European Data Protection Day, a reminder for CISOs and security directors
Each January 28th is European Data Protection Day. This date, beyond the symbolic gesture, invites companies, administrations, and security professionals to pause for a moment and review how they are protecting information.
Not only from a legal standpoint, but also from a technical and strategic perspective. For CISOs, security directors, and IT managers, this day is a good excuse to ask uncomfortable but necessary questions: from knowing what data is being managed to what threats may affect it.
European Data Protection Day: much more than just an anniversary
European Data Protection Day commemorates the signing of the Council of Europe Convention 108, the first international treaty on data protection. Since then, the regulatory framework has evolved to the GDPR, which today sets the standard in Europe.
However, compliance with regulations alone does not guarantee that data is truly protected. The legislation establishes the "what," but the "how" depends on each organization. And that's where many companies encounter difficulties.
According to data from the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA), a significant portion of security incidents are related to basic visibility failures, incorrect configurations, or exposed assets that were not being monitored.
In this sense, the European Data Protection Day serves as a reminder: protection is not a state; it is a journey.

Data protection and cybersecurity: two sides of the same coin
For years, data protection has been approached as a legal matter, while cybersecurity was seen as a purely technical issue. Today, that separation no longer makes sense.
Unauthorized access, a data breach, or a security breach don't just pose a technical problem. They have direct consequences on the privacy of individuals, in the company's reputation, and, of course, in regulatory compliance.
For security managers, this means taking a broader approach that involves identifying risks, anticipating threats, and reducing exposure, which is as important as reacting to incidents.
The current challenge: managing the actual exposure to threats
One of the biggest problems CISOs face is the lack of visibility.. Hybrid infrastructures, cloud services, external providers, remote devices… The traditional perimeter has disappeared.
This is where the Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) approach proposes moving from one-off reviews to continuous risk assessment.
CTEM: an approach aligned with European Data Protection Day
The CTEM approach aligns with the spirit of European Data Protection Day, as it focuses on prevention and continuous improvement.
CTEM is not just about detecting vulnerabilities, but about understanding the complete context:
- What assets are exposed.
- Which threats are most likely, depending on the sector.
- What impact would a breach of personal data have.
- Which risks should really be prioritized.
This approach helps security teams make decisions based on real data rather than endless lists of alerts.
Kartos by Enthec: Continuous Visibility for Companies
This is where solutions like Kartos by Enthec, bring clear value to organizations.. Kartos is designed for companies that need continuous cyber surveillance and an up-to-date view of their threat exposure.
From a CTEM perspective, Kartos allows:
- Identify exposed digital assets, including those that were not properly inventoried.
- Detect information leaks, compromised credentials, or accessible sensitive data.
- Continuous monitoring of how the attack surface evolves.
- Prioritize risks based on their actual impact on the organization and personal data.
This is especially relevant for regulated sectors or companies that manage large volumes of sensitive information, where a breach can have significant legal and reputational consequences.
In the context of European Data Protection Day, having these tools is not an extra but a key element in moving from formal compliance to effective protection.
The human factor and the need for anticipation
Not all risks come from external attacks. Human error, password reuse, or accidental exposure of information remain common causes of incidents.
According to the Verizon Data Breach Report (DBIR), the human factor is present in a high percentage of security incidents, whether due to phishing, compromised credentials, or incorrect configurations.
Continuous cyber surveillance enables us to detect these situations before they escalate. It's not about pointing fingers, but about anticipate and reduce the impact.
You might be interested in→ Cybersecurity and the human factor: the most common mistake in digital protection.
Personal data protection also outside the company
Although this article focuses on a business approach, it's important to remember that data protection doesn't end in the corporate environment. Managers, employees, and professionals are also exposed individuals.
In this sense, Qondar, Enthec's solution geared towards individuals, extends the concept of cyber surveillance to the personal sphere, helping to detect data exposures, impersonations, or leaks that can end up affecting the company as well.
Because, in many cases, a gap starts outside.
European Data Protection Day as a starting point
More than just a date for an internal memo or a social media post, European Data Protection Day can be a great time to:
- Review the organization's actual attack surface.
- Evaluate whether current tools offer continuous visibility.
- Align the security strategy with a CTEM approach.
- Involve management in the importance of protecting personal data.
Modest but well-directed steps can generate a significant impact in the medium term.
Looking ahead: from reaction to prevention
The trend is clear: The organizations that best protect data are not those that react fastest, but those that detect threats first.. Moving from a reactive to a preventive approach is one of the major challenges facing cybersecurity today.
Tools like Kartos, within the Enthec solutions ecosystem, help make that leap by providing context, continuity, and a realistic view of risk.
European Data Protection Day shouldn't be just an annual reminder. For CISOs and security directors, it's an opportunity to rethink how threat exposure is managed and whether decisions are based on up-to-date, relevant information.
Data protection today demands continuous visibility, intelligent prioritization, and anticipation capabilities.. And there, the CTEM approach is consolidated as a coherent response to a problem that continues to grow.
If you want to know how Kartos can help you improve the ongoing management of threat exposure in your company, this might be a good time to take the next step and talk to the Enthec team.
The future of autonomous AI: challenges and opportunities in cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is inextricably linked to artificial intelligence today. In just a few years, AI has gone from a temporary support tool to a structural component of threat detection, risk analysis, and incident response.
However, we are on the verge of a new evolutionary leap that still generates more questions than answers: the Autonomous AI.. It's not just about faster or more accurate systems, but a profound change in the way technology makes decisions.
And, as is often the case in this sector, every advance brings with it both clear opportunities and new risks that should be understood from now on.
What do we really mean by autonomous AI?
When we talk about autonomous artificial intelligence,it's common for concepts to get confused. Many current tools are described as "autonomous" because they perform tasks without constant human intervention. However, that doesn't mean they are intelligent.
Autonomous AI goes a step further. It doesn't need continuous instructions or detailed rules. Once its mission is defined, it acts independently,interprets the context, learns from it, and adjusts its behavior without direct supervision. In some more advanced approaches, it even considers any external attempt to influence its actions as a potential threat.
This nuance is important because it makes a clear difference between:
- Autonomous tools, which execute defined processes.
- Autonomous AI, who decides how to achieve its goals.
The latter is still in an early stage of adoption, but its development is constant and points to an ever-increasing presence in the short and medium term.

Autonomous AI and its future impact on cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is one of the areas where autonomous AI can have the most profound impact.. The reason is simple: the volume, speed, and complexity of current attacks far exceed the capacity for real-time human analysis.
Clear advantages for digital defense
From a defensive point of view, autonomous artificial intelligence opens up very promising scenarios:
- Proactive threat detection: systems capable of identifying anomalous patterns before an attack materializes.
- Real-time response: automatic decisions in response to incidents, without waiting for human validation.
- Continuous learning: constant adaptation to new attack techniques without the need for reprogramming.
In an environment where threats change every day, having solutions that evolve on their own can make the difference between a contained breach and a critical incident.
You might be interested in →The relevance of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity
Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM): the current approach
As autonomous AI matures, businesses need practical and effective solutions now. This is where
Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) comes in.
CTEM doesn't just focus on detecting attacks once they're already underway. Its goal is to constantly identify, assess, and reduce the attack surface, understanding which assets are exposed and how they could be exploited.
Kartos and Qondar: autonomy applied to cyber-surveillance
Enthec's solutions are situated within this context:
Both are cyber-surveillance tools that operate under the CTEM approach and employ artificial intelligence to automate key processes. They are autonomous tools that can operate continuously without constant user intervention.
It is important to note that the AI systems integrated into Kartos and Qondar at the moment are not autonomous and do not act on their own mission or make decisions outside defined parameters. However, they represent a significant step towards more advanced and continuously evolving digital defense models, where automation and contextual intelligence are already a reality.
Examples of autonomous artificial intelligence in future scenarios
Although their use is not yet widespread, they are already being explored as examples of autonomous artificial intelligence that help to understand its potential in cybersecurity:
- Systems that redesign defense architectures after detecting intrusion attempts.
- Agents that automatically negotiate with other systems to isolate threats.
- Platforms capable of prioritizing risks without human intervention, based on real impact and probability of exploitation.
These examples of autonomous artificial intelligence show where the sector is headed, although its mass adoption still requires time, testing, and, above all, clear ethical and legal frameworks.
Technical, ethical, and legal challenges
The arrival of autonomous artificial intelligence is not without its challenges. Some of the most relevant are:
Lack of control and explainability
When an AI makes decisions on its own, understanding why becomes more complex. In cybersecurity, this can lead to issues with auditing and regulatory compliance.
Risks of unforeseen behavior
A poorly configured autonomous AI could make counterproductive decisions, blocking critical services or interpreting legitimate actions as attacks.
Legal framework still immature
Current legislation is not fully adapted to systems that operate without direct human supervision, which raises questions about liability in the event of incidents.
According to a report by the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA), one of the major challenges of the next decade will be balancing advanced automation and human control in critical systems.
Prepare today for the immediate future
Although autonomous AI is not yet part of the daily operations of most organizations, now is the time to prepare. Adopting continuous cyber-surveillance solutions, understanding one's own attack surface, and automating risk management are the first steps toward addressing a more complex scenario.
Tools such as Kartos and Qondar within the CTEM approach, allow us to move in that direction without waiting for autonomous AI to be fully integrated into the market. They are solutions designed for the present, but aligned with the future.
Autonomous AI will mark a turning point in cybersecurity.. Its ability to learn, adapt, and act without supervision promises a more effective defense, but it will also pose significant challenges when used for malicious purposes.
In this context, it's not about waiting for the technology to fully mature, but about laying solid foundations today.. Understanding the actual exposure to threats, continuously managing risks, and relying on specialized solutions are key to avoiding falling behind.
If you want to learn how Enthec helps companies and individuals manage their threat exposure on an ongoing basis, discover Kartos and Qondar and start strengthening your digital security now.
Typosquatting, a silent threat to your organization's digital reputation
A small typo in a URL might seem insignificant. However, behind this everyday action lies one of the most persistent and least visible threats in today's digital environment: typosquatting.
This type of attack takes advantage of human oversight, something as simple as changing a letter or adding extra characters, to redirect users to malicious domains that mimic the originals.
For organizations, the impact goes far beyond simple confusion. Loss of trust, brand impersonation, credential theft, and fraud are among the common consequences. And what is most worrying is that, in many cases, the attack goes unnoticed for weeks or even months.
Continuous monitoring of the digital landscape has become essential. Solutions like Kartos from Enthec enable companies to identify and manage these risks using a Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) approach, helping detect suspicious domains, brand misuse, and other factors that jeopardize their online reputation.
If you like understanding why typosquatting is a real problem and how to anticipate it, keep reading.
What is typosquatting and why is it still so effective?
Typosquatting consists of registered web domains very similar to those of a legitimate brand,taking advantage of common spelling errors. An added hyphen, a swapped letter, or a different extension (.net instead of .com) can be enough to fool a user.
What keeps this practice from working is not technical sophistication, but the human factor: nobody types perfectly all the time or checks every link they click.
Common variations of typosquatting
Within typosquatting attacks, there are patterns that are frequently repeated:
- Simple typographical errors: duplicated, omitted or interchanged letters.
- Use of similar domains: minimal changes, such as business.com by busines.com.
- Alternative extensions: leverage domains such as .org, .info, or new TLDs.
- Homoglyphs: use of visually similar characters (e.g., lowercase “l” and uppercase “I”).
Each of these variations aims to achieve the same objective: to pass as legitimate and to confuse the user.
Real-life examples of typosquatting: when the damage is already done
Discussing examples of typosquatting isn't complicated. Large technology companies, banks, and e-commerce platforms have all experienced this problem at some point.
Documented cases
- Financial institutions: domains almost identical to official ones used in phishing campaigns, according to ENISA reports.
- E-commerce: fake pages that replicate the original design to capture payment data.
- SaaS Companies: cloned portals to steal corporate credentials.
Impact of typosquatting on digital reputation
One of the biggest dangers of typosquatting is not just the attack itself, but user perception. . For those who fall for the trap, responsibility usually rests with the brand being impersonated, even if it is not directly at fault.
Most common consequences
- Reputational damage: the user associates the negative experience with the actual company.
- Loss of customers: digital trust is fragile and difficult to regain.
- Legal risks: potential regulatory claims or investigations.
- Economic costs: from legal actions to image cleanup campaigns.
This is where prevention becomes the best way to anticipate the problem.
Typosquatting attacks: a threat embedded in broader campaigns
Typosquatting rarely acts alone. Usually, it is part of more complex strategies that combine several attack vectors.
Relationship with other threats
- Targeted phishing: fake domain reinforces the email's credibility.
- Malware: downloads that appear legitimate from cloned websites.
- Corporate identity theft: use of logos and official messages.
From a CTEM perspective,these attacks increase the organization's exposure without touching its internal infrastructure. Operating at the external perimeter is sufficient.

Why early detection is crucial
The real problem with typosquatting is that it doesn't warn you.. It doesn't generate alerts on traditional firewalls or internal security systems. Everything happens outside, on domains that don't belong to the company... but that directly affect it.
Limitations of reactive approaches
- Sporadic manual inspections.
- Complaints that arrive late.
- Dependence on a customer reporting the problem.
By the time the malicious domain is detected, the damage is usually already done.
The solution to typosquatting: continuous monitoring and a CTEM approach
Addressing typosquatting requires approaches that go beyond simply blocking domains on a case-by-case basis. The key is constant monitoring.
What should a good solution include?
- Continuous monitoring of domains similar to the brand.
- Analysis of the risk associated with each detected domain.
- Prioritizing real threats versus false positives.
- Integration with response and mitigation flows.
This is where Kartos, Enthec's solution for businesses, provides a differentiating value.
Kartos and the ongoing management of threat exposure
Kartos positions itself as a tool for advanced cyber surveillance, designed to help organizations understand and reduce their actual exposure to external threats such as typosquatting.
How Kartos helps against typosquatting
- Detects suspicious domains related to the brand, even before they are used.
- Analyzes its potential malicious use within active campaigns.
- Provides a clear view of the risk from a CTEM approach.
- Allows you to act quickly by prioritizing what really matters.
Instead of reacting when the problem erupts, Kartos helps to anticipate. This is especially relevant in environments where digital reputation is a critical asset.
Best practices for reducing the risk of typosquatting
Beyond the cybersecurity tools there are complementary measures that help reduce exposure:
Basic recommendations
- Register similar domains and strategic extensions.
- Educate employees and customers about common risks.
- Monitor brand mentions and usage on external channels.
- Integrate digital surveillance into the global security strategy.
None of these actions is sufficient on its own, but together they strengthen protection.
Typosquatting is not new, but it remains effective because it exploits something inevitable: human error.. For organizations, ignoring it means taking unnecessary risks to their image, their customers, and their business.
Adopting a Continuous Threat Exposure Management approach, supported by cybersecurity solutions for businesses like Kartos, allows us to move from reaction to prevention.
Do you want to know how Kartos can help you detect and manage typosquatting before it affects your organization? Discover Enthec's cyber surveillance solution and take a step forward in protecting your brand.
The 7 cybersecurity trends you need to know by 2026
Cybersecurity has ceased to be a purely technical matter and has become a top-tier strategic element. In a context marked by automation, hyperconnectivity, and intensive data use, anticipating cybersecurity trends for 2026, it is no longer an option but an absolute necessity for companies, institutions, and public administrations.
Investing in security today means protecting business continuity tomorrow, preserving the trust of customers and partners, and complying with an increasingly demanding regulatory framework.
Next, we analyze the cybersecurity trends for 2026 that are already redefining how digital defense and risk management are understood.
Importance of cybersecurity in the current context
The digital environment in which organizations operate is more complex and exposed than ever before. Cloud migration, hybrid work, interconnected systems, and reliance on third parties have significantly expanded the attack surface.
Cybersecurity is no longer just about preventing external intrusions. Today it involves guaranteeing the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information, protecting the digital supply chain, and having the capacity for early detection and response to incidents.
Furthermore, data protection and operational resilience regulations require organizations to adopt robust technical and organizational measures. Non-compliance not only incurs financial penalties but also directly impacts reputation and market trust.
In this scenario, staying up to date on cybersecurity trends is key to developing realistic, persistent strategies that adapt to increasingly sophisticated threats.
Discover the top cybersecurity trends for 2026
Technological evolution is progressing at the same pace as cyberattacks. Understanding where both are headed allows us to design more effective and sustainable defenses. These are the trends that will shape the short and medium term.
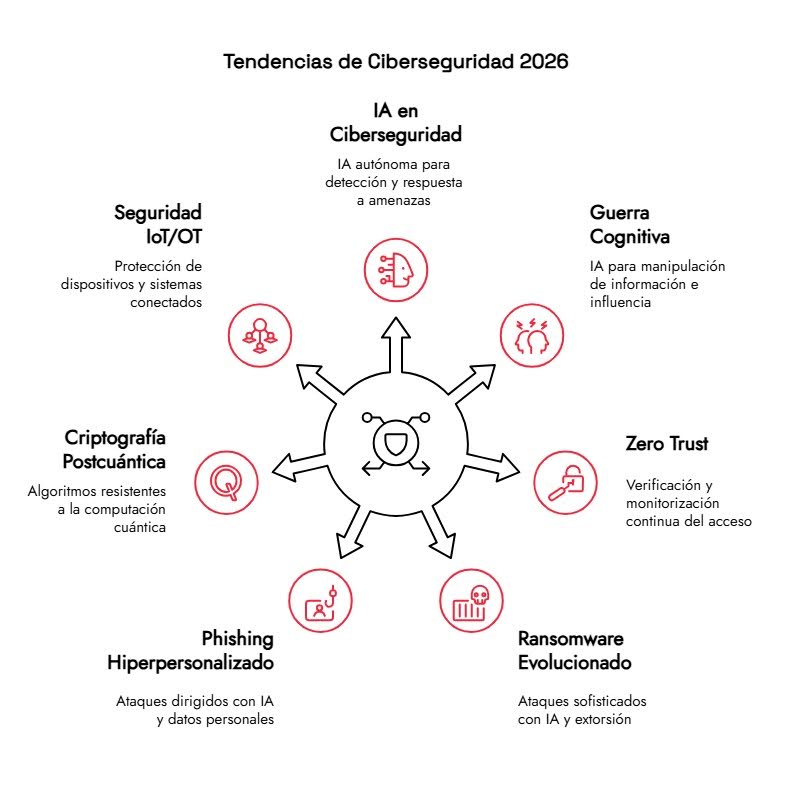
1. Artificial Intelligence and autonomous systems in cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence is no longer just a support tool, but a core component of security strategies. By 2026, the focus will shift to increasingly autonomous AI capable of analyzing complex contexts, correlating events, and making decisions without constant human intervention.
These technologies enable the detection of anomalous patterns in large volumes of data, anticipate malicious behavior, and reduce incident response times. Their value lies primarily in their ability to learn from previous attacks and adapt to new tactics.
However, this advance also poses risks. Attackers are using AI to automate campaigns and personalize attacks. It i,s and makes its detection more difficult. Therefore, defensive evolution must always be one step ahead.
Key areas of application of AI in cybersecurity
Among the most relevant uses are:
- Advanced phishing detection, analyzing emails, domains, social networks, the deep web, and the dark web.
- Reduction of false positives, a significant historical problem in security tools.
- Continuous monitoring of the digital footprint of organizations and their suppliers.
Solutions such as Kartos by Enthec integrate their own artificial intelligence to provide a precise, actionable view of risk, eliminating unnecessary noise and enabling informed decision-making.
2. Use of AI in Cognitive Warfare
Cognitive warfare represents one of the most sophisticated and worrying threats in the cybersecurity landscape for 2026. It involves operations designed to influence the perceptions, emotions, and behaviors of individuals and societies by manipulating information and leveraging generative artificial intelligence.
AI can analyze sentiment and emotions in real time, identify cognitive biases, and create personalized narratives for specific audiences. Furthermore, it enables the complete automation of disinformation campaigns, from generating content, distributing it, and measuring its impact in real time.
3. Zero Trust as a consolidated security model
The Zero Trust approach is no longer an emerging trend; it will consolidate as a benchmark standard in cybersecurity in 2026.
Its principle is clear: do not trust any user, device, or system by default.Regardless of whether it is inside or outside the corporate network, every access must be verified, authorized, and monitored.
This model is especially relevant in distributed environments with remote employees, cloud infrastructure, and multiple digital identities. Furthermore, microsegmentation limits lateral movement by potential attackers, thereby reducing the impact of a breach.
Adopting Zero Trust requires technical and cultural changes, but it offers a more realistic framework for addressing current threats.
4. Evolved ransomware: new models and persistent threats
The ransomware attacks remain at the forefront of global cyber threats and are far from stagnant; they continue to evolve. Throughout 2025, criminal organizations operating under the Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model maintained a consistent level of activity, demonstrating that this criminal scheme continues to generate profits and adapt to the environment.
Artificial intelligence has been integrated into all phases of the attack cycle, not just the development of malicious code. It encompasses everything from creating variants with greater obfuscation and evasion capabilities, to refining techniques for lateral movement within networks, to more sophisticated extortion methods that incorporate automated negotiations and psychological pressure tactics based on artificially generated content.
Looking ahead to 2026, the main concerns include:
- Multi-stage extortion: gradual leaking of information, direct pressure on customers and suppliers, and intimidation through AI-created synthetic material.
- Atomization of the criminal landscape, where small cells leverage AI tools to expand the reach of their operations.
- Faster incidents that are difficult to attribute. This complicates both the immediate response and subsequent investigations.
- Expansion of AI utilities for malicious purposes, specifically designed to automate and scale cyberattacks.
Given this scenario, organizations must review and update their backup strategies, recovery plans, and business continuity protocols. The 3-2-1 model (three copies of the information, stored on two different media, with at least one located off-site) remains a fundamental reference, complemented by regular restoration drills.
5. Hyper-personalized phishing and social engineering attacks
Phishing remains one of the most effective attack vectors and, far from disappearing, is evolving. In 2026, we are talking about
highly personalized phishing, driven by AI and by massive access to public information and previous leaks.
Attacks are no longer based on generic messages but on credible communications tailored to the recipient's context and difficult to distinguish from legitimate interactions.
To address this cybersecurity trend, organizations must combine:
- Ongoing employee training.
- Behavior-based detection technologies.
- Multi-factor authentication and access control.
Cyber intelligence platforms allow the identification of active campaigns before they impact end users.
6. Quantum computing and post-quantum cryptography
ComputingAntiquity is progressing gradually, but its implications are already present in cybersecurity trends for 2026. Its ability to solve some mathematical issues puts traditional cryptographic systems at risk.
According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the transition to post-quantum cryptography must be initiated in advance to avoid future vulnerabilities.
Although it is not yet an immediate threat, organizations should assess their critical assets, identify vulnerable algorithms, and plan an orderly migration to standards resistant to quantum attacks.
7. Security in IoT and OT environments
The expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) and connected industrial (OT) systems introduces new risks. Many devices have inherent safety limitations by design and operate in critical environments.
Protecting these ecosystems requires a specific approach that combines:
- Network segmentation.
- Continuous monitoring.
- Periodic firmware updates.
- Constant evaluation of exposed vulnerabilities.
IoT cybersecurity will remain one of the most significant trends in 2026, with a substantial impact across the industrial, energy, and healthcare sectors.
Discover our cybersecurity solution for businesses.
In this scenario, having accurate and up-to-date information is essential. At Kartos, we help organizations anticipate real threats through continuous monitoring, real-time alerts, and advanced risk analysis.
Thanks to its proprietary AI, Kartos provides a clear view of the company's digital exposure and value chain, eliminating false positives and enabling action prioritization.
Such Artificial Intelligence has evolved that enables Kartos to be the only cybersecurity solution for businesses, capable of avoiding false positives in search results, thereby ensuring effective protection.
If you want to prepare your organization for 2026 cybersecurity trends, contact our team to learn how Kartos can help you strengthen your cybersecurity strategy starting today.
Edge computing: what it is and why it poses a new cybersecurity challenge
For years, the cloud computing model has been the driving force behind digital transformation. Centralizing data and processes appeared to be the most logical option. However, the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT), the need for real-time responses, and the proliferation of connected devices have spurred the adoption of another approach: edge computing.
Understanding what edge computing is, how it works, and its security implications is now crucial for any organization managing critical data or distributed infrastructure. While edge computing offers speed and efficiency, it also raises new cybersecurity challenges that cannot be ignored.
Before we get into the subject, it's worth noting something important: the more processing points and devices a system has, the larger the attack surface. . And that's where solutions like Kartos by Enthec begin to play a strategic role.
Edge computing, what exactly is it?
When we ask the question, "What is edge computing?" we refer to a model in which data processing is performed as close as possible to its point of generation, rather than sending it to a centralized data center or the cloud.
In practice, this means that sensors, IoT devices, local servers, or gateways process information in real time, reducing latency and bandwidth consumption. Only the necessary or already filtered data is then sent to the central systems.
This approach is instrumental in environments where every millisecond counts, such as industry, healthcare, or intelligent transport systems.

How edge computing works in practice
To understand how edge computing works, it's helpful to imagine a distributed architecture with several layers:
Edge processing
Devices located at the "edge" of the network (sensors, cameras, industrial machines, smart routers) collect and analyze data in real time. Here, decisions are made quickly, without depending on the cloud.
Selective communication with central systems
Not all information travels to central servers. Only aggregated data, alerts, or historical information are transmitted, thereby reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Cloud integration
Edge computing doesn't eliminate cloud computing; it complements it. The cloud remains key for advanced analytics, long-term storage, and global coordination.
This hybrid model is powerful, but also more complex to protect.
Edge computing and examples in different sectors
Examples of edge computing help to understand why this technology is spreading so rapidly:
- Industry 4.0: Machinery that detects faults in real time and adjusts its operation without waiting for external instructions.
- Smart Cities: traffic lights that adapt to live traffic or video surveillance systems that process images locally.
- Health: Medical devices that instantly analyze vital signs, which are critical in emergencies.
- Retail: analysis of customer behavior in physical stores without depending on constant cloud connections.
All these cases share one characteristic: sensitive data, distributed devices, and the need for continuous availability.
Edge computing applications and their impact on security
The edge computing applications are typically deployed in highly heterogeneous environments. . Protecting a data center is not the same as protecting hundreds or thousands of devices spread across factories, streets, or homes.
Several challenges arise here:
- Difficulty of updating: Many edge devices are not updated as frequently as needed.
- Uncontrolled physical environments: third-party physical access to devices.
- Inconsistent configurations: Each node can have different security settings.
From a cybersecurity perspective, this requires a shift from a reactive approach to a continuous and proactive one.
Why edge computing expands the attack surface
One of the less visible aspects of edge computing is its risk exposure. Each new node is a potential entry point for an attacker. Not all edge devices have the same security capabilities as a traditional server.
This makes it critical to know what you have exposed, where, and how.
Disadvantages of edge computing from a cybersecurity perspective
Although the operational advantages are clear, it is essential not to overlook the disadvantages of edge computing, especially in matters of security:
Greater operational complexity
Managing hundreds of nodes requires specialized tools and mature processes. Without them, human error multiplies.
Limited visibility
Many organizations lack up-to-date inventories of their edge assets, making it difficult to detect vulnerabilities.
Difficulty in applying homogeneous policies
Maintaining the same level of security at all points is a real challenge, especially in hybrid environments.
These disadvantages do not invalidate edge computing, but they force a rethinking of the cybersecurity strategy.
From one-off security measures to continuous exposure management
This is where an increasingly relevant concept comes into play: the Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM).
In edge environments, one-off audits or sporadic scans are no longer enough. What's needed is:
- Identify assets in real time
- Continuously detecting vulnerabilities
- Prioritize risks based on actual impact
- Validate whether the security measures work
Kartos, Enthec's solution for businesses, is positioned precisely within this approach, not as an isolated tool, but as a system that helps to maintain controlled risk exposure in dynamic infrastructures, such as those that arise with edge computing.
Kartos and edge computing: a necessary relationship
In scenarios where processing is decentralized, visibility becomes a strategic asset.. Kartos allows organizations to:
- Have a clear view of your attack surface.
- Detect changes in exposure to threats.
- Prioritize actions based on the actual risk of the business
This is especially useful in edge computing projects, where changes are constant, and mistakes are costly.
It's not just about knowing what vulnerabilities exist, but about understanding which ones really matter and which ones can wait.
You may be interested in→ Real-time vulnerability management: a step forward in cybersecurity.
What should companies consider before investing in edge computing?
Before deploying solutions, it is advisable to ask some key questions:
- Do we have real visibility of all our assets?
- Do we know what data is processed at each node?
- Can we detect changes in threat exposure in real time?
Answering these questions is not just a technical exercise, but a strategic one.
Returning to the starting point, to understand what edge computing is, we must see it not only as a technological evolution but also as a profound change in how data and risks are managed.. Its adoption will continue to grow, driven by the need for immediacy and efficiency.
However, that growth must be accompanied by a cybersecurity approach aligned with the distributed reality.. Continuous exposure management, supported by solutions such as Kartos by
Enthec, allows you to proceed without losing control.
If your organization is exploring or already working with edge computing applications, it might be time to review how you are managing your attack surface.
Contact us and start understanding your actual exposure before a third party does.
How to detect vulnerabilities in Active Directory before they are exploited
Active Directory has been the heart of IT infrastructure in thousands of organizations for years. Regardless of company size or industry, if there's a Windows domain, there's an Active Directory managing identities, access, and permissions.
That's precisely why it has become a favorite target for attackers. Not because it's inherently weak, but because it's often to grow, change, and be inherited over time... and that's where the cracks appear.
Detecting vulnerabilities in Active Directory before they are exploited is not a one-off task, nor is it something that can be resolved with an annual audit. It's an ongoing process that combines technical knowledge, real-world visibility, and risk context. In this article, we'll see how to do it in practice, without unnecessary technical jargon, and what role the Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) solutions play in this process.
At Enthec, we work precisely on this continuous approach. Kartos, our cybersecurity solution for businesses, helps identify, prioritize, and reduce exposure to real threats, including risks associated with Active Directory. It's not just about seeing vulnerabilities, but about understanding which ones truly matter and why.
If you want to know how this translates into the day-to-day work of a security team, keep reading.
Why does Active Directory remain a critical security point?
Active Directory is not just an authentication service. It's a complete ecosystem where users, computers, servers, group policies, services, and trust relationships coexist. A small error in your configuration can have a considerable impact.
Furthermore, attackers no longer improvise. In many recent incidents, the primary objective is not to encrypt data or exfiltrate information, but to take control of Active Directory.. Once inside, everything else falls into place.

Common vulnerabilities in Active Directory
Excessive permissions and poorly managed groups
One of the most frequent problems is the accumulation of privileges. . Users who change positions, service accounts created "temporarily," or groups that no one has reviewed for years.
A user with more permissions than necessary is an open door,. and in Active Directory, those doors are usually well hidden.
Outdated accounts and weak credentials
Accounts that shouldn't exist anymore, passwords that aren't rotated, or services that work with shared credentials. All of this is still commonplace. The use of compromised credentials remains a leading cause of security breaches, especially in corporate environments.
You may be interested in→ How to manage business passwords and credentials easily and securely to avoid online threats.
Poorly configured group policies
Group Policy Objects (GPOs) are powerful, but also delicate. A poorly implemented policy can disable security controls on hundreds of computers without anyone noticing. The problem here is usually not a lack of controls, but rather a lack of visibility into its real impact.
How to proactively detect vulnerabilities in Active Directory
1. Technical audits… but with continuity
The classic cybersecurity audits are helpful, but they have a clear limit: the photo becomes outdated very quickly.. Active Directory changes every week, sometimes every day. It's recommended to move from one-off audits to continuous review processes that analyze changes in real time.
2. Analysis of attack routes
Not all vulnerabilities carry the same weight. Some are only a problem when combined with others. That's why it's crucial to analyze real attack vectors, not just bug lists. This approach allows us to answer a much more helpful question:
"If an attacker logs in with this user account, how far could they go?"
3. Correlation with real threats
This is where Active Directory security often fails. Insecure configurations are detected, but they are not linked to
active threats or to techniques currently used by attackers.
CTEM methodologies focus precisely on that: on actual exposure, not on theoretical risk.
The role of cyber surveillance in Active Directory security
Traditional scanning tools often generate lengthy reports that are difficult to prioritize. The result is predictable: urgent issues are addressed, while the rest remain unresolved.
Cybersurveillance applied to Active Directory aims to detect early signs of exposure, even before it becomes an incident.
Kartos as support in continuous risk management
Kartos, our CTEM solution for businesses, is designed to identify attack surfaces, assess their impact, and prioritize actions.. In the case of Active Directory, this translates to:
- Continuous visibility over critical configurations.
- Detection of changes that increase exposure.
- Context to identify which vulnerabilities are truly exploitable.
It's not just a technical issue but also a strategic one: helping teams decide where to invest time and resources.
Indicators that your Active Directory needs urgent attention
Frequent changes without precise control
If no one is clear on who modifies what in Active Directory, it's a red flag. Changes without traceability often lead to accumulated errors.
Recurring minor incidents
Account lockouts, unauthorized access, or recurring alerts can be symptoms of a deeper structural problem.
Excessive dependence on privileged accounts
When too many processes depend on high-privilege accounts, the risk multiplies.
Reducing that dependency is key to improving Active Directory security.
Good practices for reducing exposure to threats
Among the best practices for reducing exposure to threats, we highlight:
Periodic review of privileges
It's not a pleasant task, but it works. Reviewing who has access to what and why drastically reduces the chances of abuse.
Segmentation and the principle of least privilege
Applying the principle of least privilege is not just a theoretical recommendation. It is one of the most effective measures to limit the impact of an attack.
Continuous monitoring with a CTEM approach
This is where many organizations are moving from reacting to anticipating, relying on solutions that provide continuous visibility and intelligent prioritization.
Active Directory as part of a broader security strategy
A common mistake is treating Active Directory as an isolated element. In reality, it's connected to email, applications, VPNs, cloud environments, and external services.
Therefore, Active Directory security must be integrated into a global strategy that accounts for the organization's entire attack surface.
In this context, tools like Kartos enable a unified view that links internal vulnerabilities to external threats and suspicious online activity. Detecting vulnerabilities in Active Directory before they are exploited is not a matter of luck or simply checking off a list. It's a matter of focus, visibility, and continuity.
If you want to know how Kartos can help you identify and reduce your Active Directory's actual exposure, at Enthec, we would be happy to analyze your case and show you how to apply a CTEM approach adapted to your environment.
Contact our team and start seeing your Active Directory from an attacker's perspective, before someone else does.
What is a ransomware attack, and how to anticipate it with advanced monitoring
Most organizations and, increasingly, individuals have heard of ransomware attacks. Still, few people really know what it entails, how it originates, and, above all, how to anticipate it before it causes real harm.
In recent years, incidents of this kind have become much more sophisticated and insidious. They don't usually begin with an alarming on-screen message, but with subtle signs that go unnoticed until it's too late.
Before we get into the subject, it is worth remembering that traditional prevention is no longer an option, especially as automated attacks proliferate and cybercriminals exploit any oversight.
For individual users, Enthec offers Qondar, a customized cyber-monitoring tool that detects early warning signs, data leaks, and suspicious activity that may indicate an attack on your digital identity.. It's a continuous service that alerts you when something requires your attention, preventing a minor incident from escalating into a serious security breach.
If you are an individual and want to know whether your information is circulating where it shouldn't be, Qondar can help you start today.
What exactly is a ransomware attack?
A ransomware attack is a type of cyberattack in which malware encrypts system files or locks the victim's device, demanding a ransom for their release.. The worrying aspect is that it's not just about "kidnapping" data; many current variants also steal data before encrypting it and threaten to leak it if the ransom isn't paid publicly.

Most common types of ransomware
There are several types of ransomware, and knowing them helps to understand the risk better:
- Encrypting ransomware:. It is the most common. It encrypts documents, databases, or backups, rendering daily operations unusable.
- Locking ransomware:. Prevents access to the entire operating system. It usually affects individual users more.
- Double extortion:. First, they steal the data, then they encrypt it. This model has grown significantly since 2021.
- Targeted ransomware:. Attackers select a specific company, study it, and orchestrate a manual attack that has been prepared over weeks.
- Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS):. Anyone without technical expertise can rent a "kit" to launch attacks. This model has multiplied incidents worldwide.
Ransomware symptoms that can warn you before disaster strikes
Many attacks take days to activate. During that time, systems may show signs that, if detected early, enable action before severe damage occurs. Among the most common ransomware symptoms are:
- Teams are slower than usual for no apparent reason.
- Programs that close automatically or stop responding.
- Appearance of new background processes that you do not recognize.
- Changes to system files or folder permissions.
- Unusual login alerts on online platforms.
- Notifications of failed login attempts to your accounts.
In organizations where systems are adequately monitored, these behaviors should trigger early warnings. For individual users, detecting these signals is more challenging, and automated tools like Qondar are handy.
Ransomware: what to do if we suspect we are being attacked
There is no magic formula, but there is a series of recommended steps to take when you think you are having an attack:
- Disconnect the affected device:. Disconnect the affected device: It prevents malware from spreading to other connected computers or services.
- Never pay the ransom:. INCIBE and Europol agree that the payment could worsen the situation. It does not guarantee recovery and fuels the criminal industry.
- Review the backups:. If they are recent and isolated, they can save all the information.
- Record all possible information:. Screenshots, messages, file names, or any other trace that helps identify the variant.
- Contact professionals:. Specialized support can stop the attack, recover data, and manage internal and external communication.
Recent ransomware examples that show its real impact
Analyzing real-world incidents shows that no sector is safe. Some recent cases include:
- An attack on several London hospitals in 2024, in which medical records were encrypted, and there were threats to publish sensitive patient information.
- Education sector, with universities paralyzed for weeks as internal management platforms were encrypted.
- SMEs from different countries were attacked via RaaS and forced to halt basic operations, such as logistics and customer service.
These ransomware examples demonstrate that the target is not always a large corporation; attackers look for any vulnerability, no matter how small.
Why advanced monitoring is key to anticipating problems
This point is where the modern approach to Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) comes in. . It is a process in which weaknesses, suspicious movements, external leaks, and any data that may indicate an imminent risk are constantly analyzed.
How CTEM helps against a ransomware attack
- Identifies credential leaks before they are used.
- Monitors domains, the deep web, and external sources for dangerous mentions.
- Controls vulnerabilities publicly exposed.
- Detects anomalous behavior indicative of early-stage infection.
- Reduces the time between detection and response.
Within the Enthec ecosystem, this approach materializes in two solutions:
Kartos, for companies
A cyber surveillance platform designed for organizations that need to monitor their attack surface 24/7. It allows them to detect threats before they become incidents.
Qondar, for private users
The ideal tool for those who don't have a technical team but still want to know whether their data is at risk. Qondar continuously analyzes whether your information appears in suspicious contexts, whether your credentials are being circulated, or whether someone is impersonating you.
This is precisely why it is beneficial to anticipate a ransomware attack targeting the end user, since many campaigns begin with prior espionage or password theft.
How to realistically anticipate a ransomware attack
Anticipation doesn't depend on a sophisticated trick, but on a combination of sensible measures:
- Review passwords and always enable two-factor authentication;. many incidents begin with stolen credentials via leaks or phishing.
- Keep systems updated:. Although it may seem basic, it remains one of the most exploited weaknesses.
- Monitor digital identity:. If your data appears to have been leaked, you are likely to be targeted for future attacks.
- Keep backups offline:. Copies linked to the system are encrypted in the same way as the primary data.
- Train the staff:. It's essential in companies. An employee who recognizes a suspicious email can prevent a disaster.
Ransomware has become one of the biggest digital threats of our time. Understanding what it is, knowing its variants, and learning to identify early warning signs gives us a better chance of protecting ourselves.
And if you're an individual, remember that you don't have to do it alone. With Qondar, you can let advanced monitoring do the work for you, alerting you when it detects any signs of risk. Protecting your identity is easier when you have tools designed for it.
Do you want to know if your data is exposed? Discover Qondar and start monitoring your digital security today.
Why operational technology needs a proactive cybersecurity strategy
Industrial digitization is advancing faster than many imagine. What was once a largely isolated environment (production lines, machines, control systems, etc.) is now connected and therefore exposed.
We're talking about operational technology, or OT, an area where security can no longer be treated as an optional add-on, but as a critical part of the daily operation of any company.
Some tools stand out, such as Kartos, which provides organizations with a clear, up-to-date, and prioritized view of the cybersecurity risks affecting them. It doesn't just identify vulnerabilities; it helps assess the company's actual exposure, where the risk lies, and how to reduce it before it is exploited.
Operational technology: an industrial environment that is no longer isolated
For decades, operational technology networks operated separately from traditional computer systems. This isolation was, in itself, a layer of security. However, the need to improve efficiency, share data, and remotely control processes has led OT systems to be interconnected with IT networks and cloud services.
What does this mean in everyday life?
IT/OT convergence offers clear advantages: continuous monitoring, predictive maintenance, energy savings, and reduced downtime. But it introduces a new scenario:
-
- More entry points for external threats.
- Industrial equipment that was not designed with cybersecurity in mind.
- Complicated updates that are delayed for fear of halting production.
- Dependence on external providers whose own vulnerabilities can affect the company.
In this scenario, relying on traditional controls or one-off reviews is no longer enough. The exposure changes weekly, sometimes daily.
You might be interested in> IoT and cybersecurity: Risks and strategies to protect connected devices.
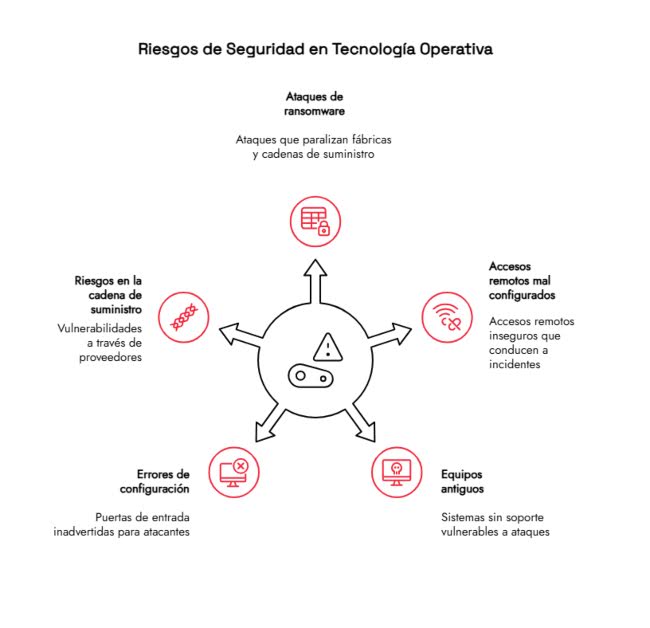
Main risks affecting operational technology OT today
Operational technology (OT) faces very different risks than those typically found in office computer systems. Here are some of the most common:
1. Ransomware in industrial environments
Ransomware attacks are no longer solely focused on stealing or encrypting data. They also aim to paralyze entire factories, disrupt supply chains, or compromise critical equipment.
2. Misconfigured remote access
Remote access is proper, yes, but it's often enabled hastily, with weak passwords, or without adequate controls. This is one of the vectors that causes the most incidents in OT environments.
3. Older equipment without support
Many industrial machines are decades old. They're still working, but they no longer receive security patches. When connected to the network, they become easy targets.
4. Configuration errors
Even a small, unmonitored open port can serve as a gateway for attackers.
5. Risks in the supply chain
Suppliers are also part of the OT ecosystem. A security breach in their network can ultimately affect the company as a whole.
All these factors make it clear that a specific protection strategy is needed for operational technology.
Why proactive cybersecurity is essential in OT
The philosophy of proactive cybersecurity is based on anticipating risks.. It is not enough to react when something goes wrong; we must identify threats before they create a real problem.
1. Operational technology cannot stop
In IT, a failure can lead to data loss or work interruptions. Serious, of course, but manageable. In OT, a failure can halt a production line, generate millions in losses, endanger workers, or affect critical services.
That's why OT security should aim to prevent incidents from their origin.
2. Threats are constantly evolving
The attackers already know the weaknesses in the operational technology. They are looking for old faults, careless configurations, or forgotten access.
. An annual review or a static analysis is not enough to keep up with them.
3. The exposure changes, although the infrastructure does not.
Even if the company does not install new machines, its exposure may vary due to:
- New connections.
- Changes in suppliers.
- Software updates.
- Human errors.
- Newly discovered vulnerabilities.
Supervision must be continuous.
What does a CTEM approach bring to operational technology environments?
The Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) is a framework that has gained traction in recent years. It enables organizations to, on an ongoing basis, understand the risks they face, their potential impact, and the actions to prioritize.
How CTEM is applied to OT operational technology
A well-implemented CTEM strategy in OT helps to:
- Identify exposed assets, including those the company may have forgotten.
- Detect insecure configurations.
- Control how the attack surface changes.
- Prioritize risks based on actual impact, not assumptions.
- Guiding teams towards faster and more informed decisions.
This is where solutions like Kartos stand out for their comprehensive approach and their ability to continuously monitor exposure without interrupting industrial operations.
Kartos: a realistic and helpful solution for protecting operational technology
Unlike other tools that focus on vulnerability detection, Kartos helps visualize the actual exposure of each asset, supplier, and process connected to the network.
Advantages of using Kartos in an OT environment
- Provides a clear, prioritized view of the attack surface.
- Identifies risks in external providers.
- Facilitates quick decision-making.
- Reduces the likelihood of incidents that affect production.
- Provides context: it not only shows vulnerabilities, but also their potential impact.
For companies with complex OT environments, this is critical. Knowing what might fail before it does is a matter of money and safety.
Proactive cybersecurity best practices in operational technology
To strengthen an OT environment, these measures are especially recommended:
1. Complete and up-to-date inventory
You can't protect what you don't know. A living inventory, not a static document, is essential.
2. Network Segmentation
Properly separating IT and OT environments limits lateral movement in the event of an intrusion.
3. Continuous monitoring
OT systems require constant monitoring to detect unexpected changes.
4. Strict access control
You have accounts with minimal privileges and remote access protected by multiple factors.
5. Constant review of the supply chain
Every vendor is a potential point of attack. The good news is that many of these measures can be automated or better managed with CTEM tools like Kartos.
Anticipating is the only viable strategy
Digital transformation is already a reality in the industrial sector. Operational technology is more connected than ever, and that brings enormous benefits… but also obvious risks. In this environment, reactive cybersecurity falls short. Companies need approaches that are up to today's challenges: continuous, intelligent, and aligned with real impact.
Solutions like Kartos help organizations understand and manage their exposure without slowing operations. That's the key: protect without stopping, anticipate without alarm, monitor without interrupting.
If your company works with operational technology and wants to understand its actual exposure to threats, start today with continuous, proactive analysis.. Discover how Kartos can help you protect your industrial environment before risks become problems.
How automation in cybersecurity helps reduce human error in online protection
Cybersecurity has been evolving for years at a pace that is sometimes difficult to keep up with. Threats change, attack methods become more subtle, and the amount of information we manage continues to grow.
Amid this scenario, one factor remains decisive: the human error,. not out of ill intent, but because we humans can't be aware of everything, all the time. Fortunately, cybersecurity automation has become an ally that helps us strengthen protection without adding complexity to daily life.
Before delving into the subject, it's worth pausing to consider a tool that perfectly encapsulates this evolution. We're discussing Qondar, Enthec's solution designed for individuals who want to manage their exposure to digital risks.. Its practical, visual, and continuous approach reveals where the sector is heading: constant monitoring, clear warnings, and the ability to make informed decisions without needing a master's degree in cybersecurity.
In short, Qondar shows how automation can be close, practical, and, above all, accessible.
Why human error remains one of the most significant security breaches
Most security incidents are not due to complex failures in highly advanced systems, but to everyday actions such as opening a suspicious email, reusing passwords, or downloading a file without thinking.
This makes sense; whoever attacks finds the easiest way to access a system,and we humans are often that weak point. While training is essential, relying solely on human attention isn't sufficient, especially in environments where we receive hundreds of notifications, messages, and tasks vying for our attention.
This is where cybersecurity automation becomes essential. It's not about replacing anyone, but about minimizing unavoidable oversights by delegating repetitive tasks, from surveillance and analysis to systems that do not get tired, do not get distracted, and do not forget.
How automation strengthens online protection
Automated cybersecurity is not an abstract or futuristic concept. It's already being implemented in companies large and small, and increasingly in solutions for individual users.. Here are some of the areas where it has the most significant impact:
1. Continuous, uninterrupted monitoring
An automated system can monitor in the background 24/7, detect unusual patterns, and provide instant alerts. This type of monitoring would be impossible if it depended solely on a person. Furthermore, it allows for anticipating attacks before they fully materialize.
At this point, automation in cybersecurity acts as a radar that never turns off.
2. Reduction of repetitive and error-prone tasks
Checking links, validating emails, verifying configurations, comparing databases… These are necessary tasks, but they are also precisely the type of processes where errors can occur due to fatigue or simple saturation.
Automating them is doubly beneficial:
- Time is gained.
- It prevents an oversight from turning into a bigger problem.
3. Incident classification and prioritization
One common problem is the number of alerts generated each day. Without automation, many go unnoticed or are addressed late. With advanced tools, incidents are ordered by severity, allowing us to react sooner where it really matters.
4. Updates and patches without manual intervention
An essential part of security is keeping everything up to date.. Automation saves headaches here, too. A self-updating system reduces risks without requiring additional time.

CTEM: the new approach that unites surveillance and automation
In recent years, the concept of CTEM (Continuous Threat Exposure Management) has gained traction.. It is not a fad or an empty word; it is a methodology that combines continuous evaluation, risk prioritization, external and internal visibility, and agile response.
Essentially, CTEM applies automation in cybersecurity to keep under control what can be compromised, how, and with what level of urgency.
Enthec's solutions, Kartos, focused on businesses, and Qondar,designed for individuals, are a clear example of this philosophy. Both monitor in real time, detect leaks or exposures, and display information clearly so that each person can make decisions based on real, up-to-date data.
The importance of automating personal cyber surveillance
When we think about digital threats, we usually picture companies, large organizations, or critical infrastructure. However, individual users are increasingly becoming targets, not because we hold big secrets, but because we accumulate data, access credentials, and accounts that attackers can exploit.
What kind of risks do we avoid with automation?
- Password leaks in external services.
- Appearance of personal data in leaks.
- Identity theft on social networks.
- Suspicious access from unusual locations.
- Involuntary disclosure of private information.
Qondar automates this surveillance and provides clear, understandable notices for everyone. . You don't need to be a cybersecurity expert to recognize the risk and take action.
You may be interested in→ 9 healthy digital habits that will protect you from identity theft and leaks.
Automation doesn't mean disengagement; instead, it means making better decisions.
It's important to clarify that automating security doesn't mean "putting everything on autopilot," but rather ensuring that essential alerts don't go unnoticed,. while maintaining a balance between technology and human judgment.
The ideal combination is:
- Automation for monitoring, classifying, and alerting.
- The person to make the final decision.
This alleviates the mental burden and enables stronger protection without requiring additional time.
Real advantages of automation in cybersecurity for businesses and individuals
Although the contexts are different, both companies and individual users can benefit from a user-based approach to automation in cybersecurity:
For companies
- Fewer errors resulting from manual processes.
- Greater visibility over the attack surface.
- Early detection of exposures in equipment, employees, or suppliers.
- Optimization of IT department resources.
For individuals
- Absolute control over one's digital footprint.
- Clear, actionable alerts without technical jargon.
- Continuous security without relying on remembering to check.
- Ongoing updates to address new threats.
Automation is about better protection, not more complexity.
Automation does not replace human care, but it does add a layer of precision and consistency that is hard to match.. In an environment where cybercriminals automate their attacks, it is logical to respond with tools that can monitor at the same scale.
If you genuinely want to understand your digital exposure, receive early warnings, and improve your personal security without complications, Qondar by Enthec is a good starting point. If your company needs more comprehensive oversight, Kartos offers a level of depth designed for organizations.
Start protecting your online identity today.
Try Qondar and discover how cybersecurity automation can give you continuous, precise monitoring tailored to your daily life.. Your digital peace of mind starts with a click.