How to prevent social media phishing

How to prevent social media phishing
Corporate impersonation or brand abuse on social media encompasses a variety of tactics ranging from fake profiles impersonating the brand to the distribution of malicious content under the brand's name.
What is social media phishing?
In the digital age, social media has become an integral part of our lives and businesses, providing opportunities to connect, share content and interact with diverse communities, including customers. However, this growing dependence has also led to an increase in phishing, fraud and scam campaigns in these virtual environments. These criminal practices have evolved to include corporate impersonation to deceive users and customers in order to obtain confidential information or illicit enrichment. Social media phishing, also known as brand abuse, involves the creation of fake accounts posing as official profiles of well-known companies or relevant individuals. As far as organisations are concerned, impersonators often meticulously copy logos, images and communication style to appear authentic. They often take advantage of active brand communication or promotion campaigns, copying them in order to maliciously lure customers. Their main objective is to trick users into revealing personal or financial information or to damage the company's image. The consequences of corporate impersonation are often serious. Customers lose trust in the brand, leading to a decrease in sales and engagement. In addition, the organisation may face legal problems if customers suffer financial losses due to the impersonation or if the impersonation has been used to commit other illegal acts.

Threats of corporate identity theft on social networks
The impersonation of corporate identity on social media brings with it a number of threats to organisations:
Falsification of profiles
Profile spoofing is at the heart of corporate impersonation on social networks. Criminals create fake profiles that mimic legitimate companies to deceive users and obtain personal or financial information. These fake profiles can become very convincing and even indistinguishable without research, using logos, images and brand language similar to those of the real company to appear authentic. They often post relevant content to appear authentic and gain followers. Once they have gained the trust of users, these profiles are often used to run a variety of scams. This can include promoting fake offers, requesting payment details for non-existent products, or directing users to fraudulent websites where they are asked to provide personal information.
Phishing through social media
In the context of social media, fraudsters use sophisticated techniques to send direct messages or posts that appear to be from a recognised organisation or institution whose identity they have impersonated. Cybercriminals have adapted these tactics to the social media environment, taking advantage of the trust and familiarity that users have with these platforms. They use social engineering tactics to trick users and obtain the sensitive information they seek. In a typical phishing scenario, criminals create fake profiles or pages that look like those of a legitimate company. They then send enticing messages or posts that may include special offers, contests or fake security alerts to lure users into clicking on malicious links. Once the user clicks on the link, they may be directed to a fake website that looks like the company's official website. The user is then prompted to enter personal or financial information, which is then collected by the criminals.
Publication of malicious content
One of the most damaging threats of brand abuse on social media is the publication of malicious content.
Malicious content can take many forms, from false and misleading information to links to dangerous websites or malicious software. This content can be used to damage a company's reputation, sow discord and create conflict, mislead customers and steal valuable information.
Impersonation of services
Impersonation is another significant threat in the context of corporate identity theft on social media. Criminals create accounts that impersonate the brand's customer service, directing users to fake or dangerous sites or luring them into a scam. These fraudulent services can range from non-existent product offers to false promises of customer support. Users, believing they are interacting with the real company, provide personal or financial information, make payments or make decisions based on incorrect information. Spoofing significantly damages an organisation's reputation. Customers who have been misled often associate their negative experiences with the real company, even holding it responsible for lack of sufficient vigilance and protection, which can lead to loss of trust and loyalty. There can also be a direct financial impact. If customers are tricked into buying fraudulent products or services, sales decrease. In addition, the organisation may face significant costs to mitigate the damage, restore its reputation or legally prove its lack of responsibility for the crime.
Preventing phishing on social networks
Preventing social media phishing is critical to protecting your customers and your organisation. A good strategy on how to prevent social media phishing needs to include:
Monitoring social networks
By continuously monitoring social media, organisations can detect fraudulent use of their corporate identity on social media and prevent cybercriminals from using the brand with impunity to deceive customers. Continuous monitoring and analysis of the data it provides also helps to identify emerging patterns and trends of brand abuse and proactively respond to the threat.

Establish a proactive protection strategy
When an organisation has a proactive social media brand protection strategy in place, the likelihood of the threat of maliciously targeted brand abuse decreases.
The proactive strategy allows the organisation to stay ahead of brand abuse, detecting identity theft on social networks in real time so that the organisation can proceed with its cancellation before it causes significant damage. You may be interested in our publication→ Proactive security: what is it and why use it to prevent and detect threats and cyberattacks?
Being active in social networks
Although it may seem paradoxical, not opening corporate profiles on the different social networks or remaining inactive on them not only does not protect against identity theft, but also encourages it. Having very active profiles on social networks allows users to become familiar with the brand's own communication and to detect impersonators more easily. In addition, active profiles make it easier to check the veracity of a profile that arouses suspicion among users.
Protecting the brand with advanced technologies
The continued sophistication of cyber-attacks requires organisational protection that is up to the task and uses advanced strategies and technologies such as artificial intelligence and automation to provide the right responses at the right time. Solutions based on artificial intelligence and machine learning identify fake profiles and malicious activity more effectively and quickly than traditional methods. In addition, they are able to automatically track active or latent fraudulent campaigns on social media until they are completely eliminated.
Consequences of corporate identity theft on social networks
Brand abuse often has serious consequences for an organisation:
Financial losses
Social media impersonation leads to a decrease in brand value due to loss of trust, as well as a decrease in revenue due to lost sales to misled or defrauded customers. After a successful social media impersonation, the organisation is forced to invest in powerful communication campaigns to regain some of its customers' trust. In addition, when cybercriminals use the impersonated corporate identity to engage in illegal activities, fees are generated to cover legal action.
Reputational damage
The reputation of a brand has a direct impact on its value. Corporate impersonation on social media damages the reputation of an organisation and its brand. Fraudsters use a company's brand to spread false information or engage in unethical or even criminal behaviour that has negative effects on the organisation's image. When this happens, the corporate image is damaged.
Legal problems
Corporate impersonation raises legal issues when fraudsters use the brand to engage in illegal activities, as the organisation will initially be held liable until it proves the impersonation. In addition, defrauded customers may hold the organisation vicariously liable for the deception due to a lack of sufficient vigilance and protection, and claim restitution for their financial loss from the organisation, either legally or administratively. This also implies a legal or administrative defence.
Loss of customer confidence
After interacting with or hearing about fake accounts that have impersonated the corporate identity, customers perceive that the organisation is not taking adequate measures to protect its brand and, indirectly, them from scams.
They then become wary of interacting with the company on social media, proceed to avoid it and are less likely to remain loyal to it.
Protect yourself from social media phishing with Kartos by Enthec
Kartos, the Cyber Intelligence platform developed by Enthec continuously and automatically monitors the web and social networks to detect domains, subdomains, websites and social profiles identical or similar to those of your organisation. Thanks to its self-developed Artificial Intelligence, false positive findings are eliminated. In addition, Kartos tracks phishing, fraud and corporate identity fraud campaigns detected until they are deactivated, with identification of the countries in which they are active, data and alarms in real time. Since this year, the Kartos platform also offers a Takedown Service for social profiles, domains and fraudulent subdomains, as well as cloned websites detected by the platform. Contact us for more information on how Kartos can help you protect your brand from cloning and abuse on the internet and social networks.
Cybersquatting: what is it and how to protect yourself?

Cybersquatting: what is it and how to protect yourself?
Cybersquatting is an increasingly widespread cybercrime that exploits the value of brands to make illegitimate profits by squatting on their domain. This cybercrime is becoming commonplace in the digital environment, so it is crucial for organisations to know exactly what cybersquatting is and how to protect themselves against it.
What is cybersquatting?
Cybersquatting is the act of registering, selling or using a domain name in bad faith, taking advantage of the reputation and commercial value of a famous brand or name with the intention of making illegitimate profits. Essentially, cybersquatting is a form of online piracy that causes harm to businesses and individuals. The term comes from squatting, which is the act of illegally occupying property, with the addition of cyber, to confine it to the digital environment. In this case, the squatted property would be the corporate domain. This is why cybersquatting is also called cybersquatting. Cybersquatters often register domain names or create subdomains that are identical or confusingly similar to popular brands in order to trick users into visiting their website. This leads users to fraudulent websites with various illegal intentions: selling fake goods, scams, data theft... In addition, cybersquatting is also often used by cybersquatters to profit from the sale of squatted domains to legitimate companies at exorbitant prices, in order for them to avoid damage to their brand. To combat cybersquatting, ICANN has developed the Uniform Domain Name Dispute Resolution Policy (UDRP). This procedure makes it easier for affected companies to recover domain names registered in bad faith. To find out more about cyber-attacks on businesses, go here→ How to protect yourself in the midst of a wave of cyber-attacks on businesses.

Differences between cybersquatting and phishing
Although both are cybercrimes that involve the misuse of names and trademarks and sometimes go hand in hand in a cyberattack, the cybersquatting and phishing are not exactly the same thing.
Cybersquatting is the registration, trafficking or use of a domain name that is identical or similar to a well-known trademark. Its aim is to make financial gain through that identical or similar domain name.
It does not necessarily involve deceiving users or stealing personal information; sometimes it is simply used to force the organisation to ransom the domain. Phishing, in turn, involves sending fake emails or creating fake websites that mimic legitimate companies or brands in order to trick users into obtaining personal information, financial information or login credentials. It aims to gain access to accounts, steal identities and commit fraud. It involves the use of social engineering techniques to manipulate victims into believing they are interacting with a trustworthy entity. Often, however, the first step in a phishing attack is cybersquatting: a real domain is used to create a fake website or profiles as the basis of the deception.
Some examples of cybersquatting
Some prominent examples of cybersquatting are:
- Registration of domain names identical or similar to famous brands with the intention of reselling them to their rightful owners at an excessive price.
- Use of domain names to divert web traffic to sites with pornographic content, misleading advertising or illegal activities.
- Blocking domain names to prevent legitimate companies from registering and using them, in order to sell them to the highest bidder.
- Creation of fake websites that mimic the appearance of well-known brands to deceive users and obtain personal or financial information.
Detection of cybersquatting
Some of the most effective strategies for detecting cybersquatting are:
- Domain monitoring. One of the most effective ways to detect cybersquatting is through regular monitoring of domain names. Such tools issue real-time alerts when a domain name that is similar to the organisation's domain name is registered, allowing quick action to be taken to protect the brand.
- Use of internet service provider (ISP) domain look-up tools. The tool shows the many variations that could be used to commit cybersquatting. These tools also indicate which domains have already been registered.
- WHOIS search. The WHOIS database is a valuable resource for detecting cybersquatting. A WHOIS search provides information on who has registered a particular domain name. In this way, an organisation can check whether a domain name similar to its brand name has been registered by someone who has no legitimate relationship to it.
- Phishing detection tools. Sometimes cybersquatters use cybersquatting in their phishing tactics to trick users into visiting their fraudulent websites. Phishing detection tools help to identify these websites and, collaterally, to detect cybersquatting.
The role of new technologies
Artificial Intelligence and machine learning are beginning to play a crucial role in the fight against cybersquatting. Their detection, analysis, learning and automation capabilities make them key tools for proactively, accurately and effectively combating cybersquatting. As cybercriminals develop more sophisticated tactics, their use will become increasingly critical. The use of AI and machine learning-based solutions allows:
- Proactive detection of suspicious domains: real-time detection and analysis of new domain registrations and patterns indicating possible cybersquatting, such as names similar to well-known brands.
- Constant monitoring of registered domains: continuous monitoring of detected suspicious domains similar to the brand, with alerts on changes in content or usage that may indicate fraudulent activities.
- Identification of cybersquatting techniques and patterns: recognition of common methods used by cybercriminals, such as addition, substitution or omission of characters in domain names.
- Reduction of false positives: accuracy in distinguishing between legitimate domain registrations and real cybersquatting cases, reducing false alerts.
- Automated real-time response: activation of automatic response protocols to block the suspect domain, notify the authorities and the affected brand and proceed to takedown.

Most used methods of cybersquatting
Cybersquatting can occur in different ways.
Homographic
It involves replacing characters in a domain name with visually similar characters, often indistinguishable to the naked eye. This method is particularly effective because of the difficulty for the human eye to distinguish between certain characters, especially in URLs.
Addition
It involves adding additional characters to an existing domain name. It is particularly effective when targeting brands with short names, as an additional character can easily go unnoticed.
Omission
In this case, it refers to the removal of characters from an existing domain name. It is quite effective when targeting brands with long names, as one less character goes unnoticed.
Domain change
It involves slightly altering an existing domain name, often by changing the order of the characters, introducing a spelling mistake or using a domain extension different from the organisation's official one. Its effectiveness is based on the very mistakes users make when typing a domain into the search engine.
Subdomain
A common cybersquatting tactic is the creation of subdomains outside one's own brand. A subdomain is an extension of the main domain name. Cybersquatters register subdomains containing the name of popular brands to trick users and redirect traffic to fraudulent sites.
How to prevent cybersquatting
Preventing cybersquatting can be a challenge, but there are several strategies that help protect the brand and domain:
- Early domain registration. Register domain names that are important to the brand early. This may include variations, common misspellings and other domain names that could be attractive to cybersquatters.
- Trademark protection. Registering the trademark provides additional legal protection against cybersquatting. If the trademark is registered, it ensures the possibility of winning a domain name dispute.
- Constant vigilance. Continuous monitoring of the domain with automated tools capable of alerting about the use or registration of domains and subdomains that are the same or similar to corporate domains is essential.
- Use of a private registration service. When registering a domain name, it is advisable to use a private registration service, so that cyber criminals cannot access the information associated with the registration.
- Legal action. Take immediate legal action to recover the domain name when cybersquatting is detected. The Uniform Domain Name Dispute Resolution Policy (UDRP) is the process for doing this.
You may be interested in our publication→ Brand protection: strategies to prevent fraudulent use.
Protect yourself from cybersquatting with Kartos by Enthec
Kartos XTI Watchbots, our Cyber Intelligence platform, uses in-house developed Artificial Intelligence to help organizations monitor their domain and detect any associated cybersquatting.
In addition, Kartos by Enthec provides organizations with real-time alerts about the existence of domains and subdomains associated with those of their brand and offers takedown services for the removal of those that are fraudulent.
Contact us to learn more about how the solutions of our Kartos XTI Watchbots Cyber Intelligence platform can help you detect and prevent cybersquatting, protect your brand, and avoid cyberattacks.
Keys to preventing data leaks

Keys to preventing data leaks
A data breach is a security incident in which confidential information is accessed or extracted without permission, which may include personal data, credentials or any other sensitive information of individuals and organisations. Here, we explain in more detail what it means and the fundamental keys to preventing a data breach.
What is a data leak?
Data leakage is one of the most common and damaging incidents in the field of cybersecurity.
A data breach occurs when confidential information is accidentally or unlawfully exposed. This can happen inside or outside an organisation, and can be the result of a cyber-attack, human error or a failure in security systems. The information leaked in a data breach varies widely in content. It can be personal data, such as names, addresses and social security numbers; financial data, such as credit card numbers and bank account details; or corporate data, such as product details and business strategies. The consequences of a data breach are generally significant. For individuals, it can end up as identity theft or financial fraud. For businesses, it can result in legal fines, loss of reputation and damage to customer relationships. Data leakage can be a quick event, where data is exposed and used immediately, or it can be a slow process, where data is collected over a long period of time before it is used.

Main types of data leakage
Data leaks are differentiated into different types such as:
Interns
In internal data leaks, data is leaked or leaked from within the organisation. It happens when employees or persons with authorised access to confidential information disclose or extract it in an unauthorised way, intentionally or unintentionally. Also, when an unauthorised person outside the organisation gains access to the organisation and its data. Generally, the latter type usually corresponds to a cyber-attack. Some of the main causes of insider leaks include:
- Disgruntled employees or employees with malicious intent who steal data for personal purposes or to sell to third parties.
- Lack of adequate controls and monitoring of the activities of users with access to sensitive data.
- Lack of clear information security policies and insufficient staff training.
- Vulnerabilities in systems and applications that allow unauthorised access to information.
- Cyber-attacks executed to obtain the information.
External
External data leaks are incidents in which confidential information is leaked without authorisation, willingly or unwillingly, by persons or entities outside the organisation, from outside the organisation.
Within external corporate data leaks, those caused by third parties represent a significant threat to an organisation. These leaks occur when an external entity that has legitimate access to an organisation's data, such as a service provider or business partner, inadvertently or maliciously exposes that information. Third parties within an organisation have access to a wide range of corporate data, from personal information of employees and customers to trade secrets and intellectual property. If they do not follow appropriate security measures, they become a weak link in the information security chain. To mitigate this risk, organisations must ensure that all third parties they work with have robust information security policies and procedures in place. This involves conducting cybersecurity audits, including data security clauses in contracts and, most effectively, automated, continuous, real-time monitoring of third-party risk.
4 causes of data leakage
Data leakage can be caused by voluntary and malicious acts or involuntary acts.
The most common causes of unintentional corporate data leaks include:
Use of suspicious software
Suspicious programmes, often disguised as legitimate software, can infiltrate an organisation's systems and give illegitimate access to confidential information. They are introduced by employees unaware of the risks or by external attackers. Once inside, these programmes collect and transmit sensitive corporate data. Infiltration of malware into the corporate system can occur through unwitting installation of malicious software, use of unauthorised messaging or cloud storage applications, downloading infected files or connecting to insecure public networks. Constant supervision and monitoring of activities is essential to detect and prevent the use of malicious software that can lead to data leaks.
Vulnerabilities in the system
Failures in firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security controls can leave data exposed to external attacks. In addition, inappropriate network configurations, such as the setting of access permissions, communication protocols, and other network settings, are likely to open unauthorised access to information. Also, lack of security patches and updates to applications and operating systems or lack of data encryption and protection make information more vulnerable to theft.
Social engineering
Social engineering is a major cause of corporate data breaches. Cybercriminals manipulate employees into revealing confidential information, often through phishing or phishing tactics. These attacks become very sophisticated, masquerading as legitimate communications from colleagues or superiors. Social engineering exploits the human tendency to trust and cooperate. To circumvent it, companies must implement cybersecurity training and awareness and appropriate security policies to mitigate this risk.
Improper design or implementation of security protocols
If security policies are not properly implemented and enforced, this creates vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit to gain access to sensitive organisational data. It is crucial that companies design robust security protocols and ensure that they are properly enforced. Ongoing training and security audits are essential to prevent data leaks, as well as monitoring user activities and reporting security incidents. Security protocols must also be regularly reviewed, tested and updated to ensure their effectiveness.
Tips to prevent data leakage
We recommend that you consider the following tips on how to prevent a data leakage:
Use two-factor authentication
Dual authentication is a security measure that requires users to provide two forms of identification before accessing systems. This can be something the user knows, such as a password; something they possess, such as a mobile phone to receive a verification code; or something inherent to the user, such as a fingerprint. This additional layer of security makes it difficult for cybercriminals to access data, even if they have obtained a password. Dual authentication is a valuable investment in protecting corporate data.

In addition, two-factor authentication can be complemented with other measures such as data encryption and activity monitoring to further strengthen corporate information security. You may be interested in our publication→ Good information security practices for your company.
Keeping equipment up to date
Outdated systems have security vulnerabilities that cybercriminals try to exploit to execute attacks. Updates include security patches that fix vulnerabilities as they are detected. In addition, newer versions of software and hardware often incorporate better security measures. It is therefore crucial that companies implement a policy of regular updates and ensure that all devices, tools, systems and applications are up to date. This requires investments in time and resources, but is an essential preventive measure to ensure the protection of corporate data.
Regulating access to confidential information
It involves implementing a system in the organisation that ensures that only authorised employees have access to sensitive data. Access control systems, such as role-based authentication, are an example of such a regulation. Limiting access not only reduces the possibility of data being compromised internally, but also reduces the risk of cyber criminals gaining access through compromised accounts.
Update data security policies
Given the continuous evolution of threats, data security policies easily become obsolete. It is therefore imperative that organisations establish a recurrent process of updating these policies to incorporate the latest technologies and procedures. In addition to adapting to changes in the technology environment, security policy updates also allow organisations to incorporate new regulatory requirements, organisational growth and change, and reviews following a security incident.
Cyber-intelligence for the prevention of data leaks
Cyber Intelligence is an essential tool for the prevention and localisation of corporate data breaches, providing the information needed to understand, mitigate and respond to threats. It enables organisations to identify and monitor suspicious activities, both internal and external, that may indicate potential or actual activity to access, extract or leak sensitive information. Cyber Intelligence is based on the collection and analysis of information about potential threats in cyberspace. It includes the identification of suspicious behaviour patterns, the detection of open security holes and exposed vulnerabilities and the prediction of future threats. This enables organisations to adopt a proactive, risk-based security approach to protect their sensitive data. One of the main advantages of Cyber Intelligence is its ability to provide a real-time view of security threats. In this way, it enables organisations to respond quickly to threats, thus minimising the impact of any data leakage. In addition, Cyber Intelligence helps organisations to better understand the threat landscape. This includes identifying threat actors, their tactics, techniques and procedures, and the types of data they are seeking. With this information, companies can develop more effective defence strategies. By incorporating Cyber Intelligence into their data cybersecurity strategy and combining advanced analytics, constant monitoring and security best practices, organisations significantly strengthen their defence posture against data breaches.
Protect your organisation's data with Kartos By Enthec
The Kartos By Enthec helps you protect your organization's data thanks to continuous, real-time automated monitoring of the external attack surface.
Using Artificial Intelligence developed in-house, the Kartos XTI Watchbots Cyber Intelligence platform can detect in real time any corporate data leak, both its own and that of your third parties, issue an alert, and locate the vulnerability that caused it.
Don't wait any longer to protect your data and negate the consequences of any leak. Contact us to learn about our solutions.
Security breach: What it is, types and how to find it
As our reliance on digital technology grows, so does the importance of protecting our systems and data against security breaches.
In this article, we explain a security breach and its main characteristics. Let’s get to them!
What is a security breach?
A security breach occurs when an unauthorized intruder bypasses a system's security measures and gains access to protected data. Breaches can result from external attacks by hackers or internal actions, such as employees accessing information they don't have permission for.
In cybersecurity, a security breach can have serious consequences. Individuals' personal and sensitive data can be stolen and used for malicious purposes, such as identity theft, running phishing campaigns, or financial fraud. Organizations can also suffer significant damages, such as loss of intellectual property, damage to their reputation, and loss of customer trust.
Security breaches can occur in any type of system or network, regardless of the information it contains. This includes, for example, computer networks, database systems, and mobile devices
With the development of the Internet of Things (IoT), even everyday devices such as refrigerators, vacuum cleaners, or thermostats can be vulnerable to security breaches.
Detecting a security breach is a challenge for organizations. Attackers often use sophisticated techniques to hide their activities so that breaches can go undetected for months or even years. For this reason, companies invest in intrusion detection technologies and tools to monitor their different attack surfaces for suspicious activity and findings.
Once a breach is detected, responding quickly to neutralize or minimize the damage is crucial. This can involve identifying and repairing the exploited vulnerability to taking compromised systems offline and notifying any affected parties.
In many cases, law also requires organizations to report their security breaches to the appropriate authorities.
You may be interested in our publication→ Information Security: 5 Best Practices to Implement in Your Company.

Types of Prominent Security Breaches
Security breaches can lead to a large number of vulnerabilities. Among the highlights are:
Confidentiality Breach
A confidentiality breach is a specific type of security breach that occurs when the confidentiality of data is violated. In terms of cybersecurity, confidentiality refers to the practice of maintaining the privacy of information, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access it.
Confidentiality breaches have different causes. An attacker can exploit a cybersecurity system vulnerability to access protected data, an employee can lose a device containing sensitive information, or a user can be tricked into revealing their password through a phishing attack.
The consequences of a confidentiality breach are often severe. For an organization, it can lead to loss of competitive advantage, reputational damage, and possible legal penalties for non-compliance with data protection laws due to security breaches, in GDPR.
Integrity Breach
An integrity breach is a specific type of security breach that occurs when the accuracy or consistency of data is altered without authorization. In terms of cybersecurity, integrity refers to ensuring that information is accurate and has not been improperly modified.
Integrity breaches can result from malicious actions, such as a hacker's attack that alters data, or they can result from unintentional errors, such as a system failure that corrupts data.
When an integrity breach occurs, data that should be trustworthy is no longer trustworthy. Many organizations use hashing techniques and digital signatures to ensure data integrity. These techniques allow organizations to detect any data tampering. However, it is not impossible that even these techniques could be compromised in a cyberattack.
Availability Breach
An availability breach is a specific type of security breach that occurs when data or systems are unavailable to authorized users when needed. Regarding cybersecurity, availability refers to ensuring that systems and data are accessible and functional when needed.
Availability breaches result from various incidents, from system failures and human error to malicious attacks.
The most common attack that causes an availability breach is a denial-of-service (DoS) attack, in which the attacker floods a system with traffic to overload it and make it inaccessible.
Users cannot access systems or data when an availability breach occurs, impacting service and business continuity. Organizations should have disaster recovery and business continuity plans to recover quickly from an availability breach.
What should I do if I'm affected by a security breach?
When an organization suffers a cybersecurity breach, it needs to act quickly to:
- Identify the nature and extent of the incident.
- Isolate affected systems to prevent further damage.
- Document details of the incident.
- Communicate the breach to stakeholders, including customers if their data is compromised.
- Inform the relevant authorities.
- Investigate and remediate the breach.
- Review and update security policies and procedures.

Keys to Prevent a Security Breach
Data breach prevention is essential in any corporate cybersecurity strategy.
Some keys to protecting your organization are:
- Awareness and education. Personnel are the first line of defense against cyber threats. The organization should provide regular cybersecurity training to keep everyone informed about the latest threats and how to avoid them.
Security policies. Establish clear policies on the use of company systems and data. This includes strong password policies, use of VPNs for remote access, and restrictions on the use of personal devices.- Updates and patches. Keep all operating systems and applications up to date. Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software.
- Firewall and antivirus. To protect your network, use a robust firewall and antivirus software that is always active and up-to-date.
- Two-factor authentication. Implement two-factor authentication whenever possible. This adds an extra layer of security, as it requires a second form of identification in addition to the password.
- Backups Make regular backups of all important data. This will allow for faster recovery in the event of a data breach.
- Incident response plan. Develop an incident response plan. It should include how to identify and report a data breach and the steps to contain and recover from it.
- Security audits. Conduct regular security audits to check the protection status and identify and remediate any vulnerabilities.
- Data encryption. Sensitive data must be encrypted to protect it in a breach.
- Vulnerability detection. Continuous monitoring of the different attack surfaces, external and internal, for real-time detection of any security breach that occurs.
If you want to learn more about cybersecurity, check out our publication→ The Cybersecurity Trends You Need to Know About.
Repercussions of a security breach
When a company suffers a security breach, these are the main consequences it must face:
Financial Damages
Security breaches have financial repercussions for businesses. Direct costs include system recovery and repair, as well as potential fines and legal penalties.
Indirect costs can include losing customers due to mistrust, damage to the company's reputation, and diminished brand value. In addition, businesses may face costly litigation from affected customers or employees.
Reputational Damage
A security breach can significantly damage a company's reputation for protecting its brand. When customer personal data is compromised, trust is eroded, leading to a decline in customer base and sales.
In addition, negative perceptions of the company can affect relationships with business partners and investors.
Reputation recovery often takes a considerable amount of time and requires high investments in security and public relations campaigns.
Data Loss
Data loss is a devastating consequence of a cybersecurity breach. Lost data can be specially protected by laws such as GDPR and include sensitive customer information, intellectual property, financial records, and more.
Its loss can mean disruption to business operations and require considerable effort to recover or rebuild data. In addition, the leaked data can be used for illicit purposes, such as identity fraud.
Kartos by Enthec helps you avoid security breaches
Kartos Corporate Threat Watchbots, the Cyber Surveillance and Cybersecurity platform developed by Enthec, allows your organization to proactively, continuously, and in real-time control key aspects to avoid security breaches that jeopardize the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of corporate data.
Through monitoring of the Internet, the Dark Web, the Deep Web, and social networks, Kartos detects exposed security breaches affecting your organization's information in real-time so that you can correct and nullify them before they are used to execute a cyberattack.
If you want more information on protecting your digital assets with Kartos Corporate Threat Watchbots, contact us and discover all the solutions we offer.
System Vulnerabilities in Cybersecurity
System vulnerabilities in cybersecurity are being exploited with increasing sophistication and precision. The risk for institutions and companies, regardless of their size, is increasingly evident. In recent times, we have witnessed numerous attacks, including on important public institutions such as the SEPE in Spain or the Colonial Pipeline, the largest oil pipeline network in the US. In this scenario, it is essential for organizations to reduce the risk of suffering a cyber attack. To delve deeper into this, in this article we will talk about system vulnerabilities in cybersecurity.
What is a Cybersecurity Vulnerability?
A vulnerability is a weakness or flaw within an information system that poses a security risk. It could originate from a configuration error, design flaws, or procedural failure.
This security “hole” represents an entry point for cybercriminals who use these vulnerabilities to enter our system and compromise its availability, integrity, and confidentiality.
Therefore, it is vital to keep our systems safe, find these vulnerabilities as soon as possible, and fix them to avoid these risks.

Difference between vulnerability and threat in cybersecurity
As mentioned, vulnerabilities are flaws, “security holes” in our system. Threats are those actions carried out by cybercriminals who exploit these vulnerabilities.
Therefore, they are different things. The vulnerability is the security breach while the threat is the action that exploits the security breach.
Generally when vulnerabilities appear, there will always be someone who will try to exploit them.
What types of vulnerabilities can I have?
We will now discuss the types of vulnerabilities we can suffer from. However, it is worth remembering that some are more important than others. We will have to assess the importance of each vulnerability, as having an exposed database is not the same as having a leaked commercial PDF.
We will now comment on the types of vulnerability by establishing the following classification:
SQL injection vulnerabilities
These vulnerabilities occur when SQL code that was not part of the programmed code is inserted. This technique alters the operation of a database.
The attacker’s hostile data can trick the interpreter into executing unwanted commands or accessing data without authorization.
Authentication vulnerabilities
These are flaws related to input data validation that allow attackers to access our system.
Another critical point here is passwords. Using insecure passwords makes systems vulnerable, and if they are easily cracked, they can lead to incursions by unauthorized third parties.
Vulnerability exposed data
Many web applications and APIs do not adequately protect sensitive data, such as financial, health, and personal information. Attackers can steal or modify this weakly protected data to commit credit card fraud, identity theft, or other crimes.
Configuration vulnerabilities
These types of vulnerabilities are due to software or server misconfigurations. It can lead to system disablement or other more powerful attacks, such as a Dos attack.
Other types of configurations are related to security, such as open cloud storage and misconfigured HTTP headers.
All operating systems, frameworks, libraries, and applications must be securely configured and patched/updated promptly.
XSS (Cross Site Scripting) Vulnerabilities
This type of vulnerability is characterized by allowing scripts from languages such as VBScript or Javascript to be executed. XSS flaws occur when an application includes untrusted data on a page without proper validation or escaping.
Cybercriminals can hijack user sessions by executing these scripts. Phishing to steal passwords and data is an example of such an attack.
Component-related vulnerabilities
Components, such as libraries, frameworks, and other software modules, run with the same privileges as the application.
An attack could result in data loss or server access if any of these components are vulnerable.
Kartos locates your organization's exposed vulnerabilities
Kartos Corporate Threat Watchbots is the Continuous Threat Exposure Management platform developed by Enthec for the protection of organizations. Thanks to its technology designed to scan the three layers of the web in search of threats, Kartos locates open gaps and exposed vulnerabilities in your organization to prevent them from being used by cybercriminals to develop an attack. Contact us to learn more about how Kartos can help you neutralize exposed system vulnerabilities and avoid the threats they entail.
Encryption: How to improve your information with advanced security
Encryption is one of the main tools for keeping us safe when we browse the Internet or use different applications.
Encryption helps us protect and keep secure our activity, the information we share, and our personal and session data.
In this context, at Enthec we develop advanced solutions in the continuous management of exposure to threats (CTEM) integrating encryption as a fundamental layer in the protection of sensitive data. With technologies that analyze and mitigate risks in real time, at Enthec we help companies protect their information against unauthorized access and data breaches.
What is encryption?
Data encryption is one of the main tools for maintaining security on the internet and in various applications. It is a cryptographic process that encodes information so that only the sender and receiver can access it.
In the field of computing and cybersecurity, encryption uses complex mathematical algorithms to protect information. For a piece of data to be considered encrypted, it must comply with certain principles:
- Privacy. Only authorized persons can access the information.
- Integrity. No external agent has modified the information. The information must be kept intact from the time it is received until it is delivered.
- Authentication: The other party's identity must be verified within this exchange of information.
- Non-repudiation: Neither party may deny the transmission of the information.
Thanks to these principles, encryption is one of the most effective methods in data security.
Types of encryption
There are two main types of encryption: symmetric and asymmetric. Both methods have their characteristics and applications.
Symmetric encryption
Symmetric encryption, also called secret key cryptography, is a cryptographic method that uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt messages between the sender and receiver.
Once both parties have access to this key, the sender encrypts a message using the key, sends it to the recipient, and the recipient decrypts it with the same key. It is the oldest form of encryption and is still relevant due to its data transmission speed.
It is ideal for the transmission of large volumes of data. Some of the most commonly used algorithms in this encryption method are:
- AES-128
- AES-256
- DES
- Blowfish
- RC4
The main drawback of this method is the need to share the secret key securely. If an attacker gains access to the key, all information encrypted with it is compromised.
Asymmetric encryption
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key cryptography or PKI, is a cryptographic method characterized by the use of two keys, one public and one private, to transfer data and information.
In this type of encryption, the sender uses the public key to encode information into an unreadable format, which can only be decrypted or read with a secret key. When sending encrypted data from the public key scheme, the receiver needs a hidden key to access the encrypted data.
This system is more secure than symmetric encryption, as the private key is never shared. However, it is a slower process involving more complex mathematical calculations. Some standard algorithms in this type of encryption are:
- RSA
- DSA
- PKCS
- ElGamal
Asymmetric encryption is commonly used in secure transactions, such as sending encrypted emails and authenticating websites using digital certificates.
Differences Between Symmetric Encryption and Asymmetric Encryption
| Feature | Symmetric encryption | Asymmetric encryption |
| Safety | It is less secure, as the key must be shared | More secure, with separate keys |
| Velocity | Faster | Slower |
| Number of keys | A key is needed per communication | A pair of keys (public and private) are used |
| Volume | Transmission of small volumes of data | The large volume of data in transit |
If you want to learn more about effective techniques for data encryption, click here→ What is data encryption: features and how it works.
How does encryption work in practice?
Data encryption is used in many areas of technology. Some examples of encryption in everyday life include:
Secure communications
Messaging apps like WhatsApp, Telegram, and Signal use end-to-end encryption to protect conversations. Only the sender and recipient can read the messages, preventing third parties from accessing the information.
Banking transactions
Financial institutions use bank encryption to safeguard customer data. Every time we make an online payment, our data is protected by encryption, preventing attackers from intercepting it.
Data storage
Companies and users encrypt files and databases to prevent and manage unauthorized access. For example, modern operating systems offer options for encrypting hard drives, which prevents a third party from being able to read the information without the corresponding key.
Digital certificates and Internet security
Whenever we access a secure website (HTTPS), our browser uses asymmetric encryption to verify the site's identity and protect data transmission. This is crucial for the security of online transactions and the protection of personal information.
Encryption Methods and Your Future
Encryption methods are also evolving with the advancement of technology. New forms of encryption based on quantum computing are currently being developed, which could change how we protect our information.
Some emerging methods include:
- Homomorphic encryption. It allows you to process encrypted data without decrypting it, which is helpful in cloud services.
- Quantum cryptography. It uses principles of quantum mechanics to ensure information security.
- Post-quantum encryption. Algorithms designed to withstand attacks from quantum computers.
Encryption is an essential tool in digital security. Knowing the different types of encryption and their applications helps us protect our information in an increasingly connected world. From symmetric to asymmetric encryption, each method has advantages and disadvantages depending on the context in which it is used.
Adopting good digital security practices and understanding data protection mechanisms is critical to maintaining online privacy. As technology evolves, encryption methods will continue to improve, providing new ways to protect our data from emerging threats.
Types of Malware and keys to prevent these attacks from affecting the security of your company
Protecting against malware involves deploying a corporate strategy based on in-depth knowledge of the threat.
From Enthec, we tell you what malware consists of and its different types.
What is malware
A malware attack is a malicious attempt to gain access to computer systems, networks, or computers to steal sensitive information, infect systems, encrypt data, or cause damage. The goals of malware include gaining unauthorized access, stealing data, encrypting information, or damaging the affected system.
Organizations must be aware of and protect against these attacks because of the serious consequences they can entail if successful, such as financial losses, operational disruptions, data recovery costs, and reputational damage.
If you're wondering how many types of malware there are, read on; we'll tell you below.
The Different Types of Malware You Need to Know About
Malware can be classified into different categories depending on its purpose:
Virus
One of the most well-known types of malware is viruses. These viruses aim to disrupt the normal functioning of the computer device, regularly replacing executable files with others that contain the device's code.
Its infection can be through removable devices, emails, or network connections.
Adware
It is software designed to display unwanted advertising on screen. One of the methods that infects the system is after downloading a program and inadvertently allowing permissions.
The other method of infection can be browsing a website, taking advantage of the vulnerability in the user's browser to perform an unintentional download.
Spyware
It is a type of malware that hides in the computer system, monitors user activity, and steals information.
In this case, it is infected through unsafe web pages, taking advantage of vulnerabilities through ads or pop-ups that, when clicked, download this type of malware.

Trojan
This malware appears legitimate, harmless software but aims to control your computer, introduce more malware, steal data, and spread to other devices.
Rear doors
Back Doors
After installation, it provides access to malicious users to control a computer remotely.
It infects computers from untrustworthy websites or downloads. It can also infect through emails.
Keyloggers
Records keystrokes made on the keyboard to store them in a file and send them over the Internet. They can be hidden on removable devices, in emails or downloads from non-legitimate pages.
Thieves
This type of malware accesses private information stored on the computer to steal and share the most sensitive data, such as passwords.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that infects a computer to take control of it and, in exchange, demands a ransom payment.
When ransomware infects your computer, it encrypts all files and folders, preventing access without a key. It is spread through attachments in untrustworthy emails or web pages.
Computer worm
They are programs that make copies of themselves by remaining in different places in the system. They can make system changes without authorization, decreasing system performance or worsening the connection.
Rootkit
This type of malware allows hackers to access your computer without your knowledge to hide the processes and files on your system for a malicious purpose. It can infect other devices with files or downloads from non-legitimate sites.
Botnets
Botnets are any group of devices that are infected and controlled remotely by an attacker to control as many devices as possible and carry out illicit activities.
It spreads through malicious code on websites after exploiting its vulnerability.
Rogueware (rogue software )
This type of malware masquerades as a security tool that launches an alert or a fake message indicating that something is wrong with the computer to click on a link to download software that solves the problem.
Cryptojacking
Cryptojacking is a type of malware that involves cybercriminals using users' devices without their consent and using the machine's resources to "mine" forms of online money known as cryptocurrencies.
Malicious Apps
These types of apps masquerade as legitimate apps or try to emulate other successful apps.
Once installed on the device, they will ask us for a series of abusive permissions or, on the contrary, they will make fraudulent use of those permissions.
Ways to get malware into a system
Malware gets into a system in different ways. Some of the most common are:
- Email: Cybercriminals often use email to distribute malware. This can be through malicious links or attachments in phishing emails.
- Internet downloads: Some websites may try to install malware on a device when you visit or download something from them. This is especially common on websites that offer freeware or pirated software.
- External storage devices: Devices such as USB drives can contain malware. If they connect to the system, malware can install itself automatically.
- Exploiting vulnerabilities: Cybercriminals often exploit software vulnerabilities to introduce malware into a system. This can be through outdated or unpatched software.
- Social media: Malicious links can also be distributed through social media platforms. Clicking on a malicious link can install malware.
- Mobile apps: Malware is often spread through malicious apps on mobile devices. These apps may look legitimate, but they contain malicious code.
You may be interested in our post→ Common types of cyberattacks.
How to identify a potential malware infection
To identify if a computer is infected with any malware types, it is crucial to pay attention to specific telltale symptoms. Some of the common signs of malware infection include:
- Slow system performance: If your computer runs slower than usual, freezes, or doesn't respond appropriately, it could indicate infection.
- Pop-up messages: The constant appearance of pop-up messages on the desktop can signify infection.
- Internet connection issues: Difficulties connecting to the internet or slow browsing can indicate the presence of malware
- Unexpected changes in the system: new icons on the desktop, files with unknown extensions, disappearance of the antivirus, or deactivation of the firewall are red flags.
- Abnormal computer behavior: Automatic actions such as opening unsolicited windows, changes in application languages, or missing files needed to run programs can be signs of infection.
Awareness to protect against malware
Since malware infection is almost always the result of social engineering techniques, malware awareness is essential in any work environment.
Knowledge is the best protection against significant damage to computer systems, including data loss, information theft, and disruption of business operations.
It's critical for everyone in any organization to understand malware, how it spreads, and how they can prevent it. This can include training on identifying suspicious emails, the importance of not downloading files from unknown websites, and the need not to click on unsolicited links.
This training and awareness must be regularly updated to prevent routine and trust from becoming vectors facilitating the attack.
In addition, workers should also be aware of the warning signs of a malware infection, such as slow system performance, frequent crashes, unwanted pop-up ads, and unexpected changes in system settings.
The time that elapses between the attack, detection, and communication is essential to protect against the malware deployed and avoid or minimize damage.

Protect mobile devices from malware
Mobile devices are now incorporated into any organization's work. Many of them are privately owned by workers, who use them outside of working hours and the work environment.
Therefore, to protect against malware, the organization must expand the scope of training and awareness to include this type of device, as long as it can access the corporate system from it.
Some recommended actions to protect mobile devices against different types of malware are:
- Regular updates: keep the operating system and all applications current. Updates often include security patches that protect against new threats.
- Security software: Install a reliable security application with antivirus and anti-malware protection. Some of these apps also include additional features such as remotely locking and wiping the device if it is lost or stolen.
- Safe downloads: Only download apps from official app stores like Google Play Store or Apple App Store. These stores typically have strict security policies and review apps for malware.
- App permissions: Review the permissions that an app requests before installing it. If an app requests unnecessary permissions for its operation, it could be a sign that it is malicious.
- Safe browsing: Avoid visiting unsafe websites or clicking on suspicious links that could install malware on your device.
- Public Wi-Fi: Be careful when using public Wi-Fi networks, as cybercriminals frequently use these networks to spread malware. It's wise to consider using a VPN when you're on public Wi-Fi.
- Screen lock: Use a screen lock to protect your device in case it is lost or stolen. This can help prevent unauthorized access to your information.
In-depth threat knowledge allows organizations to effectively protect against malware types and leverage the capabilities of new cybersecurity solutions, such as our Kartos Corporate Threat Watchbots cyber surveillance platform to prevent attacks before they materialize. Contact us to learn about our solutions!
Common Types of Cyberattacks (Part I)
In this article, we will talk about the most common types of cyberattacks.
We call cyberattack any offensive maneuver employed by individuals or whole organizations that targets computer information systems, infrastructures, computer networks, and/or personal computer devices. These attacks try to hack into a system using one or several digital acts, usually from an anonymous source, to steal, alter, or destroy a specified target.Among the common types of cyber attacks we find the following:
Malware
Malware is any software that intentionally performs malicious actions in a system without the user's knowledge. Viruses, worms, and trojan horses are different kinds of malware.
Virus
A computer virus is a small script of code that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs called hosts and inserting its code to alter how a computer operates. Of course, since this is a type of malware, it is all done without the permission or knowledge of the user.

Worm
A computer worm is a standalone malware program that replicates itself to spread to other computers. This differs from a virus because the virus needs a host program, but the worm does not. A worm often uses a computer network to spread itself, relying on security failures on the target computer to access it. Once there, it will try to scan and infect other computers.
Trojan Horse
A Trojan Horse Virus is malware that downloads onto a computer disguised as a legitimate program. It typically gets hidden as an email or free-to-download file attachment and then transfers onto the user’s device. Once downloaded, the malicious code will execute the task the attacker designed it for, such as spying on users’ online activity or stealing sensitive data.
Kartos helps you protect your organization by locating its vulnerabilities
Kartos Corporate Threat Watchbots is the monitoring platform developed by Enthec for the protection of organizations. Using its army of bots, Kartos crawls all three layers of the web, locating exposed vulnerabilities and open gaps in the organization that can be used to execute any of the common types of cyberattacks we just saw. Thanks to kartos, organizations can proactively defend themselves against these threats, preventing them from materializing. Contact us for more information on how Kartos can help you protect your organization.
How to protect your user privacy? Essential Guide to Safe Browsing
Protecting user privacy is critical in a digital world where personal information is at constant risk. Users are often unaware of how their private data is being used, which can lead to security breaches, phishing, and exposure to cybercriminals.
Sensitive data can be stolen and disclosed on the deep web if adequate protection is not in place. Many platforms collect user information through various tracking methods, exposing their privacy to potential threats.
If you are concerned about your user privacy, Qondar can become the best solution. Through continuous monitoring, it crawls the Internet, the Deep Web, and the Dark Web to identify exposed personal information, alerting in real time to potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Tracking Techniques Affecting User Privacy
Various techniques are used to collect information about users and their online habits. Knowing them is the first step to protecting yourself:
- Cookies. Small text files that store information in the user's browser and allow tracking of their online activity.
- Privacy Policies. These are documents that explain how a platform manages user data, although they are often extensive and difficult to understand.
- HTML5 elements. Browser storage systems with greater capacity than traditional cookies, allowing companies to save more data.
- IP address and geolocation. They allow the approximate location of an online user to be identified, which can be used for advertising or even malicious purposes.
- Social networks. Platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram collect information about their users, their interactions, and preferences, sharing it in many cases with third parties.
- Google services. Tools like Google Search and YouTube track user activity to personalize the experience and collect vast personal data.
- Browser fingerprint. Some websites can identify and track users using information about their browser and device, allowing tracking without cookies.
- Supercookies and Evercookies. Advanced storage methods that are more difficult to delete than conventional cookies and can persist on the user's system even after deleting the browsing history.
Tools to protect user privacy
Fortunately, various tools and techniques can improve user privacy and minimize the exposure of personal data on the Internet.
Private search engines
Some search engines respect user privacy and do not track your information or sell it to third parties:
- Ixquick. It does not log IP addresses or store tracking cookies, providing high anonymity.
- Startpage. It delivers Google results without collecting user information, combining privacy with a familiar search experience.
- DuckDuckGo. It does not store or share browsing data with other companies or generate user profiles.
- Qwant. A European search engine that respects users' privacy and does not track their online activity.
Privacy settings in browsers
Each browser offers options to improve user privacy, but they need to be configured appropriately to maximize their effectiveness:
- Firefox. It includes a privacy settings section that allows you to prevent tracking and delete third-party tracking cookies.
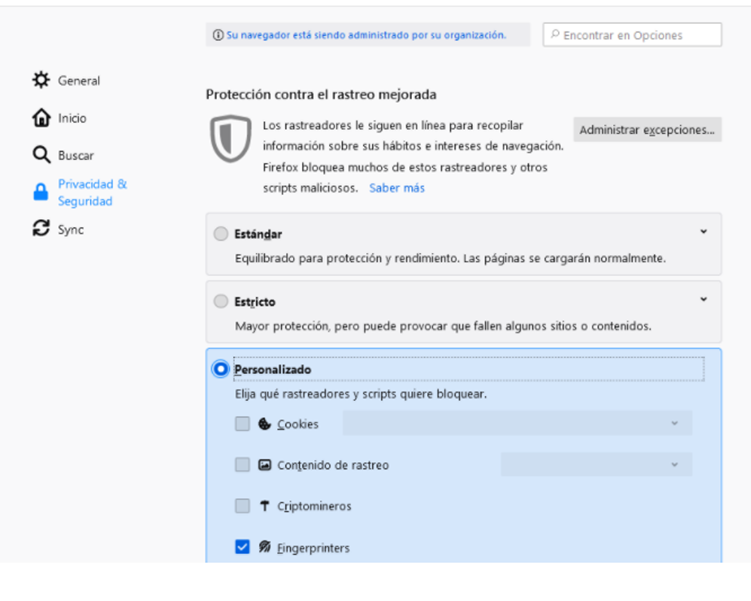
- Opera. It allows you to manage cookies, SSL certificates, and passwords and includes a built-in ad blocker.
- Chromium. It provides similar options to Firefox and Opera to protect personal information, but it depends on the user's correct configuration.
- Brave. A privacy-focused browser that blocks ads and trackers by default, offering added security from the start.
- A Virtual Private Network (VPN) hides the user's IP address and allows access to geo-restricted content, protecting privacy on public connections.
Anonymous proxies
A proxy server is an intermediary between the user and the website, hiding the IP address and protecting online privacy. Several lists of reliable proxy servers can help improve digital security, but it is important to choose services that do not store activity logs.
Other solutions to improve user privacy
- HTTPS Everywhere extension. It redirects traffic to secure versions of websites, protecting the transmitted information.
- Browser add-ons. Tools such as Click and Clean allow you to delete information stored in the browser easily.
- Privacy Badger. It blocks intrusive trackers and ads that collect personal data without user consent.
- Adblockers. Extensions such as uBlock Origin and AdGuard reduce online tracking by removing suspicious ads and scripts that may contain malware.
- Secure email. Services such as ProtonMail and Tutanota offer encrypted alternatives to protect users' privacy, prevent tracking, and keep their emails secure.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA). Adds a layer of security to prevent unauthorized access to personal accounts through temporary codes.
- Privacy-focused operating systems. Linux distributions such as Tails and Qubes OS are designed to offer high anonymity and online security.
Best practices for protecting user privacy
In addition to using security tools, it is essential to adopt responsible digital habits to minimize risks:
- Review and adjust privacy settings on social media and digital platforms regularly.
- Avoid sharing unnecessary personal information in online forms and service records.
- Regularly update passwords and use password managers to generate secure and unique keys.
- Be wary of suspicious emails and links to avoid phishing attacks and credential theft.
- Use private or incognito browsing mode when necessary to reduce tracking and prevent the storage of session data.
- Disable data collection on mobile devices by reviewing the permissions of installed apps.
- Encrypt files and devices to protect information from loss or theft.
Discover the primary keys to data encryption through our article→ What is data encryption: characteristics and operation.
Qondar: Advanced protection for user privacy
Qondar Personal Threat Watchbots is a continuous and automated monitoring tool developed by Enthec to protect users' privacy and digital assets.
Thanks to its advanced capabilities, Qondar not only allows for the detection of data breaches but also analyzes risk patterns and provides recommendations to improve digital security. Its artificial intelligence technology helps predict attacks and strengthen personal data protection.
Contact us to find out how Qondar can help you protect your online privacy and prevent your data from being compromised.












