations, comes into play. Kartos allows hospitals and health centers to have a clear and up-to-date view of their exposure to cyber threats, analyzing their digital footprint in real time and alerting them of any possible risk before it is too late.
The importance of continuous surveillance in the hospital environment
A hospital environment is much more than doctors, nurses, and patients. There are dozens of connected devices, from monitors to respirators, internal management systems, databases, emails, and mobile applications. Each of these elements can be a gateway if not adequately protected.
The continuous monitoring offered by Kartos acts as an early warning system. It identifies vulnerabilities and tracks information leaks,leaked passwords, possible domain impersonations, or suspicious network activities. It does so without installation since it works outside, analyzing the healthcare organization's public exposure.
This proactive approach does not replace other layers of defense (such as antivirus, firewalls, or access policies). Still, it complements them, providing a fundamental angle: Know how attackers see you and act accordingly.
Thanks to this type of surveillance, Hospitals can make informed decisions in advance, instead of just reacting when it's too late.

And what about regulatory compliance?
In addition to protecting sensitive data, Cybersecurity in hospitals is also a legal issue.. Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the NIS2 Directive require healthcare organizations to implement protection measures and demonstrate that they have taken appropriate actions to prevent security breaches.
Solutions like Kartos are especially useful here. They allow hospitals to continuously record threat exposure and implement corrective actions, which enhances security and facilitates audits, inspections, and certification processes.
Cybersecurity in hospitals: defense against attacks, but also prevention
A good defense is not only based on building walls, but also on knowing where attackers can enter. In a healthcare environment, where people's lives are at stake, prevention is as important as the response.
Adopting efficient solutions allows hospitals to act before a crisis occurs.. The best thing is that they do not require complex integrations or changing how IT teams work since the tool operates from the outside, with total autonomy.
Enthec, a company specialized in cyber surveillance, offers technology and strategic support to anticipate risks and maintain constant vigilance.
The human and technological challenge
Awareness of healthcare personnel is also key.. Many security breaches begin with clicking on a malicious link or using a weak password. Therefore, cybersecurity solutions must be part of the hospital culture, as hygiene or patient care are.
Kartos helps in that process by offering precise and actionable reports that allow training internal teams, prioritizing efforts, and establishing more effective security policies.
Hospitals are places of care; we cannot allow digital threats to compromise operations. Cybersecurity in hospitals is neither a luxury nor a fashion but an urgent need that must be addressed with modern tools, strategic vision, and constant commitment.
Kartos provides real-time vision that allows hospitals to anticipate problems and keep patient data where it should be: safe, secure, and available only to those who need it.
Do you want to know how to better protect your hospital against digital threats? Find out more about our Kartos solution.
What is doxing, and how to prevent your personal data from being exposed on the Internet
The Internet is a space where we share information daily. Social networks, forms, online purchases… Each action leaves a slight digital trace. Most of the time, we are unaware of how much we reveal about ourselves. This is where an increasingly well-known (and feared) concept comes into play: doxing.
What is doxing, and why should you care?
Doxing (abbreviation of dropping dox or 'release documents') refers to the public exposure of a person's data without their consent. We talk about addresses, telephone numbers, workplaces, private photos, emails, real names, and even financial or family information.
These types of attacks, which initially emerged in particular online communities, have spread in recent years and can have serious consequences: from harassment, threats, and identity theft, to the loss of employment or the appearance of legal problems.
Doxing on the Internet is not a simple hacker's game:It is a form of digital violence. And it can affect anyone.
Qondar: a solution that helps you protect your digital privacy
Before continuing, it is worth stopping at our featured tool: Qondar, a solution for personal cyber surveillance.
Qondar has been developed for anyone who wants to maintain control over their information on the network without needing advanced technical knowledge. It works like a Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) platform. It lets you detect if your data is being shared without permission in forums, leaked databases, social networks, or even the dark web.
Even if you don't know what doxing on the internet is, you too may suffer from an attack. If so, Qondar will tell you before it's too late.
Why does someone decide to dox another person?
There is no single attacker profile, nor a single motivation. Doxing, as this phenomenon is also known, can have many faces:
- Personal revenge: Ex-partners, ex-friends, or work conflicts can lead to malicious leaks.
- Extreme ideology or activism: Some users publish data about opponents to intimidate or silence them in political or social debates.
- Practical jokes or viral challenges: especially among teenagers or in toxic online communities.
- Extortion and blackmail: Once they have your data, some attackers try to obtain money or favors in exchange for not disclosing it.
Whatever the reason, the result is the same: your privacy and security are compromised.

What type of data is typically exposed when doxing?
Although the degree of exposure varies, the most common data that is published or sold in doxing cases are:
- Full name and physical address
- Phone number
- Profiles on social networks
- Personal photos
- Information about the family environment
- Employment or academic data
- Purchase or search history
A simple search in filtered databases (such as those found on the dark web) can be enough to create a detailed profile of a person. That's why prevention is key.
How to avoid being doxed: good practices to protect your privacy
To know how to protect yourself from doxing involves changing certain digital habits.. Here are some practical tips that you can start applying today, now that you understand what doxing is:
1. Check your social networks
- Use strict privacy settings.
- Avoid sharing personal information such as your address or your children's school.
- Do not post photos of documents or screenshots with sensitive data.
You may be interested→ 5 security strategies on social networks.
2. Use strong and unique passwords
- Don't repeat passwords across multiple services.
- Enable two-step authentication (2FA) whenever possible.
3. Be careful with online forms and contests
- Do you need to give out your phone number to enter that giveaway?
- Use secondary or temporary emails when possible.
4. Avoid heated discussions in public forums
- Many victims of doxing end up being attacked for their opinions.
- Participate respectfully and avoid sharing unnecessary details.
5. Do searches about yourself
- Type your first and last name in search engines to see what appears.
- Use tools like Qondar to get a complete view of your online exposure and receive alerts if anything changes.
What do you do if you have been doxed?
It may finally happen even if you have done everything possible to avoid being doxed. In this case, the most important thing is to act quickly:
- Document everything that has been published (captures, links, etc.).
- Contact the platforms where the information has been disclosed and request immediate withdrawal.
- Report the case to the Police and authorities, especially if there are threats or blackmail.
- Go to your national Data Protection Agency if your rights have been violated.
- Receive psychological support if the emotional impact has been substantial. Digital bullying can seriously affect mental health.
Is there a definitive solution?
The reality is that there is no 100% foolproof barrier. But yes, you can minimize your exposure and protect yourself from doxing to be prepared for any threat.
This is where Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) solutions, like Qondar, come into play. This tool offers you something that few solutions provide: active and personalized digital identity monitoring.
Knowing when and where your information appears allows you to act before it's too late. What is not controlled on the Internet can get out of hand in seconds.
Now that you know what doxing is, it is not a distant concept exclusive to celebrities or public figures. Anyone can be a victim. And in a society as hyperconnected as the current one, shielding our personal information has become a necessity, not a luxury.
Luckily, there are tools available to everyone to avoid this. If you are looking for an effective way to protect yourself from doxing and keep your digital identity under control, Qondar by Enthec is a solution that can help you sleep more peacefully.
Your privacy is not a simple detail to consider; it is part of your security. Start caring for her today with Qondar.










